Regeneration
advertisement

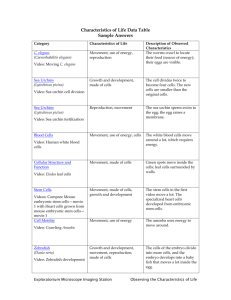
Tissue Repair Regeneration, repair & healing of injured tissues Repair responses following Injury/Inflammation Regeneration Growth of cells and tissues to replace lost structures Requires an intact connective tissue scaffold Regulation of cell populations TYPES OF CELLS • Labile cells • Stable cells • Permanent cells Labile cells • have a high rate of loss and replacement and therefore high capacity for regeneration. • squamous and glandular epithelia • haemopoeitic cells in bone marrow Stable cells • do not normally proliferate but can be stimulated to do so after damage. • • • • • renal tubular cells, hepatocytes, osteoblasts, endothelial cells, fibroblasts. Permanent cells • Permanent cells : unable to divide after initial development and therefore cannot regenerate when some are lost. • Neurons • Skeletal & cardiac muscle Cell Cycle Dolly the sheep, the first clone Ian Wilmut, who led the team that created Dolly at Scotland's Roslin Institute in 1996 Dolly Parton(singer) after whom the sheep was named STEM CELLS Regenerative Medicine Stem Cells are characterised by their prolonged self renewal capacity and by their asymmetric replication Embryonic / Adult Stem cells EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Pluripotent cells that give rise to all tissues of the body To develop Knockout mice To repopulate damaged organs Therapeutic Cloning Stem Cell Research • The Pros • The Cons • large potential for finding treatments and cures to a vast array of diseases; cancers; diabetes, spinal cord injuries, Alzheimer's, MS, Huntington's, Parkinson's and many more. The use of adult-derived stem cells, from blood, skin and other tissues, has been demonstrated to be effective for treating different diseases in animal models. Umbilical cord-derived stem cells have also been isolated and utilized for various experimental treatments. • The major con to stem-cell research is from the religious stance that life begins at conception and to destroy it to be used for research is immoral and wrong. Currently, the use of embryonic stem cells for research involves the destruction of the blastocysts formed from laboratory-fertilized human eggs. • • ADULT STEM CELLS • • • • • • More restricted differentiation capacity Usually lineage specific Located in sites called Niches Bone Marrow Haematopoietic stem cells Bone Marrow Stromal stem cells Transdifferentiation / Developmental plasticity • Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells Stem Cell Niches Bone marrow stromal cells Differentiation of embryonic cells and generation of tissue cells by bone marrow precursors Growth Factors • • • • Polypeptides Some act on many cell types Others act on restricted cellular targets Cell locomotion, contractility, differentiation, angiogenesis, growth receptors and transcription factors Signaling mechanisms in Cell Growth Signal Transduction Pathways • Receptors with Tyrosine kinase activity • Receptors lacking Tyrosine kinase activity • Seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors • Steroid Hormone receptors Transcription Factors • • • • C-myc C-jun C-fos p53 ECM and Cell-Matrix interaction