Sustainable Aquaculture
advertisement

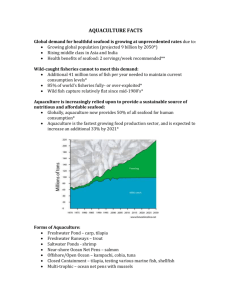
Sustainable Aquaculture Texas Envirothon -AquaticsTeacher Workshop January 11 2014 Jenny Oakley Environmental Scientist oakley@uhcl.edu Aquatic Resource Consumption • In the US, 16 ½ lbs of seafood/person/year o US population (2012): ~314million = ~5.2billion lbs/year • US imports over half of the seafood it consumes. • Global total production =148.5 million tons in 2010. Fish is good for you…right? • Institute of Medicine: recommends a diet rich in seafood. • Lean, heart healthy source of protein • But, Is all seafood safe to eat? o o o o o PCBs Heavy metals DDT Hormones Radiation? Overfishing • Definition: Catching too much fish for the system to support by reproduction. o o o o Economically extinct fisheries Fishing down the food-chain Bycatch Irreversible consequences • Overfishing Video LINK OMG, we are doomed! • Wait, is this some kind of fish story? o Sample methods o Population numbers = a guess o Middle Ground • Magnuson–Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act -1976o o o o Sustainable fisheries act of 1996 National Marine Fisheries Service (NOAA) U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service State Parks and Wildlife Department So… how do we provide food? • Aquaculture production = avg. growth of 6.3 % per year • 2010, value of aquaculture production ~ at $119.4 billion. Producer • Top 10 aquaculture producers In 2010, contributed 87.6 % of world production by quantity. China India Viet Nam Indonesia Bangladesh Thailand Norway Egypt Myanmar the Philippines Million Metric Tons 36.7 4.6 2.7 2.3 1.3 1.4 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 Aquaculture • Definition: the farming of aquatic organisms. • Output of Aquaculture: o Consumption • Direct: fish market • Indirect: fish meal or byproducts o Stock wild populations • TPWD = 40 million fish in public lakes, ponds, and saltwater bays What is being produced? • Major cultured species: o o o o o o Freshwater Fishes: 56.4% Molluscs: 23.6% Crustaceans: 9.6% Diadromous Fishes: 6.0 % Marine Fishes: 3.1% Other: 1.4% Aquaculture Types Farm/Tank vs Ranch/Cage Aquaculture Products Fish Amphibians Invertebrates Reptiles Plants Is Aquaculture the Answer? Environmental Impacts • Loss of natural habitat o Water needs • Coastal areas: Mangroves • Riparian zone: Rivers • Loss of genetic diversity o Brood Stock Environmental Impacts Cont. • Water Usage o Intake screens o Water rights • Pollution o o o o Eutrophication Thermal pollution Disease and Pathogens Antibiotics, steroids, & drug resistant pathogens Environmental Impacts Cont. • Escapees o Invasive species • Asian Carp LINK o Genetic pollution • Predator Control o Permitted and Unpermitted control of birds, marine mammals, etc. • Physical removal • Sonar Environmental Impacts Cont. • Feeding Fish with Fish? o Wild caught fish used to feed aquaculture o Farming carnivores LINK Sustainability of Aquaculture • Proper site selection o Permitting requirements • Reduce overfeeding o Cuts costs of food o Reduces nutrient buildup o Helps maintain D.O. levels • Polyculture/Aquaponics o Utilizes natural foods efficiently o But is it possible large-scale? Sustainability of Aquaculture Cont. • Grow vegetarian fish & feed vegetarian food LINK • Closed Loop/Recirculating Systems o Addresses: Water needs, outfall pollution o Increase costs with expensive and complex filtration systems Sustainability of Aquaculture Cont. • Avoid overstocking o Reduced stress o Reduced disease/pathogen outbreak • Minimize antibiotic use • Sell and Buy Locally o Reduce transportation footprint • Stock native species o Temperature requirements What can you do? • Make ocean-friendly seafood choices o Avoid unsustainable seafood in the grocery store or restaurants o Ask, where your seafood came from! o Try to eat locally grown seafood (Regional) o Spread the word! Questions? Jenny Oakley oakley@uhcl.edu Dichotomous Key