electricity anesthesia
advertisement

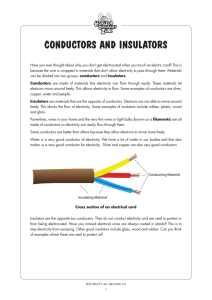
Anesthesia Department ELECTRICITY & ELECTRONICS “For Anesthetist” By Prof. Gamal Elewa, MD Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture , the post-graduate student will be able to: 1. Know types of electricity and clinical applications 2. Know General Electricity applications in anesthesia 3. Understand Equipment: Defibrillators, Cardiac Pace Makers, Electro-cautery (surgical diathermy), Others: computer 4. Consider Electrical Safety and Avoid Electrocaution © General Electricity • Definitions • Types of electricity: Static vs Dynamic. AC vs DC. High vs low pressure lines • SI units: currenr (A), electr. Potential (V), resist (Ω), .. • Classification of substances according to their electrical conductivity: conductors, semi- conductors, insulators © Types of electricity • Static vs Dynamic • Clinical importance of static electricity • Direct vs AC current © Direct & Alternating Current • DC: Flows in one direction • AC: Periodically reverses its direction (sine wave): -Wavelength: distance between 2 waves -Frequency: no. of waves/cycle -Velocity: wave length X Frequency © ELECTRICAL SI UNITS • • • • • • Frequency: Hertz (Hz)= cycle/sec Power: Watt (W) Electrical current: Ampere (A) Electrical Potential (EMF): Volt (V)=W/A Electrical Charge: Coulomb (C)=As Electrical Resistance (Impedance, Reactance): Ohm (Ω)=V/A (Ohm’s Law) • Electrical Inductance: Farad (F)=As/V • Electrical Capacitance: Henry (H) =Vs/A © Electrical Conductivity • Conductors: Metals, e.g. cupper, lead, platinum, gold, silver • Insulators: glass, plastic, rubber, wood, mica, porcelin, ceramic • Semiconductors: Silicon, germanium, selenium - Used in: transistors, thermistors, diodes, some transducers - Affected by temperature, e.g. thermistors General Electricity • WHEAT STONE BRIDGE: R2/R1= R3/Rx R2 R 2 Rx y x R1 R3 Medical Equipment • • • • Defibrillators Cardiac Pace Makers Electro-cautery (surgical diathermy) Others: computer Defibrillator • Definition • Physical and Clinical Principles • Indications & uses: Cardioversion & Defibrillation • How applied? • Precautions • Automated types Pace Maker • • • • • • Definition Principle Uses (Indications) Types Terminology Precautions Pacemaker Identification Chamber paced Chamber sensed Response Programmable of generator to sensed P or R waves Multi-site pacing (when 2 atria or ventricles are paced) O V A D O V A D O(asynchro nus) T=triggered I=inhibited D=dual=T+I O A V D O(fixed function) P(rate/output) M= multiprogram C=communicatin R=rate modulating Electro-cautery (Diathermy) • Def • Principle • Types: Unipolar vs Bipolar, coagulation vs cutting • Precautions: general, with pacemaker Electrocution • Types: Macro-shock Micro-shock • Why? • Prevention Summary of important points Electricity Definitions Types & Applications Equipment Hazards & Their Prevention © Examples of questions to assess the ILOs -Wheatstone bridge: principle and clinical applications - Electrical cautery: precautions with pacemaker -Physical principle of defibrillators & their types - Hazards of defibrillators -Difference(s) between: * Direct & alternating currents, * Monophasic & biphasic defibrillators, * Static & dynamic electricity © • THANK YOU