2012 Partial Volume Effects in Arterial Spin Labeling MRI
advertisement
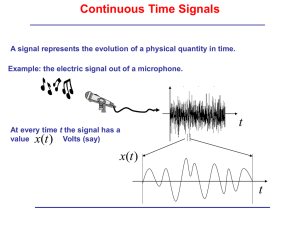
By: Tracy Ssali Medical Biophysics 3970z April 4th 2012 Supervisors: Keith St. Lawrence, PhD Udunna Anazodo, PhD candidate Brain Tissue consists of Grey Matter (GM) White Matter (WM) and Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) Perfusion in the brain is indicative of function Irregular flow in grey matter is indicative of disease state [1] Arterial Spin Labeling is a novel technique used to measure perfusion in the brain Established techniques require radioactive exogenous tracers which cannot be used on certain patient populations, and require long clearance times.[2] ASL MRI uses magnetized water molecules in arterial blood as a tracer to measure tissue perfusion non-invasively Creating the control image Creating the tagged image Arterial blood is magnetically labeled using radiofrequency pulses A delay time is allowed for the blood to reach the brain When the labeled water interacts with the magnetic field, it affects the signal being produced Subtract ASL Image ≈ CBF Adapted from Wolf and Detre Neurother Vol. 4, 346–359, July 2007 Perfusion images are taken in quick succession Information from the labeled blood must be captured before it relaxes Blood water has a half life of around 1-2s[3] Pettersen Br J Radiology 2006 Point spread blurring Resolution is not fine enough to resolve GM, WM and CSF Voxel size is approximately 3 x 3 x 3mm [2] Partial Volume Effects (PVE) correction Estimates the partial signal contribution based on the contrast information from anatomical MRI image volume Kernel Regression Algorithm Based on the size of the kernel the algorithm assesses a radius around the centre point to reassign a partial volume Signal – Mean signal of GM, WM or CSF Noise – Standard deviation 40 20 Deibler et al AJNR march 2008 To measure the signal to noise ratio before and after the partial volume effects correction 5 Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome Patients (CRPS) Image Preprocessing Remove the pixels representing the skull Motion correction Wolf and Detre Neurother Vol. 4, 346–359, July 2007 PVE correction Implemented an In-house written MATLAB code created by Asllani et al. [2] Images from 5CRPS were processed using a kernel size of 5 and 9 Kernel filter Adjust the kernel size from to 5, 7, 9, 11 and 15 1 patient’s data Significant decrease (P<0.05) in the SNR Variation in the voxels due to the noise could have prevented the code from working as intended Results & Discussion SNR Before and After PVE correction Signal to Noise Ratio K=5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Subject 1 Subject 2 Subject 3 Subject 4 Subject 5 CRPS Patient Uncorrected SNR PVE corrected SNR Inconsistent Results There is no significant difference (P>0.05) It is likely that the algorithm is not functioning as intended Results & Discussion SNR Before and After PVE correction Signal to Noise Ratio K=9 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Subject 1 Subject 2 Subject 3 Subject 4 Subject 5 CRPS Patient Uncorrected SNR PV corrected SNR Subject 5 Results & Discussion Larger kernel have a greater SNR Small kernel sizes are sensitive to noise and variance Kernel Size vs SNR 4 Signal to Noise Ratio 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 5 7 9 11 Kernel Size Uncorrected Signal Corrected Signal 15 The SNR decreased after the PVE correction Kernel size needs to be chosen carefully Our in-house implementation of the PVE correction needs to be fine tuned [1] Tracy, Melzer R. "Arterial Spin Labelling Reveals an Abnormal Cerebral Perfusion Pattern in Parkinson’s Disease." Brain 134.3 (2011): 845-55. [2] Asllani, Iris, Ajna Borogovac, and Truman R. Brown. "Regression Algorithm Correcting for Partial Volume Effects in Arterial Spin Labeling MRI." Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 60.6 (2008): 1362-371. [3] Xu, Guofan, Howard A. Rowley, Gaohong Wu, David C. Alsop, Ajit Shankaranarayanan, Maritza Dowling, Bradley T. Christian, Terrence R. Oakes, and Sterling C. Johnson. "Reliability and Precision of Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion MRI on 3.0 T and Comparison with 15O-water PET in Elderly Subjects at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease." NMR in Biomedicine 23.3 (2010): 286-93. Print. Questions?