2012 Cellular imaging at 3 T
advertisement

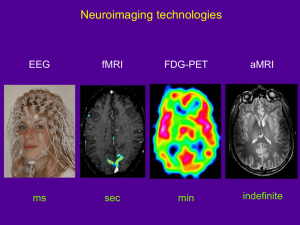
Cellular imaging at 3 T: Detecting Cells in Inflammation using Active Labeling with Super paramagnetic Iron oxide Azhar Hosein Faraz Medical Biophysics Western University Robarts Research Institute Under supervision of: Dr. Paula Foster 4th April 2012 Immune Response and Inflammation • Tissue injury caused by bacteria, trauma, chemicals, or any other phenomenon –Inflammation. • Walling- off • Within minutes after inflammation occurs macrophages already present in the tissues (microglia, Kupffer cells,..) begins their phagocytic action. • The second line of defence within the first hours of inflammation begins are the large number of neutrophils that invade the inflamed area. Imaging Immune Cells with MRI • In Vivo Labeling of Cells with Iron Particles Iron oxide contrast agent Labeled cells Intravenous (i.v) administration Phagocytosis Iron oxide-based MRI contrast agents Iron-labeled cells In gel Adapted from Modo, M. et al. Mol. Imag, 2004 Effect of iron is to cause signal loss in MRI images Aim of study • To detect inflammatory cells in the mouse brain by in vivo 3T MRI in a model of neuroinflammation. Methods Normal Healthy Mouse (C57/Bl6, n=2) MRI Pre-Scan of body Iron Oxide (Fe) injected Intravenously (IV) to Mice Fe - Bone marrow - Liver - Spleen Monocytes MRI Body 24 hours Post-injection (Fe) Inject mice with : LPS (lipopolysaccharide) 48 hours Post-injection (Fe) Model of Neuroinflammation - Neurotoxic - Over activation of microglia MRI Body 6 days Post-injection (Fe) MRI Brain 9 days Post-injection (Fe) Imaging Cells (3T cellular MRI) at Robarts Custom-built high performance gradient - Only lab in the world - research imaging experiments at clinical magnetic strength - pulse sequence known as, bSSFP. Solenoid radio frequency coil 3T clinical system Image Analysis: Body Images • Measuring mean signal intensity of different image slices in Liver, Bone marrow, and Spleen. • Standard deviation (SD) of Noise present in each slice. • SNR Signal to Noise ratio Mean signal intensity / SD of Noise Present in each scan slice Image Analysis: Brain Images • No. of Voids present in Brain MRI scan • Mean signal intensity of each discrete region of signal void • Fractional signal loss in % ∆𝑠 𝑠 = 𝑆𝐼 𝑏𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 −𝑆𝐼 ( 𝑉𝑜𝑖𝑑) 𝑆𝐼 ( 𝑏𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛) × 100 • Clear canvas software used for analyze of MRI scan images. Results Whole Mouse Body BSSFP Images Before Iron Injection Tail Head Post Injection Iron • In vivo labelling of liver, spleen and bone marrow macrophages Results: SNR • Liver > Spleen > Bone marrow MRI Brain • Voids present in brain Results: FSL • FSL is related to the amount of Iron in discrete reigns of signal void. • Can be related to the number of iron-labeled cells. SUMMARY • Changes in SNR suggests that cells take up iron in the liver, spleen and bone marrow - the numbers of iron-labeled cells is different for each organ and varies in mice. • This work indicates that pre-labeling immune cells with iron allows us to track their involvement in inflammation in the brain • This study has been done for first time Future directions • To prove that signal loss in the brain is due to the accumulation of immune cells • To determine which kind of cells are presenting in brain, using histology and experiments with transgenic mice. • To obtain body images over a prolonged time period, to better understand the time course of cell uptake and retention of iron. Acknowledgment • Supervisor : Dr. Paula Foster • Research funding : MS society • Thanking Jonatan Snir, for imaging ?