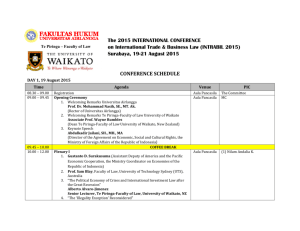
Using Appropriate New Technolgies to Enhance Distance Students
advertisement

MIT LINC 2010 Using appropriate new technolgies to enhance distance students’ learning at Universitas Terbuka, Indonesia Aminudin Zuhairi & Rahmat Budiman Universitas Terbuka, Indonesia May 2010 OUTLINE • Country and institutional context • Use of new technologies at Universitas Terbuka (UT), Indonesia • Distance students’ characteristics • Prospects and future challanges • Conclusion INDONESIA • The largest archipelago and fourth largest nation in the world • Over 224 million people living in about 4,000 of total 17,000 islands • Located along the equatorial line in South-East Asia • Ranks 111th or medium in the 2009 human development index • GDP per capita of US$ 3,712 (PPP), and an education index of 0.84. INDONESIA 3,500 miles (1,919,440 Km2) – 17,000 islands Population > 224 millions GDP per capita US$ 1,140 (PPP US$ 3,712) Higher education in Indonesia • State and private institutions • 82 state institutions and one state open university, i.e., Universitas Terbuka (UT). • 2,545 private institutions • Accommodates more than 4.5 million students • 1.67 million students in state system • 2.27 million students in private system • 0.6 million students in state institutions operated by the government outside the Ministry of National Education • Participation rate about 15 per cent • Failed legal reform for change to become autonomous institutions as separate legal entities Universitas Terbuka #1 • Cater for the nation’s needs for quality ODL • Established on the 4th of September 1984 as the 45th state university in Indonesia • A single-mode distance teaching university with main missions • To upgrade the qualifications of inservice teachers • To provide improved access to quality higher education to working adults and recent high school graduates Universitas Terbuka #2 • A mega-university with over 640,000 students and over 750,000 alumni • 4 Faculties • Teacher Training and Educational Sciences • Mathematics and Natural Sciences • Social and Political Sciences • Economics • The Graduate School offering Masters in Management, Public Administration, and Fishery Management • Head Office and 37 Regional Offices Use of new technology at UT#1 • Continuous improvement in academic quality and relevance, access to services, and internal management • Improved learning support services through • Access points to services • Quality of service • Network of partnership • Image building • Quality assurance Use of new technology at UT#2 • Access to a variety of learning support • Develop students’ independent learning through self-direction using a variety of methods and appropriate technologies • Capacity building of students, study groups, provision of various kinds of learning support, and use of new technologies • Access to services by students through the use of new technologies • Educating distance learners on the use of new technologies Use of new technology at UT#3 • UT at the forefront of innovation in the use of internet-based teaching and learning • Enhancing use of internet for teaching and learning at a distance • Increasing trend of using online learning by students • Improved online services for tutorials, webbased supplementary materials, selfexercise, examination results dissemination, online counseling, information dissemination, online examination, administrative services IT in ODL Model Model of ODL in Relations to Technology Use Multi Media Audio Cassette • Video Cassette • Computer-based learning (e.g. CML/CAL) • Interactive Video (disk and cassettes) • Tele-learning Audio conference • Video conference • Audio Graphics • TV/Radio Broadcasts and Audio conference • Characteristics of Technology UT Website UT Online Learning #1 UT Online Learning #2 UT Online Learning #3 UT-Online Learning #4 Log in UT M-Learning UT student characteristics • Over 600,000 students (2009) • Residing in different parts of the country and overseas locations • Over 95% working adults • Over 1.5 million students enrolling • Over 1 million alumni Trends in student enrolment 1.200.000 1.031.152 1.000.000 800.000 600.000 388.727 400.000 200.000 301.917 255.549 80.800 0 1984 - 1988 1989 - 1993 1994 - 1998 1999 - 2003 2004 - 2009 Active and registered students 700.000 600.000 Non-Pendas; 85.983 Non-Pendas; 66.829 500.000 400.000 300.000 Pendas; 536.974 Pendas; 411.160 200.000 100.000 0 Active Registered Technology for student’s learning • • • • • • Multimedia learning packages Broadcast programs Online tutorials Web-based supplements Online examination Other online Open Educational Resources (OER) Open Educational Resource (OER) • Portal Guru Pintar Online (Online Smart Teacher Portal): http://gurupintar.ut.ac.id/ • Portal E-Humaniora (E-Humanities Portal): http://e-humaniora.ut.ac.id/ Online programs to widen access#1 • Master of Management (MM) online • Overcoming barriers of attendance in face-to-face tutorials • Students living in remote areas, or working overseas • Online academic services: independent learning by self-study, online tutorials, online communication (blogs, synchronous communication, and video conference) • Online assessment Online programs to widen access#2 • Bahasa Indonesia for Penutur Asing or Nonnative Speakers (BIPA) online • Delivered through the E-learning platform including multimedia learning materials, assignments and learning activities • Stimulate language competence in listening, reading, writing, and speaking • Competencies expected • Communicating in Bahasa Indonesia • Using Bahasa Indonesia in formal communications and (for academic purposes Prospects and future #1 • Challenge for UT is to provide quality university distance education accessible to students • Maintain access to learning resources through ICT • Inccrease ICT literacy • UT Online • Introducing web-based academic and administrative services • Training in online learning services • Enhancing uses of ICT • Educating students and society to use new technology for lifelong learning Prospects and future #2 • Continuous improvement of online programs and services • Launching mobile learning services and customer relationship management (CRM) • Upgrading of ICT infrastructure and facilities • Capacity building of staff Prospects and future #3 • New technologies to enhance lerning, teaching and management • Virtual laboratory for science courses • Online examination system and online registration • Academic programs: digitising learning materials accessible by students online; use of Open Educational Resources (OER); issues on copyright, access rights, and cost impacts of opening up access to digital learning materials; continuing education programs; graduate programs Prospects and future #4 Examination system • Quality and secure examination flexible for students • Modernisation in preparation and production of examination papers through digital printing • Database of cases for examination results to respond to students’ queries satisfactorily • Management information system for examination papers: information database of test items, life cycle, usage, writers, etc Prospects and future #5 IT uses • Improving teaching and learning and supporting management • Use of IT-based database and networking • Data maintenance and enhancement of IT service effectiveness • IT Help Desk services • Electronic billing system for payment of fees • Use of IP-telephone using VPN (Virtual Private Network) • Use of IVR (Interactive Voice Response) • Enhanced LAN capacity to control transactions and networking • Online registration Conclusion • Limited ICT infrastructure within easy access by students • Increasing trends in uses of new technologies in ODL • Uses of technology to enhance ODL • Continuous innovation and improvement of learning and teaching with newer technologies • Investment in new technologies • Development of human resource capacity • Anticipate advances in new technologies • Wise use of appropriate new technologies MIT LINC 2010 Thank you. Terima kasih. aminz@mail.ut.ac.id, aminudin.zuhairi@gmail.com








![IUCGH Kick Off AKA [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008297000_1-7bff0da2cb71141ac93fa2b4b11695f4-300x300.png)