Types of Volcanoes
advertisement
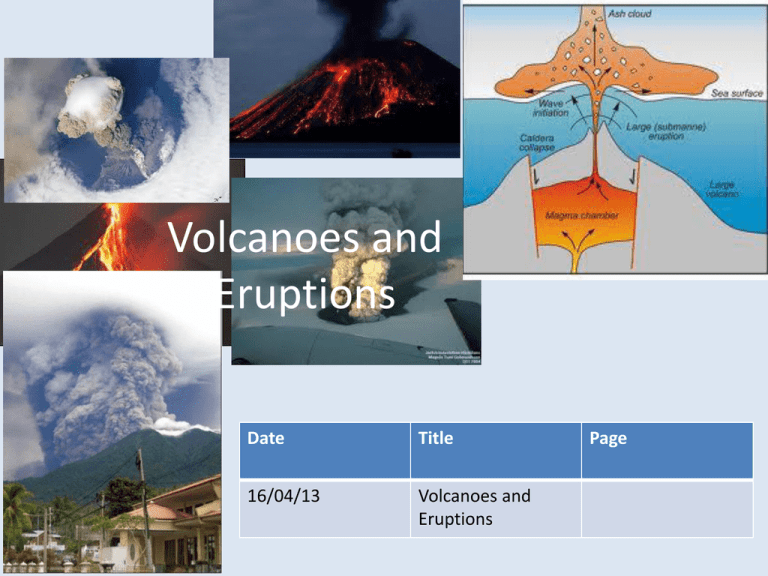
Volcanoes and Eruptions 8SCIENCE Date Title 16/04/13 Volcanoes and Eruptions Page Review • Where do volcanoes form? – Plate boundaries • How do volcanoes form? – Heat and pressure from inside the Earth produces magma and pushes up to the surface • What is a hotspot? – Very hot areas in the mantle that produce volcanoes although they are not found on plate boundaries • • Identify the cause of each volcano below using the words: subduction, rift, and hot spot. • a) In 1973, a town in Iceland called Vestmannaeujar was surprised when lava began erupting from a vent or crack in the Earth’s surface. The Earth’s crust seemed to split apart._______________________ • • • b) Scientists feel that the Cascade Mountains, extending from California to British Columbia, are still forming. Two plates are colliding, forcing magma up from the mantle to form the mountain. _____________________ • • c) Mauna Loa in Hawaii is the “growing mountain”. In 1969 and 1974, it erupted and poured out lava through a hole in the Earth. This lava called and hardened into rock. Below it, molten lava continues to flow. _____________________ Types of Volcanoes • Shield • Cinder cone • Composite Introduction to the three types of volcanoes • Three types of volcanoes • As you view the video clip, try to think of some of the similarities and differences between the three types of volcanoes. Shield volcanoes • Quiet eruption that produces lava and spreads out in flat layers • These layers build to form slightly sloping sides • Ex: Hawaiian islands produces 2 different types of lava: – Pahoehoe (smooth) - A’a (rough and chunky) Pahoehoe and A’a lava A’a lava Pahoehoe Cinder cone volcano • Explosive eruptions that throw lava and rocks high into the air • These bits of rock and hardened lava are called tephra – Tephra layers build up to form steep sided volcanoes Tephra lava Tephra lava erupted from the 1980 Mount St. Helens Eruption in Washington State Composite volcano • Produces eruptions that are quiet then violent • Cycles of lava and tephra form different layers • Usually found where one plate is forced under another(subduction zone) Let’s review with animations… • Types of Volcanoes What causes an eruption to be quiet or violent? • Amount of water vapor and other gases trapped in magma – High gas content = more violent eruption – Gases are trapped in magma and pressure builds up – As magma moves closer to the surface, there is less pressure and the gas can escape • Amount of silica (silicon and oxygen) present in magma – Low in silica = more quiet eruption Other volcanic structures • Not all magma flows to the surface • Some may rise from the volcano and cools underground to form other rock structures • Erosion of the rock layers make these visible to us today CALDERAS IN OREGON (US) AND PHILLIPINES DEATH VALLEY, CALIFORNIA SHIPROCK, NEW MEXICO COLOMBIA