Ch. 9.3 * Cell Cycle Regulation
advertisement

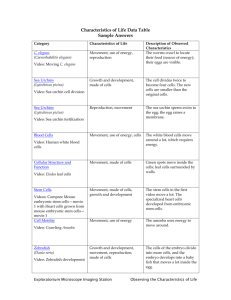
Questions of the Day! List the portions of Interphase and what happens in each part. List the steps of mitosis and the dance moves associated with the steps Sometimes a cell’s DNA changes during the process of the cell cycle. What do you think happens if the changed cell is allowed to reproduce? What measures would need to be in place to ensure that a changed cell is not allowed to divide? CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Normal cell cycle is regulated by cyclin proteins The cyclins and the cyclin dependent kinases (enzymes) control the different stages of the cell cycle. The cyclins bind to the CDK’s. The stop lights represent quality control checkpoints. If all is clear, and there are no cell issues (abnormal DNA, etc.), a cell is allowed to continue to develop and reproduce. CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Answer the following questions… What do you think happens if a checkpoint fails? What if a cell is not adequate or is abnormal and is allowed to reproduce? CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Cancer Uncontrolled growth and division Failure of the cell cycle regulation Failure of the immune system Crowds out normal cells killing the organism CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Causes of cancer – carcinogens and genetics Carcinogens – environmental factors and substances that cause mutations in DNA that lead to cancer. (Cigarettes, radiation, UV sunlight exposure) Cancer caused by exposure to carcinogens is preventable. Mutations in DNA are completely random. The more exposure to carcinogens the more the mutations occur. If cancer runs in a family, the rate of mutation is high and it is essential to avoid carcinogens to reduce the risk of cancer. CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Apoptosis – programmed cell death. Protects organisms from cancerous growths. Allows death of cells that are too damaged to repair. Ex. Leaves of plants turning color and falling in autumn CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION Stem cells – are unspecialized cells…Adult and Embryonic Have not picked a specific job yet Can be encouraged through stem cell research to become a specific cell (brain cell, heart cell, nerve cell) Adult stem cells are mainly used for repairing tissue. Stem cell research controversy. Using embryonic stem cells…what are the issues/ethics involved for using embryonic stem cells as opposed to adult stem cells? TASKS! List all of the ways that the cell cycle prevents mutated cells from reproducing. Discuss fully what cancer is and what causes it. Discuss why stem cell research is important and the possible medical applications that this research could bring. CH. 9.3 – CELL CYCLE REGULATION