Mode of action and therapeutic implications (PPT / 2216.5 KB)
advertisement

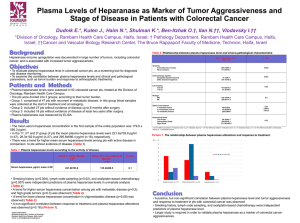
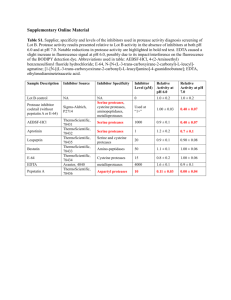
Heparanase in diabetic nephropathy: Mode of action and therapeutic implications Dr. Tzahi Neuman Cloning the Heparanase Vlodavsky et al. Nat Med. 1999 Jul;5(7):793-802. Hulett MD, Parish CR. Nat Med. 1999 Jul;5(7):803-9. Kussie et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Jul 22;261(1):183-7. Toyoshima M, Nakajima M. J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 20;274(34):24153-60 Heparan-sulfate (HS) glycosaminoglycans at the cell surface and in the ECM •HS is a key element in the self-assembly, and barrier properties of the ECM (particularly, BM). •HS is responsible for sequestration of the heparin-binding growth factors (i.e., bFGF, VEGF, KGF) in the ECM. Adapted from Sasisekharan et al., Nature Reviews Cancer 2002 Heparanase Activity 1. Enables cell movement through extracellular barriers during the processes involving cell migration (i.e., tumor invasion, implantation, extravasation of blood borne cells, etc). 2. Releases heparan sulfate-bound GF from ECM depots, making them available for growth factor-dependent processes (i.e., tumor growth, neovascularization, wound healing). Processing and activation of proheparanase by Cathepsin L Pro-Hpa 65 kDa Cathepsin L Cathepsin L inhibitor 65 kDa 65 kDa 50 kDa Processing 8 kDa 50 kDa 8 kDa + - + + - + + + The role of heparanase in Diabetic Nephropathy using the STZ model Changes in heparanase expression, HS content, and albuminuria in WT&KO mice in response to STZ-induced diabetes. Histopathologic changes in the kidneys of WT&KO mice in response to STZ-induced diabetes. Effect of heparanase inhibitor on albuminuria and renal damage in diabetic mice. Effect of Heparanase inhibitor on albuminuria and TGFb expression Summary 1. Heparanase is a predominant mammalian enzyme that cleaves heparan sulfate 2. Heparanase is overexpressed in the diabetic kidney 3. There is essential involvement of heparanase in the pathogenesis of DN. 4. Deletion of the heparanase gene protects diabetic mice from diabetic nephropathy (DN). 5. Heparanase inhibitor decreases the extent of albuminuria. Summary (continue) 1. Heparanase enhances macrophage and thus increases the kidney-damaging properties of macrophages. 2. This findings will help in developing effective strategies to disrupt the heparanase-driven sequence of events in diabetic kidney disease, and in designing novel therapeutic interventions in DN