Internal Forces and Climate

Internal Forces and Climate
I. Introduction
I. Introduction
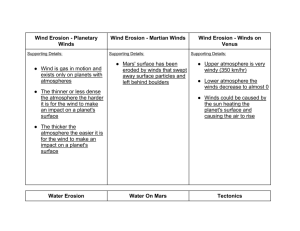
Erosion rate: 14 cm per 1000 years
Erosion rate: 4 cm per 1000 years
I. Introduction
Erosion rate: 4 cm per 1000 years, or 0.000131 ft/yr
Rate x Time = Distance
I. Introduction
Erosion rate: 4 cm per 1000 years, or 0.000131 ft/yr
Rate x Time = Distance
.000131 ft * Time = 20,000 ft yr
Time = ???
I. Introduction
Erosion rate: 4 cm per 1000 years, or 0.000131 ft/yr
Rate x Time = Distance
.000131 ft * Time = 20,000 ft yr
Time = 152 million years
I. Introduction
Erosion rate: 4 cm per 1000 years, or 0.000131 ft/yr
Rate x Time = Distance
.000131 ft * Time = 20,000 ft yr
Time = 152 million years
II. The endogenic effect
A. Overview
II. The endogenic effect
“The difference between the two masses
A. Overview represent a balance in endogenic mechanics”
Archimede’s Principle: An object is immersed in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid
displaced by the object.
II. The endogenic effect
B. Epeirogeny
“uplift or depression on a regional scale, with minimal disruption of original rock structure” e.g.: isostacy
C. Orogeny and Tectonic Geomorphology
D. Volcanism
D. Volcanism
Two overlying controls:
• Silicon content of magma
• Temperature of magma
D. Volcanism
1. Lava Plains and Plateaus
D. Volcanism
1. Lava Plains and Plateaus
2. Shield Volcanoes
Shield volcanoes
– Tall volcanoes –3 or 4 miles tall
– Wide base – Diameter of ten of miles
Mauna Loa, HI
Mauna Loa, HI
D. Volcanism
1. Lava Plains and Plateaus
2. Shield Volcanoes
3. Cindercone Volcanoes
Cinder cones
– Short, narrow cone,
– Steep sides
– Violent eruptions
Lassen Volcanic National Park, CA
Lassen Volcanic National Park, CA
D. Volcanism
1. Lava Plains and Plateaus
2. Shield Volcanoes
3. Cindercone Volcanoes
4. Composite Volcanoes
Composite or stratovolcanoes –
– Tall volcanoes – 1 to 2 miles high
– Violent eruptions
Mayon Volcano, Phillippines
Mt. St. Helens, WA
III. Climatic Geomorphology
A. Overview
“Examine the relationship between landforms and climate”
CLIMATE-PROCESS SYSTEM
MORPHOGENETIC SYSTEM
III. Climatic Geomorphology
A. Overview
B. Geomorphic Response
“response time”
III. Climatic Geomorphology
A. Overview
B. Geomorphic Response
“response time”
Milankovitch Cycles
Orbital Eccentricity
100,000 yr cycle
Axial Tilt
41,000 yr cycle
Precession of Equinoxes
(wobble effect)
11,000 yr cycle