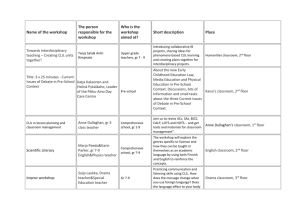
CLIL Basics
Content and Language
Integrated Learning
CLIL
Content and Language Integrated Learning is an approach or method which integrates the teaching of content from the curriculum with the teaching of a non-native language .
CLIL
Aims
to develop learning strategies
to stimulate critical thinking
to develop creativity
to raise motivation
CLIL
Advantages
communicative skills
cognitive skills
real content / information
intercultural skills
CLIL
Bilingual education – Luxembourg, Canada
Immersion – total immersion x partial immersion; early immersion x late immersion
Types of CLIL
Soft CLIL
↕
Hard CLIL
CLIL
aims: content and language
also develops learning strategies and skills
4 Cs
4 Cs
Content
curricular subjects taught in CLIL
some programmes develop crosscurricular links
we need to analyse content for its language demands and to present content in an understandable way
4 Cs
Communication
the language used for learning the content
learners participate in meaningful interaction
teachers encourage peer and group feedback as well as self-evaluation
4 Cs
Cognition
CLIL promotes cognitive – thinking skills
we develop learners ‘ cognitive skills
(e.
g.
reasoning, creative thinking, evaluating)
4 Cs
Culture
role of culture, understanding ourselves and other cultures
different languages, different social and cultural backgrounds
CLIL provides opportunities to introduce a wide range of cultural contexts – learners become aware of global as well as local citizenship
CLIL
L ANGUAGE
content-obligatory language
content-compatible language
CALP – cognitive academic language proficiency
BICS – basic interpersonal communication skills
CLIL
C OGNITIVE S KILLS
processes that our brains use when we think and learn
develop from a very young age
from information processing / concrete thinking skills – identifying and organising information
to abstract thinking – reasoning, hypothesising
CLIL
LOTS or Lower order thinking skills
remembering
identifying
ordering
defining
checking understanding
reviewing learning
CLIL
HOTS or Higher order thinking skills
reasoning
inquiry and discussion
creative thinking
evaluating
hypothesising
Bloom‘s Taxonomy
Creating
Evaluating
Analysing
Applying
Understanding
Remembering
Thank you! myska.t@email.cz
References
Bentley, Kay – The TKT Course CLIL Module, CUP
Bentley, Kay – Primary Curriculum Box, CUP
Deller, Sheelagh and Price, Christine - Teaching Other
Subjects through English, OUP
Calabrese, Immacolata and Rampone, Silvana – Cross-
Curricular Resources for Young Learners, OUP
Project 3 Fourth Edition Pracovní sešit s poslechovým CD a přípravou na testování, OUP
Project 5 Fourth Edition Pracovní sešit s poslechovým CD a přípravou na testování, OUP http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_Nations