What controls community composition
advertisement
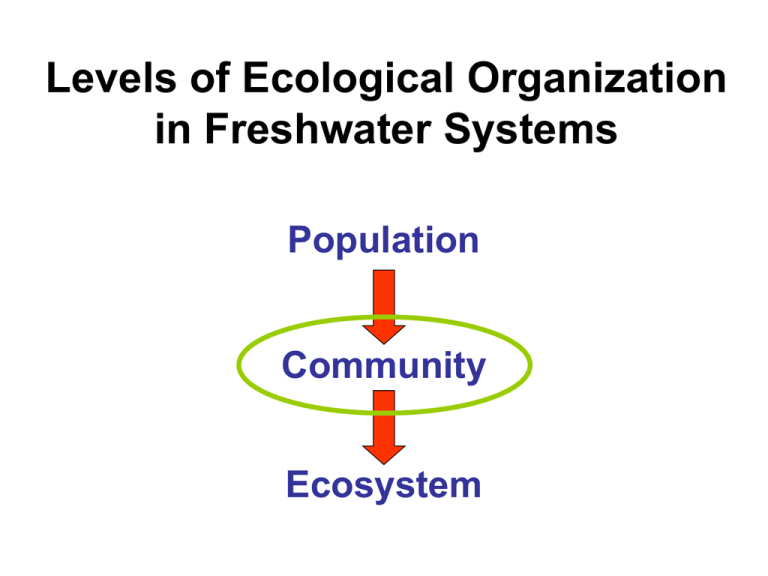
Levels of Ecological Organization in Freshwater Systems Population Community Ecosystem Community Ecology in Freshwater Systems What controls species composition (aka, diversity)? • What causes species composition to change over space and time? What are the consequences of variation in species composition? • Why does “biodiversity” matter in freshwater systems? What is a community? • A group of interacting species occurring in a particular place, at a particular time. How do we describe freshwater communities? • Species richness • Relative abundance • Diversity indices (e.g., Shannon, Simpson’s) How do you describe a community? • Species richness: 4 How do you describe a community? • Diversity indices: richness weighted by relative abundance > Food Webs, Functional Groups, and Trophic Levels Levels ~ Diversity Sp. 10 Sp. 7 Sp. 1 Sp. 2 Sp. 8 Sp. 3 Sp. 9 Sp. 4 Sp. 5 Sp. 6 Assumptions: • Individual species occupy one level Sp. 7 Sp. 6 Sp. 7 Sp. 1 Sp. 7 Sp. 7 Sp. 2 Sp. 5 Sp. 3 Sp. 4 Assumptions: • Individual species occupy one level • These systems are rare: Sp. 3 Sp. 5 Sp. 2 Sp. 1 Sp. 1 Sp. 2 Sp. 3 Sp. 4 Variation in community composition over space Variation in community composition over time Spring Fall What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment > Limiting resources > Limiting conditions Limiting Resources: Some thing a species or group of species uses to survive. Limiting Condition: Some attribute of the environment that a species or group of species must tolerate to survive in a particular place. What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species > Predation (+ / -) > Competition (- / -) > Mutualism (+ / +) Predation and Community Composition • Trophic cascades …and galaxiid hell. (Flecker and Townsend 1994) Predation and Community Composition • Trophic cascades No Fish (Flecker and Townsend 1994) Predation and Community Composition • Trophic cascades • Significant effect of “fish species” on total invertebrate density. •Significant negative effect of “fish” on species richness, no effect of “fish species”. (Flecker and Townsend 1994) What isn’t insect richness telling us about the effect of trout on community composition? (Flecker and Townsend 1994) Predation and Community Composition • Super predators!! No Fish Fish Competition and Community Composition Disruptive selection Proportion of Population • The ghost of competition past Diet breadth Competition and Community Composition • The ghost of competition past Competition and Community Composition • The ghost of competition past What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment AND • Interactions among species Abiotic Biotic effects on community composition Dicosmoecus “Resistant Grazer” (Wootton et al. 1996) Abiotic Biotic effects (Wootton et al. 1996) = Unregulated Regulated Abiotic Biotic effects (Wootton et al. 1996) What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Ecosystem age What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Ecosystem age - Successional ponds - Ephemeral streams and ponds What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Ecosystem age • Disturbance Disturbance and community composition Good Colonizers + Good Competitors Good Competitors Minimally Disturbed Good Colonizers Extensively Disturbed (Connell 1978) Disturbance and community composition Disturbance and community composition Kadashan River Basin, SE Alaska • Response of riparian plant communities to flood frequency. • Frequency = number of times per year that the mean elevation of a site was inundated. (Pollock et al. 1998) Disturbance and community composition (Pollock et al. 1998) What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Ecosystem age • Disturbance • Productivity Productivity and community composition VS. Productivity and community composition Population Size The paradox of enrichment Time (Rosenzweig 1971) The paradox of enrichment Low and Moderate Productivity Population Size Population Size High Productivity Time Time (Rosenzweig 1971) What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Age • Disturbance • Productivity • Size and Complexity Size and community composition Hypothesis: As size increases, so does habitat heterogeneity, resulting in more “niches” that can be filled by more species. Size and community composition What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Age • Disturbance • Productivity • Size and Complexity ? Size versus Productivity • Sampled 25 lakes in North America that varied in size AND productivity. • Used N isotopes in top-predators fish to determine food-chain length leading to that predator. 15N < 15N Maximum Trophic Position < Maximum Trophic Position (Post et al. 2000) Size versus Productivity (Post et al. 2000) Size versus Productivity (Post et al. 2000) What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Age • Disturbance • Productivity • Size and Complexity ? What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Age • Disturbance • Productivity • Size and Complexity • Colonization and Extinction Colonization, extinction, and community composition Island Biogeography Theory (MacArthur and Wilson 1987) Colonization, extinction, and community composition Island Biogeography Theory • Effect of increased isolation Colonization, extinction, and community composition Electric Fishes (Fernandes et al. 2004) Colonization, extinction, and community composition Tributary “Isolated” “Connected” (Fernandes et al. 2004) Colonization, extinction, and community composition (Fernandes et al. 2004) What controls community composition (i.e., species diversity)? • Interactions with the abiotic environment • Interactions among species • Age • Disturbance • Productivity • Size and Complexity • Colonization and Extinction