B11-5-02 Immune Response
advertisement

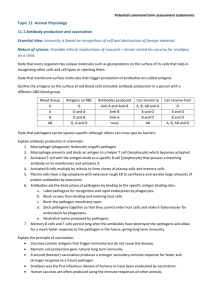
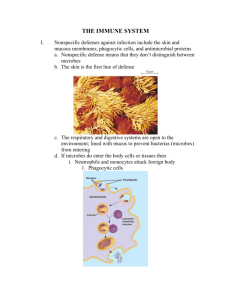
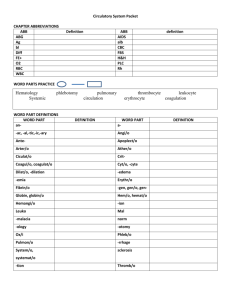
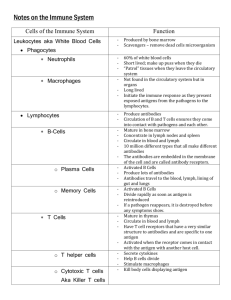
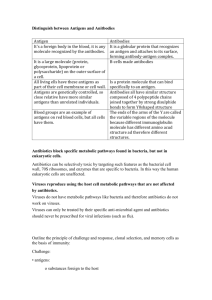
3rd Line – Immune Response B11-5-02 – Body’s response to viruses/bacteria Immune System Video The 3 Lines of Defense The 1st line of Defense Barriers The 2nd line of Defense Inflammatory response The 3rd line of Defense Immune response Immune system distinguishes “self” from “non-self” Do not react with our own cells Generates specific response to specific invaders Builds up resistance against Pathogens Antigen Tailored to an individual threat Most effective Memory component Improves response time Immune Response Two types of specific immune response Antibody-mediated Cell-mediated Antibody-Mediated Immunity Antibody-Mediated Immunity Production of antibodies specific to a given antigen Antibodies bind to the antigens on invaders and kill or inactivate them Antigens are molecules that cause antibody production Response provided by B cells (lymphocytes derived from bone marrow) Lymphocyste Video In Response to Infection A few days after an infection Antigens cause the production of large amount of the antibody capable of interacting with it Specific antibodies bind specific antigens Antibodies Antibodies bind antigens in a lock-and-key fashion Forming antigen-antibody complex Type of protein Immunoglobulin Y shaped molecules with Two heavy chains Two light chains Antibodies Cont. Identify Antigens as either Self Nonself Bind non-self antigens clumping them together making them inactive Antibodies Cont. Body only has antibodies for pathogens that a host has encountered When a new pathogen invades the body, B-cells “learn” about new antigens and develop appropriate antibodies The B-Cells then circulate though the body, releasing antibodies that bind to new antigen Antibodies Video 1 Antibodies Video 2 Antigens Protein or polysaccharide that is present on the plasma membrane Cell-Mediated Immunity Cell-mediated Immunity Require direct physical contact with antigens Does not involve the production of antibodies Response provided by T-Cells (lymphocytes derived from the thymus) Four types 1. Cytotoxic (Killer) T-Cells Defend the body by destroying Foreign cells Infected cells Cancerous cells Recognizes viral antigens on plasma membrane of host cell Attaches to plasma membrane of host cell Secrete enzymes that digest host plasma membrane Punching holes Infected cell’s cytoplasm leaks out and the cell dies The dead cell and its contents are removed by phagocytes 2. Helper T-Cells Regulate immune response by … Secreting messenger proteins Direct contact with other cells Helps Killer T-Cells and B-Cells to perform their function Are destroyed by the HIV virus in patients with Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 3. Suppressor T Cells Reduce the immune response of B cells and T cells to keep them in check 4. Memory T Cells Remain in the body awaiting the reintroduction of the antigen Grab a Text Read and Make Notes 13.3 INDUCED IMMUNITY Active Immunity (250) Passive Immunity (251)



![Immune Sys Quiz[1] - kyoussef-mci](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006621981_1-02033c62cab9330a6e1312a8f53a74c4-300x300.png)