Attention Skills
advertisement

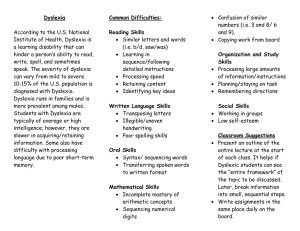
Understanding and Improving Attention NAMI 2011 “The idea that the brain can change its own structure and function through thought and activity is, I believe, the most important alteration in our view of the brain.” “The Brain That Changes Itself” by Norman Doidge Research Research Has Has Confirmed Confirmed Neuroplasticity Neuroplasticityof ofthe theBrain Brain Brain function Brain function in in children with children with no no reading reading disability disability Brain function function inBrain children within children with developmental developmental dyslexia dyslexia Children with Children with dyslexia showed dyslexia showed increased brain increased brain function after only function afterofjust eight weeks 8 weeks of training intense training Brain Plasticity - Neuroplasticity • Imagine the difference between telling a child or an adult that she has a brain disorder VS • She can be like an athlete and with practice re-wire her brain to work better for her How We Learn Model of Processing New & Known Information Auditory Processing Logic & Reasoning Working Memory Visual Processing Long-Term Memory Learned Information Output New Attention Known Input Processing Speed DECISION Cognitive Skill Efficiency Academic Performance Real Life Symptoms • Can attend to what I’m interested in – Can’t focus when it bores me • Can complete work at the last minute – Can’t get much done ahead of time • Can work under pressure – Can’t work without the threat of failure or rejection • Can be fun and enthusiastic – Can’t easily regulate emotions • Can start well with new endeavors – Can’t sustain performance to completion Attention • Sustained Attention • Divided Attention • Selective Attention The The The inability to stay on task for long periods of time, to ignore distractions, or to multitask will limit the student’s other cognitive skills! THIS IMPACTS ALL ACADEMIC AREAS Sustained Attention •Loses interest quickly •Gets frustrated when something gets too difficult •Daydreaming Training Attention Skills Selective Attention • Easily distracted • Need the environment to be quiet and stable to stay on task Training Attention Skills Divided Attention • Struggle to multi-task • Very deliberate in completing one task before moving to the next • Can get easily overwhelmed Training Attention Skills What Do Attention Issues Impact? • Short-term memory • Think-pad of our brain – combines info from environment with long-term memory • 7 “chunks” of information • Struggle to synthesize • Multi-step directions/careless mistakes What Do Attention Issues Impact? • Processing Speed • Working too slowly on tasks • Requiring personalized attention to grasp new concepts • Struggling to meet deadlines or complete timed activities/tests • Struggling with anything timed Impact of Technology • Technology rewards distracted thinking and superficial learning. • Internet delivers a waterfall of visual, auditory and tactile sensory stimulation • Cornell University study results L Reactive vs. Focused Attention • Reactive attention system – hardwired and automatic (required for survival) • Focused attention system – prefrontal cortex, required when paying attention to something not stimulating Most youth have an overdeveloped reactive attention system and underdeveloped focused attention system Unlock Potential Thank You