S. saprophyticus
advertisement

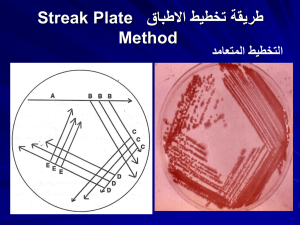
Staphylococcus Gram + cocci In clumps Staphylococci 3 major species: S.aureus, S.epidermidis, and S.saprophyticus) Infections are primarily associated with pathogenic strains of S.aureus Many virulence factors Comparison of the 3 major species (Table 64.1 p416) All three species appear similar by Gram stain. S. aureus S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis Media Used to Distinguish Staphylococcal Species MSA S. aureus ferments manitol causing the media to turn yellow S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus do not Therefore, the media remains red DNAse Test: Confirms S.aureus DNAse (an enzyme that degrades DNA) On medium containing DNA and methyl green, a positive result is a clearing around the bacterial growth S. aureus S. saprophyticus Gram+ cocci in clumps Manitol fermentation (MSA media) DNAse+ S. epidermidis Gram+ cocci in clumps No Manitol fermentation (MSA media) DNAse- Procedure: Divide a MSA plate into 3 sectors; inoculate (single line inoculation) the plate with S.aureus, S.saprophyticus and S.epidermidis Divide a DNAse plate into 3 sectors; inoculate the plate with the 3 organisms listed above as described above MSA and DNAse Plates S. aureus S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis Novobiocin Sensitivity Test S. aureus and S. epidermidis Used to distinguish S.saprophyticus from S.epidermidis and S. aureus Identifies the novobiocin-resistant S.saprophyticus S. saprophyticus Page 147 S. saprophyticus S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis S. epidermidis Procedure: Divide a Mueller-Hinton Agar Plate into two sectors Inoculate (create a small “lawn” of bacteria in each sector) with S.epidermidis and S.saprophyticus Place a novobiocin disk in the center of each “lawn” Invert plate; incubate Catalase Test Determines the ability of microbes to degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by producing the enzyme catalase H2O2 is produced during aerobic respiration; must be degraded catalase 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 Catalase Test Results Upon addition of H2O2 , Catalase positive organisms release oxygen gas (seen as bubbles) Present in Staphylococcus Coagulase Test Coagulase: an enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin in plasma to form clots. S. aureus express coagulase. S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus do not. S. aureus S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis Gram+ cocci in clumps Manitol fermentation (MSA media) DNAse+ Novobiocin sensitive Coagulase+ Catalase+ Gram+ cocci in clumps No Manitol fermentation (MSA media) DNAseNovobiocin resistant CoagulaseCatalase+ Gram+ cocci in clumps No Manitol fermentation (MSA) DNAseNovobiocin sensitive (Zone of inhibition) CoagulaseCatalase+ Catalase + + + Page 146