Symptoms-Solutions-Dyslexia-Literacy

Reid & Diane Lyon www.ReidLyon.com
Symptoms & Solutions: dyslexia, literacy, intervention, accommodations, and modifications
SESSION II: (Q & A)
Friday, October 14, 2011
2:30 p.m. - 4:00 p.m.
Fundamental Learning Center
Dyslexia page was last modified
Oct. 8, 2011
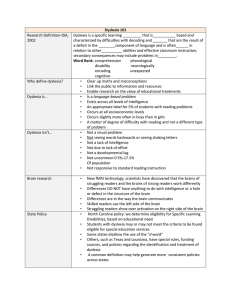
• Dyslexia is a broad term defining a learning disability that impairs a person's fluency or comprehension accuracy in being able to read, [1] and which can manifest itself as a difficulty with phonological awareness, phonological decding, othographic coding, auditory shotterm memory or rapid naming.
[2][3] Dyslexia is separate and distinct from reading difficulties resulting from other causes, such as a non-neurological deficiency with vision or hearing, or from poor or inadequate reading istruction.
[4][5] It is believed that dyslexia can affect between 5 to 10 percent of a given population although there have been no studies to indicate an accurate percentage.
[6][7][8]
LANGUAGE COMPREHENSION
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
VOCABULARY KNOWLEDGE
LANGUAGE STRUCTURES
VERBAL REASONING
LITERACY KNOWLEDGE
WORD RECOGNITION
PHON. AWARENESS
DECODING (and SPELLING)
SIGHT RECOGNITION
The Many Strands that are Woven into Skilled Reading
(Scarborough, 2001)
Skilled Readingfluent coordination of word reading and comprehension processes
Effective Reading Instruction
“Reading instruction effectiveness lies not with a single program or method but, rather, with a teacher (parents) who thoughtfully and analytically integrates various program, materials, and methods as the situation demands.”
(Duffy & Hoffman)
READING INSTRUCTION MUST BE
INTEGRATED FROM KG- G12
• If a critical component is missing, students who are at risk will not develop the essential skill
• Success and failure in reading are opposite sides of the same coinit’s the same theory, not two theories, one for success and another for failure
• Instruction is the key!
Many people who struggle with reading…..
…..
.
are delayed in the development of phonemic awareness.
have had less exposure to print and the alphabet .
have vocabulary that are usually less well developed
– ½ in poor children compared to other children.
have a range of experience and conceptual knowledge that is often limited or different compared to other students.
What the National Reading Panel Says
About the Role of Vocabulary in
Reading Instruction http://www.nationalreadingpanel.org/
What the National Reading Panel Says
About the Role of Vocabulary in
Reading Instruction
Learning in rich contexts is valuable for vocabulary learning. Vocabulary words should be those that the learner will find useful in many contexts. When vocabulary items are derived from content learning materials, the learner will be better equipped to deal with specific reading matter in content areas. http://www.nationalreadingpanel.org/
What the National Reading Panel Says
About the Role of Vocabulary in
Reading Instruction
There is a need for direct instruction of vocabulary items required for each specific text.
Repetition and multiple exposure to vocabulary items are important. Students should be given items that will be likely to appear in many contexts.
(Reprinted from National Reading Panel, 2000, p. 4-4) http://www.nationalreadingpanel.org/
Reading Comprehension Non-Negotiables
A student must be able to read correctly, approximately 95 percent, of the words accurately in text to comprehend what is read.
MOREOVER, to comprehend, a student must know the meanings of 90 to 95 percent of the words being read.
What does it take to comprehend text?
• Readers who read well are active readers
• Readers who have clear goals in mind for their reading comprehend well.
• They constantly evaluate whether the text, and their reading of it, is meeting their goals.
• Readers who read well typically look over the text before they read, noting such things as the structure of the text and text sections that might be most relevant to their reading goals.
WHAT DOES IT TAKE TO UNDERSTAND
WHAT YOU READ?
Read different kinds of text differently. For example, when reading narrative, attend closely to the setting and characters
When reading expository text the reader frequently construct and revise summaries of what they have read.
E xpository text is nonfiction reading material. The intent of these written works is to inform as a fact text processing occurs not only during ‘reading’ as we have traditionally defined it, but also during short breaks taken during reading, and even after the ‘reading’ itself has commenced. (started)
Reading Fluency
• Fluency is partly an outcome of word recognition
(Could make developing Speed into a game!)
• “ability to read connected text rapidly, smoothly, effortlessly, and automatically with little conscious attention to decoding” (Meyer, 2002)
• “rate and accuracy in oral reading” (Shinn et al.,
1992)
• “ immediate result of word recognition proficiency”
(NRP, 2000)
Why have we, as a Nation, not met our reading goal?
The sheer magnitude of the reading crisis in America
The sheer complexity of reading development and reading difficulties vary
The complexity of an effective classroom with effective leadership in the school
(implementation: time, $, people power)
http://www.rfbd.org/
Reading for the
Blind and
Dyslexia, DVD and Books on
Tape made a huge difference in
Kyle’s and my life.
Example:
Phonological
Awareness: Students learn to identify and manipulate the sounds in spoken words including skills such as oral segmenting and oral blending.
www.freereading.org
Letter Sounds:
Students learn to say the most common sound for printed letters.
Sounding Out:
Students learn to decode printed regular words
Word Recognition:
Students learn to recognize common regular words by sight
Time
Management
Problem solving
Thinking
Studying Skills
Learning w/ others http://www.studygs.net
Response-to-Intervention Requires
• High quality core reading instruction.
• High quality core is differentiated.
• Differentiation requires adjusting instruction based on student performance data.
• Students with performance indicating risk for failure receive additional small group instruction (Tier 2)
ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/publications/practiceguides
/
Assisting Students Struggling with Reading: RtI
U.S. Department of Education
Institute for Educational Science
What Works Clearing House
Free so:
Order some
Print some
Share …….
Florida Center
Reading Research http://www.fcrr.org/ disseminate nformation about research-based practices related to literacy instruction and assessment for children in preschool through
12th grade.
Ed.gov/parents/needs/specied/edpicks.jhtml
Federal website
Learn the Law!
Learn about Federal
Funded
Research
Office of Special
Education and
Rehabilitative
Services, Overview
Information; Training and
Information for
Parents of Children
With
Disabilities--Parent
Training and
Information Centers http://www.ed.gov/progra ms/pirc/index.html
http://www.readingrockets.org/
Website For:
• Parents
• Teachers
• Principals
• Librarians
• En espanol
Colorín
Colorado
http://www.interdys.org/
IDA Website Dyslexia
• News
• Literature
• Articles
• Research
Know who you are listening to!
http: / / www . ahead.org website
“AHEAD envisions educational and societal environments that value disability and embody equality of opportunity
.”
AHEAD is a professional membership organization for individuals involved in the development of policy and in the provision of quality services to meet the needs of persons with disabilities involved in all areas of higher education.
Written by many who walked the walk!
• The Crisis in Our Classrooms
Blaunstien, Lyon
• Armed with the Facts:
Shaywitz
• I Could Not Read Until I was 30
Diane Lyon
• A Parent’s Journey
Ankney
• A Parent’s Pressure Cooker
Garza
• Changing the Odds
Marion Joseph and many more chapters….
What the National Reading Panel Says
About the Role of Vocabulary in
Reading Instruction
www.ReidLyon.com
Resources www.deniseeide.com/
Free pdf: Google
Susan Hall 90% reading goal talkingfingers.com/store/conte nt/making-speech-visible
Resources dyslexia.yale.edu/About_ShaywitzBios.html
http://www.leavingjohnnybehind.com/
Free pdf: Google
Free pdf
A Parent's Guide to Helping Kids with Learning
Difficulties peterswife.org/LD/ParentsandReading.pdf
Questions to
Reid and Diane?
Thank you for your attention!
For questions or to schedule a workshop email Diane :
Reading 4 all@ tx .rr.com
or visit: www . ReidLyon.com