PowerPoint 演示文稿
advertisement

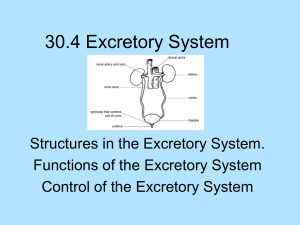
NUCLEAR MEDICINE IN GENITOURINARY SYSTEM Main contents Renal Function Test Renogram Quantitative Function Test 1. Effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) 2. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Renal Imaging Anatomy and physiology Radiopharmaceuticals Dynamic imaging Glomerular filtration:99mTc-DTPA Tubular excretion:131I-OIH, 99mTcMAG3, 99mTc-EC Static imaging:99mTc-DMSA Renogram Principal Metabolities and useless material first filtrated by glomeruli or secreted by renal tubules and then passed outside the body. Agent 131I-OIH is an urinary excretory substance, and can secreted by renal tubules after injection into the body. The time-activity curve obtained during the transit, secretion of 131I-OIH through the kidney and excretory route called renogram. Method 1. Patient preparation Hydration state for more than 6h. Drink 500 ml water 15 min before test for maintenance a steady state of urine flow. 2. Position Supine position comfortable for the patient and easy to inject. 3. Kidneys localization a. Anatomical b. X ray c. Ultrasonic 4. Tracer dose and duration 131I-OIH 5-10uCi injected (i.v.) as a bolus. The radioactivity over the both kidneys was recorded as long as 20 min, obtain the timeactivity curve. Interpretation Qualitative analyses -- normal curve 1. 1st phase or vascular phase, rapidly rising, lasting about 30 sec. 2. 2nd phase or uptake/functional phase, slowly rising, lasting about 3 min. 3. 3rd phase or excretory phase, slowly descending, lasting about 15 min. Normal Renogram Quantitative analyses Normal values left (min) right (min) peak time (Tmax) 3.24±0.72 3.45±1.13 half excretory time 4.94±1.8 5.06±2.27 Qualitative analyses -- abnormal curves 1. Parabola type Slow rising and slow falling. Mild renal insufficiency. 2. Low level prolonged type Lowed height of phase 1, while phase 2 and 3 merged each other. Severe renal injury. 3. Low level descending type Significant low phase 1 with gradual down slope, without phase 2 and 3. Nonfunctional kidney. 4. Constantly rising type phase 1 normal, continued uprising phase 2, without phase 3. Urinary obstruction. 5. High level prolonged type phase 1 normal, phase 2 rising gradually. Urinary obstruction with renal insufficiency. 6. Stepwise drop type phase 1, 2 normal, phase 3 dropped step by step. Spasmodic ureter. Advantage Simple and cheap. Disadvantage The detector position is according to normal positions of kidney, bladder and heart. May cause result error if the organ position is variation. Mixed uptake of renal parenchyma and collecting system. Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF) Clearance of the volume (ml) of plasma per minute during the first pass of the injected material through the kidney. Method 131I-OIH renogram with precordial record of time-activity curve. Normal value Total 521.73±153.35 ml/min, decreased with age. Clinical usage 1. Diagnosis of renal disease. Decreased in acute and chronic nephritis, paralleled with the changes of renogram. 2. Therapeutic monitoring. 3. Monitoring rejection of transplant kidney Decreased ERPF. Glomerular Filtrate Rate (GFR) The volume of plasma (ml) filtrate through the glomerulus per minute called GFR, somewhat similar to the creatinine clearance. Method 99mTc-DTPA injected as a bolus, the time- activity curve of both kidney obtained and the GFR calculated. Normal value Total 80--100ml/min, decrease with age. Clinical usage 1. Increased GFR a. Early stage of diabetes. 2. Decreased GFR a. Renal insufficiency. b. Late stage of diabetes. c. 3nd stage of hypertension. d. Azotemia and uremia. Renal Imaging Morphological study of the kidney to find any anatomical abnormality and also its function. It consists of static and dynamic study. Dynamic renal imaging Intravenous injection imaging agent. Dynamic acquisition of both kidney and bladder. Can display renal perfusion, function and urine drainage. Method •Drink 300ml water 20-30 min before imaging. •Void bladder before imaging. •Supine position, put detector behind the patient. •Intravenously inject 4-8mCi agent. •First phase:2s per image,total 30 images. •Second phase: 1 min per image,total 29 images. Normal image of first phase Abnormal types of image and interpretation •Delayed visualization of renal artery, the kidney image is small and weak. ——pathological changes of the trunk of renal vascular renal atrophy. •Focal absence of uptake inside the kidney. ——focal ischemia or other benign lesion. •Occupation lesion with normal or higher uptake. ——probable malignant disease. Normal image of second phase Abnormal types of image and interpretation •Kidney is not visualized. ——absence of kidney or the renal perfusion or function totally absent. •uptake. Delayed appearance and subside of renal ——damaged perfusion or function •uptake Persistent uptake in renal parenchyma, but no in pelvis. ——diffuse renal tubular block. •Dilation of renal calices, pelvis or ureter. ——urinary obstruction •Uptake beside the urinary system ——urine leakage •Delayed visualization of bladder ——upper urinary obstruction significantly decrease of urine flow. or Indications •Investigate the renal function and urine drainage. •Diagnose of renal vascular disease. •renal parenchyma disease involvement. •Diagnose of acute upper urinary obstruction.. •Function of diseased or residual kidney. •Transplant kidney evaluation •Diagnose urine leakage. •Differential diagnose of abdominal tumor. Calculus Of Bilateral Kidney & Obstruction Calculus Of Bilateral Kidney & Obstruction Right Nephrohydrops Renal Inadequacy Polycystic Kidney Polycystic Kidney Horseshoe Kidney Pelvic Kidney Rejection of Transplanted Kidney Rejection of Transplanted Kidney Rejection of Transplanted Kidney None function of Transplanted Kidney