Chapter 16 regents ppt
advertisement

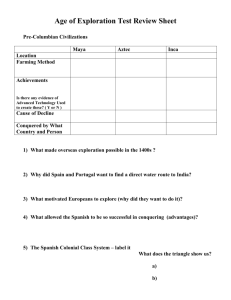
Regents Questions Mr. C. Dennison Cardinal Hayes HS 1 Age of Exploration During the 1500s, technological advances in navigation, naval engineering, and mapmaking contributed directly to the start of the ______________. 2 Hernán Cortés The conquest of Tenochtitlán by ________ in 1521 led to the fall of the Aztec Empire. 3 Enlightenment The Scientific Revolution and the _________- emphasized the value of human reasoning. 4 Columbian Exchange ____________global transfer of foods, plants, and animals during the colonization of the Americas. 5 explorers The Portuguese and the Chinese were active _______. 6 Africa Vasco de Gama (Portugal) and Zheng He (China) sailed near ____. 7 Mercantilism Which economic theory, developed in the 17th century, supported European colonialism? socialism bartering mercantilism feudalism 8 Atlantic Mercantilism – was responsible for the development of new _______ Ocean trade routes. 9 Western The astrolabe and improvements in cartography (map making) helped Europeans to explore the _______ Hemisphere. 10 Columbian Exchange The transfer of new products and ideas encouraged economic growth under the _____________. 11 Inca Expeditions of Hernán Cortés and Francisco Pizarro led to the destruction of the Aztec and ____ empires. 12 waterways During the Commercial Revolution - trading centers most often developed – along _________. 13 Scientific The heliocentric model, the development of inductive reasoning, and the work of Descartes are all associated with which revolution? 14 Scientific Revolution Sir Isaac Newton, Galileo Galilei, and Johannes Kepler are all directly associated with the ___________. 15 trade Under the concept of Mercantilism Controlling _____ is a key to increasing power. 16 Portugal and Spain During the 15th century, which two European countries began sea voyages of exploration? 17 people Columbian Exchange – goods and ______ were transferred between Europe, Africa, Asia and the Americas. 18 slave Several European countries participated in the ____ trade. 19 native Plantations in the New World used enslaved Africans to replace ______ populations. 20 Spain _______ had the most influence on the colonization of Latin America in the 1500s. 21 balance of trade One goal of mercantilism creation of a favorable ___________. 22 foods One effect of the Columbian exchange was the introduction of new ____ to both Europe and the Americas. 23 contradicted Seventeenth-century scholars Galileo and René Descartes faced serious challenges to their scientific theories because their ideas ________ traditional medieval European beliefs. 24 economic One impact of the Columbian exchange on the lives of Europeans was that a combination of new products and ideas promoted _________ growth. 25 military Spanish conquistadors were able to conquer the Aztec Empire because - Spanish soldiers made effective use of their _____technology. 26 mercantilism What was the primary economic policy used by the Spanish with their Latin American colonies? embargoes boycotts tariffs mercantilism 27 peninsular Spain and Portugal were able to engage in exploration due to – their _________ location. 28 navigational The journeys of Vasco da Gama, Bartholomeu Dias, and Christopher Columbus became possible due to development of new ______ instruments and technology. 29 encomienda The _________ system in colonial Latin America led to the use of forced labor. 30 The encomienda was a legal system that was employed mainly by the Spanish crown during the Spanish colonization of the Americas to regulate Native American labor. In the encomienda, the Spanish crown granted a person a specified number of natives for whom they were to take responsibility. In theory, the receiver of the grant was to protect the natives from warring tribes and to instruct them in the Spanish language and in the Catholic faith: in return they could extract tribute from the natives in the form of labor, gold or other products. In practice, the difference between encomienda and slavery could be minimal. Many natives were forced to do hard labor and subjected to extreme punishment and death if they resisted.[1] In the former Inca Empire, for example, the system continued the Incaic (and even pre-Incaic) traditions of extracting tribute under the form of labor. 31 central Art. 31. All Indians held in encomienda by the viceroys, by their lieutenants, royal officers,prelates, monasteries, hospitals, religious houses, mints, the treasury, etc., are to be transferred forthwith to the Crown. . . Art. 38. Lawsuits involving Indians are no longer to be tried in the Indies, or by the Council of the Indies, but must be pleaded before the King himself. . . — New Laws issued by Emperor Charles V, 1542–1543 One purpose of these laws was to reduce local authority and increase _________ control. 32 potatoes One significant effect of the Columbian exchange was that _______ were introduced into the diet of some Europeans. 33 colonies According to the European policy of mercantilism, _______ should benefit the mother country. 34 inflation Prices in Spain rose as colonies supplied large amounts of gold and silver. This suggests that Spanish imports of gold and silver led to ________. 35 empire The term _____ is best defined as an extensive territory under the rule of a single authority. 36 37 Commercial Which revolution in Europe is most closely associated with the rise of capitalism, the formation of guilds, and the growth of banking systems? Commercial Scientific Agrarian Glorious 38 Scientific During the _______ Revolution in Europe Scientists questioned traditional beliefs about the universe. 39 Spanish The social class system in Latin America during the 16th and 17th centuries was dominated by the ______ -born nobility. 40 cultural interactions The use of the terms Encounter and Columbian exchange represents attempts to describe the nature of ___________. 41 Middle Passage The _______is best defined as the forced journey of enslaved Africans to the Americas. 42 Europe Under the triangular trade system -most manufactured goods were produced in ______. 43 observation and experimentation Which pair of ideas were central to the Scientific Revolution? *social stability and economic self-sufficiency *observation and experimentation * technology and military expansion * scarcity and interdependence 44 diverse One result of the Age of Exploration was that most Latin American populations became more culturally ______ (different). 45 indigenous The term ________ means - originating and living or occurring naturally in an area or environment. 46 indigenous The encomienda system in Latin America exploited _____ (native) peoples. 47 mercantilism During the first Global Age (A.D. 1450–1770), European countries obtained both a source of raw materials and a reliable market for their finished goods by developing the policy of ___________. 48 Diaspora The African _______ refers to the forced migration of African peoples from their homeland. 49