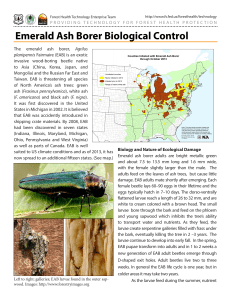
Trunk injection
advertisement

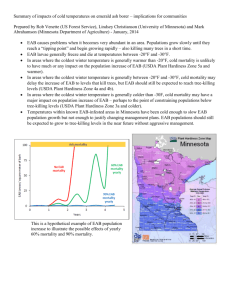
EAB Update Lee Townsend Extension Entomologist Agenda • Identification and Impact • Current status • Control options – Homeowner & Commercial applicator • Biological control • General information and questions EAB calendar Pupa April - May Inactive October - April Adults out mid-May Feeding June - October Adults mid-May – July • Larvae feed under bark June – October; disrupt transport of water, nutrients, carbohydrates • Healthy trees killed within 2-3 years of first symptoms Emerald ash borer in KY •EAB info - US http://www.emeraldashborer.info/ •Emerald ash borer - KY http://pest.ca.uky.edu/EXT/EAB/welcome.html 12 counties > 5 mill ash stems 54 counties > 2 mill 2012 EAB Risk Map Red = infested Brown = high Orange = medium Yellow = low EAB Survey 2012 – 1,700 traps Year Traps 2008 2009 2010 2011 3,065 5,665 6,000 6,825 Positive # Beetles Counties 0 0 10 200 9 182 11 219 New 2011 Anderson Bracken Boyle Garrard Hardin Scott Woodford Anderson, Franklin, Henry, Owen, Shelby, Woodford Boone, Kenton, Campbell Greenup - Boyd Boyle - Garrard Fayette - Jessamine Hardin Jefferson – Oldham 2012 Adult emergence 1st emergence mid- May 450 to 500 dd base 50 Peak June – July about 750 dd 70 to 140 dd ahead for 2012 Ohio State Recommendations • Imidacloprid when EAB first found – within 15 mi high risk – in quarantine zone – low to moderate risk • Use Tree-äge when EAB pressure increases • Use high rate of Tree-äge at infestation peak • Monitor and treat as needed after peak infestation Treatment Options • Systemic Soil Injections / Drenches: – Imidacloprid (e.g. Merit, Xytect, Bayer Advanced Tree & Shrub 12 Month Insect Control) – Dinotefuran • Systemic Trunk Injections: – Imidacloprid (IMA-jet, Imicide) – Emamectin benzoate (TREE-äge) • Systemic Trunk Sprays: – Dinotefuron (Safari) • Bark and canopy sprays: Astro, Onyx Realistic Expectations • Insecticides can protect ash trees from EAB; success is not guaranteed • Insecticides are not effective in eradicating infestations Homeowner options • 12 mo Tree & Shrub (imidacloprid) • 12 mo Tree & Shrub (dinetofuran) • Ace Caps (acephate) Imidacloprid (12 month products) Product Tree & Shrub (1.47%) quart Protect & Feed (1.47%) quart Landscape Formula (2.94%) gal Granular Tree & Shrub + Fertilizer (1.1%) Rate/ in 1 fl oz 1 fl oz $/inch $0.60 ($.20 dia) $0.71 0.5 fl oz $0.53 0.25 cup ? Dinotefuran (Safari) • Green Light Emerald Ash Borer Killer (2% G) • Tree & Shrub Insect Control with Safari 1/2 to 2/3 cup per inch of tree diameter • Apply early to mid-May $5.33/lb $5.70/lb Acecap 3/8” Insecticide Implants • 5 per pack $9.50 - Arborists / Commercial Applicators Imidacloprid (Group 4) • Drench, soil injection, trunk injection • Merit, Xytect, etc. Safari 20 SG Insecticide (dinotefuran) (Group 4) • • • • • • Trunk spray – 12 to 24 oz/gal Use 1 gal per 40” to 50” trunk dbh 1 – 4 weeks for uptake Spray from root flare to 4’ to 5’ above ground Low pressure - 10 to 20 psi Do not apply to wet bark or within 12 hrs of rain Safari 20 SG Insecticide • $390 / 3 lb container • Low rate = $2.48/ in circumference • High rate = $3.10 /in circumference Tree-äge Emamectin benzoate • • • • Restricted Use – Acute human toxicity $559/liter $399 injector Cordless drill • $3.15/ inch circumference • 3 yrs with high rate Professional Use Products Soil injection / Drench Imidacloprid Merit Trunk injection Imidacloprid IMA-jet Arborjet Imicide Mauget Pointer Wedgle Bidrin Injecticide- B Mauget Emamectin Tree-age Arbojet benzoate Trunk Spray **Dinotefuran Safari + PentraBark Application April to May May to June May to June May to June May to June May April to May Professional Use Products Preventive Bark & Foliage Cover Sprays bifenthrin Onyx carbaryl Sevin cyfluthrin Tempo permethrin Astro 2x at 4-week intervals – 1st application at black locust bloom Trunk Injections • Absorbed more quickly than drench • Large trees > 12” dbh • Where drenches are not practical – near water, etc. • Potentially injure trunk, especially if repeated Summary • Insecticides can offer protection against EAB • Success not assured – annual treatments may be needed • Factors in successful treatment not understood yet • Inventory ash – set priorities 1 CEU – Cat 10 Email your license number to me today Lee.Townsend@uky.edu Importing natural enemies Spathius agrili • Attacks EAB larvae – detects infested trees, injects egg into EAB larva • Affects up to 90% of EAB larvae in Chinese trees • 3 to 4 generations per year • Winter as pupae under bark Tertastichus plannipennisi • Attacks EAB larvae – detects infested trees, injects egg into EAB larva • 50% success rate • Up to 127 adults per EAB larva • Winter as larvae under bark Oobius agrili • • • • • Attacks EAB egg At least 4 generations per year 60% success rate Up to 62 eggs/wasp Winter as larvae in egg Importing natural enemies Environmental impact • Are they specific to intended host? • Can they be reared successfully for mass release? • Is our climate suitable? What does the future hold? • Will North American ash will follow the model of Dutch elm disease - individual trees have reduced life span but are able to reproduce • OR American chestnut - individual trees die before they can reproduce • OR something entirely different Factoids • Ash in sunny, open conditions preferred over shaded locations within canopies • Blue ash appears to be less attractive than green or white but is attacked as other ash species die • Stressed ash trees may be preferred but once EAB is abundant healthy trees are attacked, too • 1.5” diameter to mature trees EAB Hosts • Only infests ash (Fraxinus) in the US • EAB or “a closely related beetle” in Asian attacks species of elm, walnut, and Pterocarya (wingnut) • Green ash appears to decline more rapidly that white ash under similar conditions Dispersal • Unassisted rate in Michigan appears to have been about 6 mi/year (0.6 mi/yr cited, too) • On edges – EAB galleries up to 800 yds from potential source • BUT most within 100 – 200 yds • 1.7 mi average by mated female Eggs • 50 to 90 eggs / female • In bark crevices • Hatch in about 2 weeks • Rough bark Alternate hosts • Given no alternative, female EAB will lay eggs on alternate species • “Ovipositional mistakes” do occur in the field but appear to be rare • Privet appears to be a suitable host for small EAB larvae Recommendations change, keep fishing for new information … Don’t believe everything you read Don’t wait too late to ask for help EAB Biology Lee Townsend Extension Entomologist • Saplings may die after 1 year of attack • Large ash trees may die within 3 to 4 years of initial infestation Adult feeding Adults live 3 to 6 weeks Edge feeding on foliage Foliage feeding • 5 to 7 days before mating • 5 to 7 days after mating Egg-laying choices (lab) Larva • Up to 1 inch long • Feed in phloem and cambium • Finished by October Larvae • Serpentine galleries in phloem and cambium • Extensive damage to waterconducting tissue • Packed with frass New wood Old wood Pupate – mid-April 2 to 3 weeks from start of pupation to and adult