Chapter 18 Interactions of Living Things
advertisement

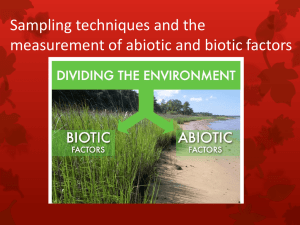
Pages 532-537 Section 1 Bell Ringer Describe Abiotic and Biotic factors in your journal. The Environment Ecology Study of the interactions among organisms and their environment. Ecologists Scientists who study environmental relationships Organize the environmental factors that influence organisms into 2 groups ABIOTIC BIOTIC Comparing Abiotic and Biotic Factors Abiotic Non-living parts of the environment Examples: I. Water II. Light & Temperature III. Air IV. Soil Comparing Abiotic and Biotic Factors Biotic Factors Living or once-living organisms in the environment Examples: I. Levels or organization II. Population III. Communities IV. Ecosystems V. Biomes VI. The Biosphere Video Time http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rNfmew9C508 Bell Ringer Describe the “biome” in which we live. Must answer with at least 5 sentences. Be in depth and cover what is observed in this area. Abiotic Factors 5 Factors: Water Light Temperature Air Soil Abiotic Factors 1. Water All organisms need water to survive Organisms are made of 50%-95% water Respiration, photosynthesis, digestion, and other important life process can only occur with presence of water 95% of Earth’s surface water is found in oceans Examples of Water Pacific Ocean-Kauai, Hawaii Dale Hollow Lake Cumberland River & Lake Cumberland Bayou-Gueydan, LA Abiotic Factors 2. Light Availability of sun light is a major factor in determining where green plants and other photosynthetic organisms live Energy from Sun is changed into chemical energy Algae-lives near water surface Dense forest have very little photosynthetic plants, why? Plant Examples The Garden of Eden-Kauai North Shore-Kauai Kipu Ranch-Kauai -conifers Abiotic Factors 3. Temperature Regional temperature also determines which plants and animals can live there Some areas of the world have fairly consistent temperature year round Other areas have season during which temperatures vary Arctic, Desert, Mid-Atlantic, Tropical, Arid, and Mild Temperature Variations Rain Forest-Brazil Arctic Plain-Antarctica Mojave Desert-CA Appalachian Mts-TN Great Plains-Kansas Tropical Island-FL Keys 4. Air Abiotic Factors Composed of a mixture of gases including Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Carbon Dioxide. Plants & Animals depend on the gases in air for respirations (breathe) All species are affected by weather Weather- 8km to 16 km (from surface) Ozone Layer-20km to 50km (from surface) Few organisms live at extreme air pressures 5. Soil Abiotic Factors Varies greatly from one environment to another Soil Type-determined by amount of Sand, Silt, and Clay it contains Various soils contains different amounts of nutrients, minerals, and moisture Soil affects every organism in an environment! Soil Top Soil-rich in nutrients and moisture (plant crops) Red Clay-sub soil-very acidic (use as filler dirt) Bed Rock-mostly limestone/sandstone (paving stone) Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors do not provide everything an organism needs for survival Organisms depend on other organisms for: Food Shelter Protection Reproduction Biotic Factors Biotic Factors Include: Bacteria Protists Fungi Plants Animals Levels of Organization 1. Organism: one individual from a population Mallard Drake “GreenHead” Levels of Organization 2. Population: all of the individual of one species that live in the same area at the same time. Levels of Organization 3. Community: the populations of different species that interact in some way Levels of Organization 4. Ecosystem: all of the communities in an area and the abiotic factors they interact with Levels of Organization 5. Biome: large region with plants and animals well adapted to the soil and climate of the region Levels of Organization 6. Biosphere: The level of biological organization that is made up of all the ecosystems on Earth Biosphere Where Earth’s organisms live Can be found 11,000 m deep in the ocean 9,000 m high on the mountains 4.5 km high in atmosphere Extremophiles Includes top part of Earth’s crust, all the waters that covers the Earth’s surface, the surrounding atmosphere, and all biomes!