Kind of lesions in dermatology 1- Primary Skin Lesions 2
advertisement

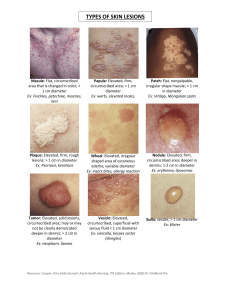
IN THE NAME OWNER OF BEAUTY Morphology & Terminology Of Skin Lesions Morphology & Terminology of Skin Lesions Kind of lesions in dermatology 1- Primary Skin Lesions 2-Secondary Skin Lesions 3- Special Skin lesions PRIMARY LESIONS macule Flat, circumscribed skin discoloration that lacks surface elevation or depression Vitiligo Ink tattoo Patch Flat, circumscribed skin discoloration, a very large macule Vitiligo Papule Elevated, solid lesion <0.5 cm in diameter B.C.C Intradermal Nevi Plaque Elevated, solid”confluence of papule”>0.5 cm in diameter that lacks a deep component Psoriasis M.F Nodule Elevated, solid lesion>0.5 cm in diameter, a largerdeeper papule Lipoma Rheumatoid nudule Vesicle Plaque that contains clear fluid ,a blister Herpes simplex Herpes zoster Contact dermatitis Bulla Localized fluid collection>0.5 cm in diameter, a large vesicle Pemphigus vulgaris Bullous pemphigoid Bullous impetigo Pustule Papule that contains purulent material Folliculitis Impetigo Acne Pustular psoriasis Wheal (Hive) Firm,edematous,plaque that is evanescent and pruritic, a hive Urticaria Urticaria pigmentosa SECONDARY LESIONS Crust A collection of cellular debris ,dried serum,and blood A scab antecedent primary lesion is usually a vesicle,bulla or pustule Impetigo Capitis Tinea Erosion A partial focal loss of epidermis, heals without scarring TEN Perleche Scale Thick stratum corneum that results from hyperproliferation or increased cohesion of keratinocytes 4S Scarlet fever Ulcer A full-thickness, focal loss of dermis,heals with scarring Bed sore Syphlis Fissure Vertical loss of epidermis and dermis with sharply defined walls, crack in skin Perleche Eczema Scar A collection of new connective tissue, may be hypertrophic or atroohic scar implies dermoepidermal damage Burn Acne Atrophy Thinning of the epidermis, dermis or fat that cause depression in the skin surface Morphea SPECIAL SKIN LESIONS Excoriation Linear erosion included by scratching Scabies Atopic Dermatitis Prurigo Comedo Folliculocentric collection of sebum and keratin Acnea DLE Milia Millia are tiny pimple-like spots usually on a Newborn baby Tiny white cyston the surface of the skin Sun Damage Cyst Nodule that contains fluid semisolidmaterial Acne Pilar cyst Burrow An elevated channel in the superficial epidermis produced by parasite such as mite sarcoptes scabiei Scabies Lichenification Focal area of thickened skin produced by chronic scratching or rubbing Atophic Dermatitis Telangiectasia Small, dilated ,superficial blood vessels that disappear with pressure CREST Syndrome Scleroderma Rosacea Petechiae A small purplish spot on a body surface caused by a minute hemorrhage<0.5 cm Vasculitis DIC Purpura A small purplish spot on a body surface caused by a minute hemorrhage>0.5 cm Platelet Disorder