Healthy Eating and Target Groups
advertisement

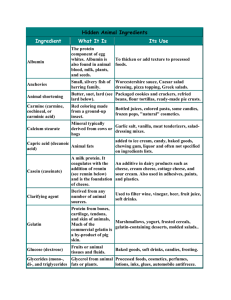
Healthy Eating and Target Groups Learning objectives:To find out what we should eat and why? To present the information in a memorable way Protein Function Growth of body cells, maintenance and repair Source of energy Examples Meat, fish, eggs, cheese, milk, yoghurt, lentils, quorn, tofu, TVP. Fats Function Concentrated form of energy Protects the vital organs Assists absorption of fat soluble vitamins Acts as insulation layer under the skin Examples Butter, lard, margarine, oils, cream, oily fish, milk and meat Carbohydrates Function Energy Breaks down to produce glucose Excess stored as body fat Examples Starch- flour, rice, bread, pastry, pasta, potatoes Sugar- sugar, honey, soft drinks, cakes and chocolate Vitamin A Function Increases the ability to see in dim light Maintenance of healthy skin Growth of bones and teeth Examples Liver, oily fish, eggs, milk, cheese, margarine, butter, tomatoes, apricots, and carrots Vitamin B’s Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Niacin (Vitamin B3), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2), Thiamin (Vitamin B1), Folic acid Functions It helps maintain a good working order of your nervous system. Releasing energy from protein and carbohydrates. Carries oxygen around the body Processes folic acid Keeps skin and eyes healthy Examples - Found in Healthy balanced diet, meat, fish, flour, milk, cheese, eggs, yeast extract, some fortified breakfast cereals, rice, flour, vegetables and dried fruit. Vitamin C Function Gives resistance to infection Binds body cells together as connective tissue Aids the absorption of iron Maintenance of skin Examples Blackcurrants, peppers, broccoli, cabbage, strawberries, tomatoes, new potatoes, Vitamin D Function Formation of bones and teeth Assists the absorption of calcium Examples Oily fish, margarine, egg yolk, liver, cod liver oil Iron Functions Formation of red blood cells Transports the oxygen around the body for the production of energy Examples Liver, kidney, corned beef, cocoa, egg yolk, curry powder, wholemeal bread,green leafy vegetables, hard water Calcium Function Develops and maintains bones teeth and nails Clotting of the blood Functions of muscles and nerves Examples Cheese, white bread, milk, canned fish, eggs and nuts Healthy Eating Learning objectives To reflect upon nutrition To discuss healthy eating A balanced diet with plenty of nutrients Low in sugar foods Low in salt Low in fat High in fibre – fruit, vegetables and wholewheat cereals Healthy Eating Why Low Fat? Fats Most people know that we should be cutting down on fat. But did you know it's even more important to try to replace the saturated fat we eat with unsaturated fat? We need some fat to keep us healthy. Fats are a source of energy, they help us to absorb some vitamins and contain important things called essential fatty acids. But lots of people eat more fat than they need or is good for them Good fats Bad fats Polyunsaturates, and to a lesser extent, monounsaturates, have been shown to lower blood cholesterol levels and therefore help in reducing the risk of heart disease. Saturated fats are those which are directly produced from animals and people who eat a ot of them are likely to develop heart disease and high cholesterol Found in rapeseed oil, sunflower oil, soya oil and vegetable oil. Found in meat, butter, lard, cream, cheese Why low sugar? We all know we should eat less sugar, it provides calories for energy, but it has few other nutrients, so we should try to eat these types of foods only occasionally. Sugary foods and drinks can cause tooth decay, particularly if you have them between meals. Sugar is converted to acid in mouth which in turn acts on the enamel of the teeth. This includes fruit juice, honey, cakes, biscuits and sweets. The sugars found naturally in whole fruit are less likely to cause tooth decay. Why low salt? Most people in the UK eat too much salt. This can raise blood pressure, which increases your risk of heart disease and stroke. Adults should eat no more than 6g salt a day. Many food have hidden salt such as some breakfast cereals, soups, sauces, ready meals and biscuits, Why high fibre? We often lack sufficient fibre in out diet and we should try to increase this otherwise we may suffer from a variety of diseases such as: Bowel/breast cancer Digestive problems Diabetes Heart disease Constipation Obesity Fibre is found in wholemeal flour, fruit and vegetables Design Task Adapt the recipe for a Lasagne, taking into account the healthy eating guidelines! Produce a labelled diagram showing the ingredients and amounts. Adapted Recipe Healthy Option Recipe 500 gm minced beef 1 onion 1 beef stock cube 1 can tomatoes 1tblsp tomato puree 200g lasagne pasta 300ml milk 25g butter 1 tblsp flour 50g grated cheese