Living v. Nonliving
advertisement
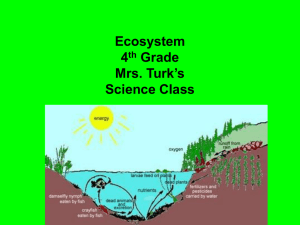
Living v. Non-living Unit 1-1 Notes Mr. Hefti – Pulaski Biology Please make a t-chart that is about half a page in size in your notes and list the living and non-living things you are about to see in the appropriate columns. Living Non-living Are bones (1) living? What about algae (2)? Garbage(3)? Freshly cut tree(4)? Lichen (5) Is a fossil (6) alive? NaCl (7) Iron (8) Water (9) These substances can be found in living things… does that mean they are living? What about the rocks (10)? The crayfish (11)? Pollutants (12)? Insects (13)? Moss (14)? Sunlight (15)? Honeybee (16) ??? Honey (17) What about viruses (18)? Stump (19) Dirt (20) Is it dead or alive? Living or non-living? Carcass (Free) How did you do? Living (1) Bones (2) Algae (4) Freshly cut tree (5) Lichen (11) Crayfish (13) Insects (14) Moss (16) Honeybee Non-living (3) Garbage (6) Fossil (7) NaCl (8) Iron (9) Water (10) Rocks (12) Pollutants (15) Sunlight (17) Honey (18) Viruses (19) Stump (20) Dirt (Free) Carcass 8 Characteristics of Life • Biologists characterize life by these functions: – Nutrition – Transport – Respiration – Excretion – Synthesis – Regulation – Growth – Reproduction Biotic / Abiotic • Biotic: living, once living, or from something living Examples: - Plants - Animals - Dead leaves - Bacteria - Scat (animal droppings) • Abiotic: non-living and never was living Examples: - Oxygen - Wind - Minerals - pH - Water - Rocks Please make a t-chart in your notes (this time a quarter of a page) and list the biotic and abiotic factors in the following picture of a rotting log ecosystem. Use your imagination to identify things that just might be there… Biotic Abiotic Rotten Log Ecosystem Factors Biotic Fungus Bark Bacteria Moss Ants Spores Worms Abiotic Sunlight Moisture Soil Oxygen Carbon dioxide