Document
advertisement

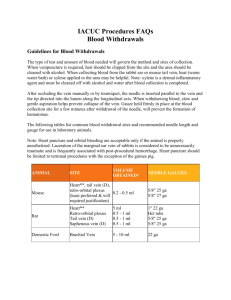
Institute of Surgical Research „A” Modul – Surgical Techniques A3. Practical Modul Surgical interventions: Injection, peripheral vein access; Intravenous infusion, infusion pumps; Suturing techniques, surgical knots, sutures Injections Indications: • oral drug delivery is not possible • drug metabolism is altered by ingestion • quick or prolonged action Devices: • Syringes: Luer: plastic, single-use, sterile volume range: 1(tuberculin), 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 60 ml • Hypodermic needles: Luer: metal + plastic tip (size: color-coded scale, G=gauge); „Butterfly” ; Braunüle (needle + cannula). Giving an injection: may lead to infection (sterility!) may lead to air embolism (remove air from the syringe!) Injections 1. Types of injection techniques: intracutaneous ic. into the skin layers subcutaneous sc. into subcutaneous tissue intramuscular im. into muscle intravenous iv. into vein Injections 2. Intravenous Sites: forearm (v. mediana cubiti, v. cephalica), dorsal veins of hand and foot. Needles: 18-23 G „Butterfly”: with injection port Braunüle: Apply a tourniquet centrally to the vein, puncture the vein at 30 to 45 degree angle and in the direction of the vein, remove tourniquet, and give the injection slowly. Central venous catheter Sites of punction: 1. V. jugularis interna: medial to the pulsing carotid artery 2. V. subclavia: 1/3 – 2/3 part of the clavicula Normal CVP value: 2-6 mmHg. Advantages: - quick and high volume of infusion, - administration of hypertonic solution/drug, - repeated blood sampling. Insertion of central venous catheters 1. Introduce a Braunüle into a periferal vein 2. Remove needle 3. Insert a flexible guide-wire into the central vein 4. Remove the Braunüle cannula 5. Insert – then remove a dilator cannula 6. Insert the central venous cannula, remove guide-wire Infusion therapy Indications: fluid and electrolyte balance, continuous medications nutrition Transfusion = blood or blood components Devices: glass bottle/plastic bag with fluid, sterile fluid administration set, - spike for puncturing the bag, - tubing, drip chamber, - roller clamp (flow regulator) sterile needles (Braunüle). Infusion pumps Infusion pumps: accurate, slow delivery of drugs/infusions Types: Volumetric pumps - long-term delivery of iv or ia infusions, transfusions. Syringe pumps - small volume (iv, ia) delivery of drugs/infusions with syringes. Perioperative fluid replacement Colloids Artificial Crystalloids Natural (albumin) Isotonic: Salsol Ringer’s lactate Gelatine 4% (35 kDa; Gelofusine) Hydroxyethyl starch (HES) 6%; 130 kDa; Voluven; 6% and 10 % HES 200 kDa; HAES-sterile Dextran 10% (40 kDa; Rheomacrodex) Dextran 6%-os (60-70 kDa; Macrodex) Gloving Alone (without assistance) Holding needle holders Mounting a needle holder and threading a needle Interrupted: Simple suture Interrupted: Vertical mattress suture Continuous: Simple suture Continuous: Intracutan suture Continuous: Purse-string suture