Chapter 21: Blood Vessels
advertisement

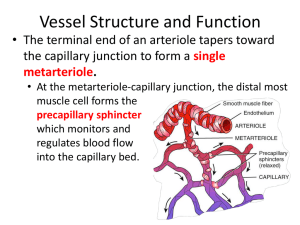
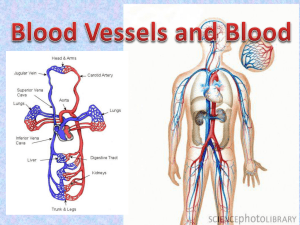
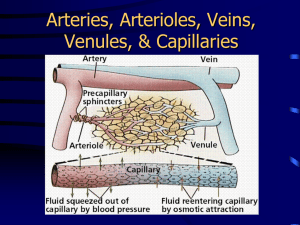
Chapter 21: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Vessel Structure - General All vessels same basic structure 3 wall layers (or tunics) Tunica adventitia (externa) - elastic and laminar fibers Tunica media thickest layer elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers Tunica interna (intima) endothelium – non-stick layer basement membrane internal elastic lamina Lumen - opening Structure/function relationship changes as move through cardiovascular tree Tunic thickness and composition variable throughout cardiovascular tree Vessel Structure – Elastic Arteries Elastic (conducting) arteries Near heart Thick walls More elastic fiber, less smooth muscle Lose elasticity with aging Vessel Structure - Elastic Arteries Aorta and elastic arteries Can vasoconstrict or vasodilate Large arteries expand, absorb pressure wave then release it with elastic recoil - Windkessel effect Help to push blood along during diastole With aging have less expansion and recoil Vessel Structure – Muscular Arteries Muscular (distributing) arteries Deliver blood to organs More smooth muscle Less elastic fibers Vessel Structure - Arterioles Arterioles Distribution of blood in organs Composition varies depending on position - more muscle, less elasticity nearer heart Regulate flow from arteries to capillaries Flow = ΔP/R vary resistance by changing vessels size Site of blood pressure regulation Vessel Structure - Capillaries Microcirculation connects arteries and veins Found in nearly every tissue in body Higher the metabolic rate, more capillaries in tissue Muscle many caps (>600/mm2) Cartilage none Vessel Structure - Capillaries Allow exchange of nutrients and wastes between blood and tissue Capillary structure - simple Basal lamina - connective tissue Endothelial cells Structure/function Flow Regulation Regulation by vessels with smooth muscle Metarterioles connect arterioles to venules through capillary bed allows flow through capillary bed w/out flow through caps Flow Regulation True capillaries Pre-capillary sphincter ring of smooth muscle open/close to control flow regulated by chemicals Intermittent vasomotion – caps open for flow 510X min Types of Capillaries 3 types of capillaries 1. Continuous capillaries continuous endothelial cells except for cleft between cells tight junctions between endothelial cells prevent most things from leaving caps most capillaries in body Types of Capillaries 2. Fenestrated capillaries fenestrations (slits) allow for filtration of small substances glomerular capillaries in kidney Types of Capillaries 3. Sinusoid capillaries wider gaps between endothelial cells allowing RBC’s to exit the caps found in liver Vessel Structure - Veins Venules Collect blood from caps carry it to veins Structure changes with position Become more vessel-like (walls) as move from capillaries Vessel Structure – Veins Veins Interna thicker than arteries Media thinner, less muscle Externa thick Valves Pressure low High compliance - change volume easily with small change in pressure Varicose veins Vessel Structure - Histology Very different morphology under light microscopy Tunica media thickness differentiates artery from vein Vein Artery Artery Vein Vessel Structure/Function At rest 60% of blood located in veins and venules Serve as reservoirs for blood, “storing” it until needed Particularly veins of abdominal organs, skin ANS regulates volume distribution Vasoconstrict Vasodilate Open areas of circulation to be supplied with blood veins at rest caps during exercise Can “shift” volumes to other areas as needed Vessel Structure/Function 0.75 L/min Rest CO = 5 L/min Vessel Structure/Function CO = 25 L/min Heavy 20 L/min Exercise 0.75 L/min Rest CO = 5 L/min Physiology of Circulation Flow = ΔP/R or CO = MAP/R MAP - mean arterial pressure Higher pressure to lower pressure with resistance (R) factor Blood pressure Pressure of blood on vessel wall Measurement of pressure of a volume in a space Systole/diastole - 120/80 BP falls progressively from aorta to O mm Hg at RA Regulation of Blood Flow Resistance - opposition to blood flow from blood and vessel wall friction Factors that affect resistance (R) Viscosity - V R thickness of blood dehydration, polycythemia R proportional to vessel length garden hose vs. straw obesity Vessel diameter changes in diameter affect flow vessel wall drag – blood cells dragging against the wall laminar flow – layers of flow R inverse proportional to radius4 decrease in r by 1/2 R 16X only important in vessels that can change their size actively Regulation of Pressure, Resistance Systemic vascular resistance (Total Peripheral Resistance TPR) All vascular resistance offered by systemic vessels Which vessels change size? Resistance highest in arterioles Largest pressure drop occurs in arterioles Relationship of radius to resistance in arterioles important due to smooth muscle in walls Systemic Blood Pressure Arterial Blood Pressure Pulsatile in arteries due to pumping of heart Systolic/diastolic Pulse pressure = systolic (minus) diastolic Q - Windkessel effect on pulse pressure? A Q - Decreases pulse pressure - What is the effect of hardening of the arteries on pulse pressure? A - Increases pulse pressure Systemic Blood Pressure Capillary Blood Pressure Relatively low blood pressure Low pressure good for caps because: caps are fragile - hi pressure tears them up caps are very permeable - hi pressure forces a lot of fluid out Systemic Blood Pressure Venous return Volume of blood flowing back to heart from systemic veins Depends on pressure difference (ΔP) from beginning of venules (16 mmHg) to heart (0 mmHg) Any change in RA pressure changes venous return Help for venous return Skeletal muscle pump muscles squeeze veins force blood back to heart valves prevent back flow Respiratory pump inhaling pulls air into lungs helps to pull blood back into thorax Velocity of Blood Flow Velocity of blood flow - inversely related to total cross sectional area (CSA) of vessels Aorta Total CSA 3-5 cm2 Velocity 40 cm/sec Capillaries Total CSA 4500-6000 cm2 Velocity 0.1 cm/sec Vena Cava Total CSA 14 cm2 in vena cava Velocity 5-20 cm/sec Vessel Structure - Function Capillary Function Site of exchange between blood and tissues Delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes Slow flow allows time for exchange Mechanisms of nutrient exchange Diffusion - O2, CO2, glucose, AA's, hormones diffuse down [ ] gradients If lipid soluble, can travel through cell If water soluble, between cells Capillary Fluid Exchange Fluid movement Fluid filtered and reabsorbed across capillary wall Starling’s law of the capillaries Forces driving the movement of fluid Hydrostatic pressure capillary (HPc) Hydrostatic pressure interstitial fluid (HPif) Osmotic pressure capillary(OPc) Osmotic pressure interstitial fluid (OPif) Net filtration pressure (NFP) is a sum of all Capillary Fluid Exchange On average 85% of fluid filtered at arteriole end is reabsorbed at venular end Maintaining Blood Pressure Short Term Mechanisms - CNS Neural Control - Cardiac centers in medulla Vasomotor center medullary area dedicated to control of blood vessels sends sympathetic output to blood vessels Vasoconstricts or vasodilates as needed tone - normal amount of vasoconstriction or vasodilation can vary tone which varies delivery of blood receives input from different sources baroreceptors chemoreceptors Maintaining Blood Pressure – Short term mechanisms – CNS reflexes Baroreceptor initiated reflex Located at carotid sinus and aortic arch Monitor changes in blood pressure Regulate activity of Sympathetic Nervous System (vascular tone) Maintaining Blood Pressure – mechanisms – CNS reflexes Short term Chemoreceptor initiated reflexes Carotid bodies, aortic bodies Monitors changes in chemicals (O2, CO2, [H+]) CO2, H+, O2 (stresses) result in sympathetic activity and BP Maintaining Blood Pressure – Short term mechanisms – CNS reflexes Influence of Higher Brain Centers (areas above medulla) - Cortex and Hypothalamus Not involved in minute to minute regulation Influence vasomotor center depending on conditions public speaking temperature regulation Maintaining Blood Pressure - Short Term Mechanisms - Hormones Renin - Angiotensin - Aldosterone Renin enzyme from kidney results in formation of Angiotensin II (AII) AII vasoconstrictor stimulates ADH, thirst stimulates aldosterone - Na+ reabsorption Why/how would these things affect blood pressure? Maintaining Blood Pressure - Short Term Mechanisms - Hormones Adrenal medulla - Epi and Norepi CO (HR, SV) Constrict abdominal, cutaneous arterioles/venules Dilate cardiac, skeletal muscle beds Why/how would this affect blood pressure? Maintaining Blood Pressure - Short Term Mechanisms - Hormones Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus Retains fluid (inhibited by alcohol) Vasoconstriction at high levels Why/how would this affect blood pressure? Maintaining Blood Pressure - Short Term Mechanisms - Hormones ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) Released from atrial cells in response to BP Vasodilator, Na+ and water loss, opposes Aldosterone Why/how would this affect blood pressure? Maintaining Blood Pressure Long Term Regulation Renal mechanism Volume in a space Regulate space in the short term – we just talked about it! nervous control hormones Regulate volume in the long term The kidneys! BP, urine flow to BP BP, urine flow to BP Control of Blood Flow Autoregulation (local control) - local automatic adjustment of blood flow to match tissue needs Physical changes Warming - vasodilation Cooling - vasoconstriction Chemical changes - metabolic products Vasodilators Vasoconstrictors Myogenic control smooth muscle controls resistance stretch contraction, stretch relaxation Blood Flow in Special Areas Skeletal Muscle Wide variability in amount of flow Sympathetic regulation from brain in response to level of activity α receptors - vasoconstrict β receptors - vasodilate Metabolic regulation in tissue low O2 vasodilate to increase flow hi O2 vasoconstrict to decrease flow Brain Very little variability in flow Stores few nutrients so flow must be maintained! Metabolic regulation Blood Flow in Special Areas Skin Supplies nutrients, aids in temperature regulation, provides a blood reservoir Metabolic and sympathetic regulation Lungs Low pressure (25/10), low resistance Flow regulated by O2 availability in the lungs hi O2 vasodilate to increase flow – opposite to muscle low O2 vasoconstrict to decrease flow – opposite to muscle Heart Variable flow depending on activity Metabolic and sympathetic regulation Regulation of Blood Pressure CO = =MAP/R MAP CO x R