Good Better Best powerpoints
advertisement

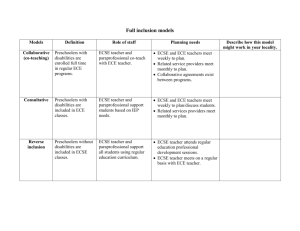
Good, Better, Best Professional Development Resources That Support Each Young Learner The Presentation Team Patricia M. Blasco Camille Catlett Laurie Dinnebeil Tracey West Western Oregon University (OR) FPG Child Development Institute (NC) University of Toledo (OH) FPG Child Development Institute (NC) Introductions Introductions Overview of 325N The programs under this focus area must enhance or redesign their curricula by: (1) incorporating evidence-based and competencybased practices and content in special education into each course; and (2) providing at least one practicum experience in a program that serves children with disabilities ages birth through five and their families. Required Competencies to be Developed (i) Collaborating and working effectively with licensed and certified professional practitioners, as appropriate. (ii) Implementing social-emotional and behavioral interventions and classroom management practices. (iii) Implementing instructional strategies to support early development and learning or academic achievement. (iv) Using technology to enhance children’s development and access to natural learning opportunities or improve student achievement and participation in the general education curriculum. Required Competencies (continued) (v) Observing and collecting data for progress monitoring. (vi) Communicating effectively with children and families. (vii) Assisting in the implementation of transition plans and services across settings from EI to preschool, preschool to elementary school, elementary school to secondary school, and secondary school to postsecondary education or the workforce, as appropriate. (viii) Working with children and families from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds, including English learners with disabilities and high-need children with disabilities and their families. Pooling Data to Answer Questions • Needs assessment was adapted from federally funded Crosswalks project • Data pooled among 5 grantees • Northampton Community College • Tacoma Community College • University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill • University of Toledo • Western Oregon University • 2 programs administered a 36item survey while the other 3 administered a 28-item survey Overview of Needs Assessment • Survey has 3 sections: EC and EI Content Areas, Instructional Strategies and Demographics • EC and EI Content: Using a scale of 1 (Low) -5 (High), respondents indicated their current level of knowledge, emphasis on ECSE content in the courses they teach, knowledge of where to access resources related to ECSE content, and comfort teaching the content with regard to the statements • Instructional Strategies: Using a scale of 0 (None) – 5 *High), respondents indicated their skills and emphasis on ECSE content and skills in the courses they teach Who were the Participants? • 116 early childhood faculty from 12 community colleges in North Carolina, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, and Washington • #s of faculty respondents in each of the CCs surveyed ranged from 3 to 51 • The demographics of the faculty were similar to findings from national surveys (Early & Winton, 2001; Maxwell, Lim & Early, 2006) Faculty Knowledge and Skills: Top Areas of Need • Using AT to enhance children’s development and access to natural learning opportunities • Using AT to enhance children’s participation in the general curriculum • Implementing transition plans Knowledge of relevant state and federal regulations • Using EBPs in EI and ECSE • Embedded intervention strategies • Using data from progress monitoring • Implementing IFSPs and IEPs • Implementing social/emotional intervention strategies • Implementing instructional intervention strategies Research Question What is the relationship between faculty members' knowledge, skills and comfort level related to ECSE topical areas and the degree to which they are addressing those areas in Community College program coursework in ECE ? Using AT to Enhance Children’s Access to Natural Learning Opportunities 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Current level of knowledge & skill Current level of comfort Current level of emphasis • Levels of emphasis in courses taught were correlated to knowledge and skills (r(113) = .56, p <.01) as well as to comfort level (r(95) = .37, p<.01) . Using EBP in EI & ECSE 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 Current level of knowledge & skill Current level of comfort Current level of emphasis 0 • Levels of emphasis in courses taught were correlated to knowledge and skills (r(86) = .60, p<.01) as well as to comfort level (r(85) = .59, p<.01) Lessons Learned About Associate Degree Programs Articulation…articulation …articulation! Lessons Learned continued Inconsistent emphasis on knowledge acquisition and knowledge acquisition + knowledge application Lessons Learned continued Preparing ECE professionals for diverse positions Lessons Learned continued • Workload of community college faculty members • Resources (or lack thereof) available to community college faculty members Lessons Learned continued Nature of the typical student enrolled in an associate degree program An effective teacher can have a stronger influence on student achievement than poverty, language background, class size, or minority status The Real Early Learning Challenge: Meeting the Needs of Each & Every Child Setting the Stage • Meeting the needs of each and every child • Knowledge acquisition and knowledge application • Evidence-based practices • Cultural and linguistic diversity Our Work is Guided by… SCRIPT-NC Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina Using Familiar Resources in More Explicit Ways SCRIPT-NC Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina Areas of Targeted Change Program Practices Coursework Practica Capturing a Vision Identify knowledge, skills, and dispositions you want future graduates to have Deconstructing/Reconstructing Courses • Overview of Course • Course Description • Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) • Assignments • Required Materials/Texts • Course schedule/outline Student Learning Outcomes Assign ment 1234- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Course Title Introduction to Early Childhood Education Child, Family, and Community Child Development I Child Development II Child Guidance Children with Exceptionalities Language and Literacy Experiences Early Childhood Capstone Practicum Alignment with DEC & NAEYC standards (22,24) Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Children and Families Transitions (21) Communicating Effectively with Children and Families (19, 20) Observing and Collecting Data (13, 14) Use of Technology (9, 10) (7) Early Development/ Academic Achievement (5) Collaboration with special education colleagues (4) Social-emotional/ Behavioral Interventions EC Special Education Content (6, 8, 11, 15, 16, 27) Evidencebased/Competencybased Practices (1) Areas of Emphasis in Redesigned Syllabi Areas of Emphasis in Course Practica Site Inventory Identifying PD Needs Two Components of Evidence-Based Professional Development The PD content focuses on specific research-based teaching and intervening practices SCRIPT-NC Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina The PD delivery focuses on evidence-based methods for building practitioners’ knowledge and application of evidence-based practices Resources to Support the Process CONNECT The Center to Mobilize Early Childhood Knowledge http://connect.fpg.unc.edu/ National Center on Quality Teaching and Learning 15-Minute In-Services Expansions Thick and Thin Conversations Asking Questions Engaging Children in Conversations 15 Minute In-Services Collecting and using work samples Expansions Engaging Children in Conversations Fostering Children’s Thinking Skills Zoning: Staffing to Maximize Learning Asking questions National Professional Development Center on Inclusion ACCESS PARTICIPATION [SYSTEMIC] SUPPORTS Early childhood inclusion embodies the values, policies, and practices that support the right of every infant and young child and his or her family, regardless of ability, to participate in a broad range of activities and contexts as full members of families, communities, and society. The desired results of inclusive experiences for children with and without disabilities and their families include a sense of belonging and membership, positive social relationships and friendships, and development and learning to reach their full potential. The defining features of inclusion that can be used to identify high quality early childhood programs and services are access, participation, and supports. Landing Pads A sampling of evidence and resources, related to each feature, to support your learning and professional development needs Find them online at http://npdci.fpg.unc.edu/resources/qualityinclusive-practices-resources-and-landingpads NPDCI CONNECT 8 EBP Landing Pads Available NPDCI CONNECT Heartland Equity & Inclusion Project SCRIPT-NC Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina Landing Pads http://scriptnc.fpg.unc.edu/resource-search SCRIPT-NC CONNECT Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina EDU 144 Landing Pad SCRIPT-NC CONNECT Supporting Change and Reform in Preservice Teaching in North Carolina After 2 years, what’s changed? Change and the Need for Transfer • PD involves change • Transfer - implementing skills occurs in the setting • Transfer does not automatically happen • New skill has to be changed to meet needs in the setting Use of Persona • Faculty developed persona of a typical scholar in their program: • Provides project team with clear understanding of comprehension level of scholars • Provide materials that are appealing and appropriate for reading level and knowledge acquisition Action Plans to Go • Faculty completed action plans: • Intended outcomes • Activities to achieve outcomes • Timeline • Person responsible Practicum Checklist Intentional Assignments • Make sure that every component of the course syllabus is aligned and consistent with goals and objectives of the course • Be specific about course assignments—make sure that they reflect the course goals and objectives • Instead of adding new goals and objectives to a course, embed EI/ECSE content into existing course components Designing a Follow-up Support Plan • Provides opportunity to: • answer question about implementation • address problems • collect implementation data • Use evaluation measures, instruments, procedures on-going during the year