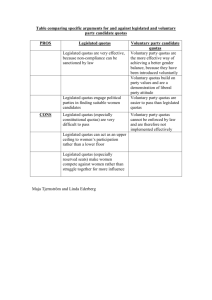
TRADE and Fair Trade Market
advertisement

TRADE Global Trade Fair Trade Market Charities, Celebrities and Lobbying Trade • A) the buying and selling of goods or services: Eg: tea trade, cotton trade, tourist trade. • B) the particular area of business or industry: Eg: home trade, foreign trade, import trade, export trade, retail trade, wholesale trade. Review: • The wholesaling process is an intermediate step in the distribution of merchandise. Wholesalers are organized to sell or arrange the purchase or sale of goods for resale (i.e., goods sold in bulk to other wholesalers or retailers). • The retailing process is the final step in the distribution of merchandise; retailers are, therefore, organized to sell merchandise in small quantities to the general public. Introduction notes: • International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. • In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP) . • Industrialization, advanced transportation, globalization, multinational corporations, and outsourcing are all having a major impact on the international trade system. • Increasing international trade is crucial to the continuance of globalization. Without international trade, nations would be limited to the goods and services produced within their own borders. • International trade is typically more costly than domestic trade. The reason is that a border typically imposes additional costs such as tariffs, time costs due to border delays and costs associated with country differences such as language, the legal system or culture. • But what is the impact of international trade? TRADE and Globalisation Does globalisation damage local (goods, services or cultures)? Does globalisation have an impact on living standards? Does it increase competition between companies? • What about the Fair Trade Market? A new area giving hope to smaller producers to survive after suffering from globalisation. • Is the fair trade marekt a solution to the world to tackle poverty and save farmers from bankruptcy? • Key words: subsidies, deregulation, wealth, prosperity, survival, dumping, tariffs, quotas, customs, breaking into new markets, booming or declining trade, protectionism. Key words and Definitions: find the definitions Open borders - (trade)Barriers – Subsidy - Customs – Quotas – Restrictions – Tarrifs - Dumping - Free port • Something which restrains or obstructs access between countries (similar to obstacle). • Free movement of good, services or people (eg: Schengen Agreement). • A port or an area of a port in which imported goods can be held or processed free of customs duties before re-export. • The selling of goods in quantity at below market price. • Taxes on goods coming into or going out of a country. • official rule that limits or controls what can happen in trade. • A limit on amount/quantity of something (goods or services). • The government department responsible for collecting the tax on goods that have been brought into the country (also to make sure illegal goods are not imported or exported). • Money given by the government to certain producers to help them produce without losing money. Key words and Definitions (key) • (trade)Barriers: something which restrains or obstructs access between countries. (similar to obstacle) • Open borders: free movement of good, services or people (eg: Schengen agreement ) • Free port: A port or an area of a port in which imported goods can be held or processed free of customs duties before re-export. • Dumping: the selling of goods in quantity at below market price • Tarrifs: taxes on goods coming into or going out of a country. • Restrictions: official rule that limits or controls what can happen in trade. • Quotas: a limit on amount of something (goods or services) • Customs: the government department responsible for collecting the tax on goods that have been brought into the country. (also to make sure illegal goods are not imported or exported) • Subsidy: money given by the government to certain producers to help them produce without losing money. Find correct meaning for the following terms: Developing industries - Strategic industries - Liberalise – Deregulation - Laisser faire. • New (infant) or restructured industrial sectors. (can be harmed by trade competition in its early stages) • An industry that a government considers to be very important for the country's economy to remain competitive or not be too dependent on other countries (it is protected). • to become more liberal. • to remove regulations or controls. • unrestricted freedom in commerce. Find meanings for… key • Developing industries: New (infant) or restructured industrial sectors. (can be harmed by trade competition) • Strategic industries: an industry that a government considers to be very important for the country's economy to remain competitive. • Liberalise: to become more liberal • Deregulation: to remove regulations or controls • Laisser faire: unrestricted freedom in commerce • Dumping is an informal name for the practice of selling a product in a foreign country for less than either (a) the price in the domestic country, or (b) the cost of making the product. • It is illegal in some countries to dump certain products into them, because they want to protect their own industries from such competition. See dispensa page 78 Why trade with EU? Complete he folllowing sentences with the words below: Suppliers - freeing up - business – measures – businesses – market – paperwork - member country – employ – benefits - wealthiest - single market - sales- purchases. • • • • • • - - Trading with the EU countries offers a number of key ………to ………. . The EU’s 28 member states include some of the world’s…..and most productive countries. The EU is a huge……………………..in which to sell your goods and services – it also gives you access to a huge source of …….… . At the core of the EU is the …….. – the programme of …… the trade of goods and services and the movement of people between EU countries. The aim is that doing ……... with other EU countries should become increasingly like doing business within your own country. The following are some of the ………which EU countries should have introduced to make easier to trade with each other: Reduced bureaucracy and ……..…… - for instance, trade with the EU can be recorded on your VAT form in the same way as any of your ……..and ………..in your country. Harmonised standards Movement of people – Citizens of any ……. have the right to travel, live and work in any EU country. You can also …………..EU citizens to work in your country. Why trade with EU? Fill in the missing words: KEY • • • • • • - Trading with the EU coutries offers a number of key benefits to suppliers . The EU’s 28 member states include some of the world’s wealthiest and most productive countries. The EU is a huge market in which to sell your goods and services – it also gives you access to a huge source of businesses. At the core of the EU is the– the programme of freeing up the trade of goods and services and the movement of people between EU countries. The aim is that doing business with other EU countries should become increasingly like doing business within your own country. The following are some of the measures which EU countries should have introduced to make easier to trade with each other: Reduced bureaucracy and paperwork - for instance, trade with the EU can be recorded on your VAT form in the same way as any of your purchases and sales in your country. Harmonised standards. Movement of people – Citizens of any member country have the right to travel, live and work in any EU country. You can also employ EU citizens to work in your country. Trade Celebrities and Charities • Here we will be talking about the involvement of celebrities in international politics and economies. • Celebrities hope or aim to change/influence the relationship between governments and charities. • Key terms: • debt relief campaign: debt cancellation) • to lift quotas (to get rip of – take away limits on quantiities of goods produced) • duties (taxes on goods). • Lobbying, (effort/attempts to persuade). • Boycotting (a protest where people refuse to buy or use a product or service). • A charity: a non-profit making organisation providing assistance for poor countries. • Subsistence farming: self sufficient farming. SEE DISPENSA CHAPTER TOO