MRSA Swabs for De-escalation of Antibioti
advertisement

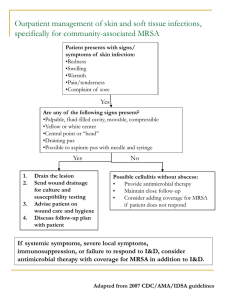
Role of MRSA Swabs for De-escalation of Antibiotics in HCAP Colleen Linsenmayer, Pharm.D. PGY2 Internal Medicine Pharmacy Resident Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center This speaker has no actual or potential conflicts of interest to disclose in relation to this presentation Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) • Increasingly important pathogen in pulmonary infections • Incidence of MRSA healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP) is predicted to be 2-26.5%. • Associated with significant morbidity and mortality Niederman MS et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388-416. Dangerfield B et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):859-62. IDSA HAP Guidelines HAP, VAP or HCAP suspected Late onset (≥5 Days) or risk factors for multi-drug resistant (MDR) pathogens Broad spectrum antibiotic therapy for MDR pathogens (Including MRSA) Niederman MS et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388-416. IDSA HAP Guidelines Consider de-escalation of antibiotic based on: 1) Results of lower respiratory tract cultures are available 2) Patient’s clinical response How do you de-escalate in absence of adequate lower-respiratory cultures? Niederman MS et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388-416. MRSA Colonization • Identifying patients with MRSA colonization may guide initial antibiotic treatment and isolation measures • MRSA swabbing is a standard method for screening in many facilities for MRSA screening Dangerfield B et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):859-62. MRSA Nasal Colonization • MRSA nasal colonization can be reliably detected using nasal swab PCR test • Presence of MRSA nasal colonization has been correlated with the development of subsequent MRSA infections Dangerfield B et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):859-62. Boyce JM et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1163-8. Predictive Value of MRSA Nasal Swabs for MRSA Pneumonia Result 95% Confidence Interval Sensitivity (%) 88.0 67.6 – 96.9 Specificity (%) 90.1 86.6 – 92.8 Positive predictive value (%) 35.4 24.0 – 48.7 Negative predictive value (%) 99.2 97.4 – 99.8 Test Characteristic Dangerfield B et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):859-62 MRSA Nasal Swabs Negative Predictive Value (NPV) Clinical Trial Population Culture Site NPV Non-ICU Any Body Site 98% Robicsek et al. All admissions/ ICU transfers Any Body Site 98% Robissek et al (Subgroup) All admissions/ ICU transfers Respiratory 98% Sarikonda et al ICU Respiratory 84.4% Harris et al. Harris AD et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2010;54(8):3143-8. Robicsek A, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2008 ;46(2):588-92. Sarikonda KV, et al. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(10):1991-5. Discontinuation of Empiric Vancomycin Population: patient receiving empiric vancomycin for suspected or proven HCAP with no adequate lower-respiratory cultures If nasal + throat MRSA cultures were negative then de-escalation of vancomycin was recommended Results: no difference in mortality compared to previous study of pneumonia patients who underwent de-escalation of antibiotics when respiratory cultures were not obtained Boyce JM et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1163-8. Debunking Myths “The patient’s nasal swab may be negative because they received empiric vancomycin therapy prior to the admission nasal swab” Vancomycin has been shown to have little effect on staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization and seldom would eradicate MRSA in the first several days of therapy Boyce JM et al. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1163-8. Clinical Pearl Empiric HCAP Treatment Patient meets the following criteria: 1) Blood cultures negative x 48 hours 2) Negative MRSA nasal swab Consider discontinuation of MRSA-directed antibiotic Summary • MRSA pneumonia is unlikely in patients who are not colonized and have no evidence of MRSA bacteremia • Data suggests that MRSA PCR nasal swabs have negative predictive value of up to 99% for MRSA pneumonia • A negative MRSA swab can be reasonably used to guide antibiotic de-escalation for HCAP Role of MRSA Swabs for De-escalation of Antibiotics in HCAP Colleen Linsenmayer, Pharm.D. PGY2 Internal Medicine Pharmacy Resident Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center