nervous system
advertisement

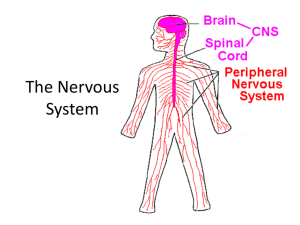
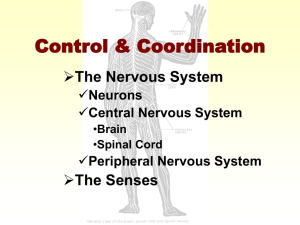
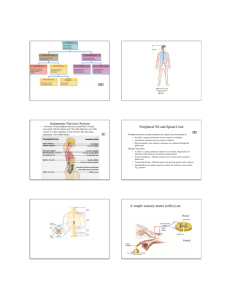
NERVOUS SYSTEM MCGONIGLE Intro to Psychology Nervous System Made up of the spinal cord and the brain Neurons : Nerve cell – the neurons transmit messages to the spinal cord and to the brain. ( knee reflex) 3 types of neurons. Types of Neurons Sensory Motor Neurons Neurons Interneurons neurons. – found between other Dendrite Branches that extend from the cell body to most neurons. Receive information and transmit impulses toward the cell body. (hot stove/step on a nail) Cell Body of Nucleus Cell Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons – limited ability to repair damaged cells. (Pat’s story) Axons Long tubelike structure attached to a neuron Transmits impulses away from cell body + toward another neuron, muscle cell or gland. Spinal Cord Long column of nerve tissue about as thick as your index finger. Generally speaking – 18” long (c shaped) Vertebra - bones that make up back (6 C) Connective tissue- spinal meninge – help protect spinal cord. Brain Cerebrum: largest and most complex part of the brain. Billions of neurons– conscious thought, learning, memory ( long + short) Brain cells – do not reproduce Left Hemisphere Right side of the body Language Thinking Reasoning Analyzing Right Hemisphere Music Talents ( singing/ playing instruments) Art ( painting/ drawing) Spatial Relationships ( Maps/ Graphs) 4 Lobes of the Brain Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Frontal Lobe All voluntary movements ( hand/eye coordination) Use of language – foreign languages. Parietal Lobe Sensory Heat Cold Pain Touch Information : Occipital Lobe Vision – eyes- Optic nerve Do we see w/ our eyes or brain? Temporal Lobe Hearing + Smell (connected- memory) Memory Thought Judgment Cerebellum 2nd largest part of the brain. Coordinates movement of skeletal muscles (jock/nerd) Receives messages from sensory neurons in the inner ear. Maintains body posture + balance. Brain Stem 3” stalk of nerve cells and fibers that connect spinal cord to the rest of the brain. Incoming and outgoing messages pass through the brain stem. Medulla Oblongata Lowest part of the brain stem Regulates Reflexes: heartbeat + respiratory rates coughing, sneezing, vomiting Pons 1” in length Above the medulla Pathway- connects nerve impulses to other parts of the brain. Helps regulate breathing. Midbrain Highest part of the brain stem Controls Turning eyeball movement and pupil size your head at an unexpected noise Thalamus Page 60 in textbook Important Relay center for incoming impulses ( nail/ hot stove) Receive Above info from eyes and ears. the hypothalamus.. Hypothalamus Controls and balances body processes to regulate: ( means under the thalamus) Body temp (sweat) Appetite Regulate Sleep Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus controls Metabolism Sexual (discuss disturbances) Development (behavior) Emotional Responses (aggression) Peripheral Nervous System Consists of all nerves that are not part of the Central Nervous System Carries messages between CNS and the rest of the body 2 Parts: Autonomic + Somatic Autonomic Nervous System Consists of Network of nerves divided into 2 smaller networks. “Fight/Flight Reflex- responses” spontaneous response of body to stimulus. Somatic Nervous System Sensory Relay messages from receptors to: Eyes Ears Nose Tongue Skin Neurons Parasympathetic Nervous System During rest and relaxation Opposes Slows actions of sympathetic system down body functions: heartbeat, lowers blood pressure, opens blood vessels. Vocab Quiz on Thursday From Central Nervous System to the Pons Terms 1-15