Leadership Behavior and Attitudes
advertisement

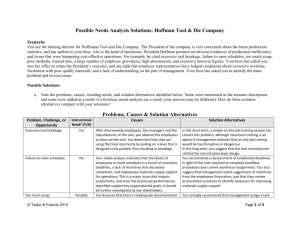
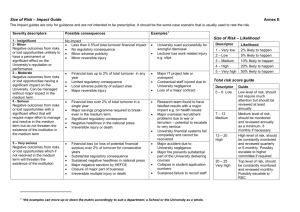
Leadership Behavior and Attitudes What leaders do Introduction • Leadership traits endow the leader with the potential to be a good leader • Examination of what leaders do helps explain what makes a good leader • People with the traits are more likely to engage in leadership activities. (kirkpatrick and Locke) • Leadership is getting work done—leader and followers have a working relationship with each other.(Stogdill) • In the 1940’s major research efforts were launched at Ohio State University and the University of Michigan Ohio State University Study • 2 key factors that account for most of the varience in leadership behavior. • Initiating Structure • Consideration Initiates Structure • Specifies tasks and procedures • Who does what and how. Initiating Structure • Includes behavior in which the supervisor organizes and defines group activities and his relation to the group. This he defines the role he expects each member to assume, assigns tasks, plans ahead, establishes way of getting things done and pushes for production. Consideration • Creates and envorinment • Provides support, warmth, friendship and trust. Consideration • Includes behavior indicating mutual trust, respect and a certain warmth and rapport between the supervisor and his group. This does not mean that this dimension reflects a superficial “pat-on-theback”, “first name calling” kind of human relations behavior. This dimension appears to emphasize a deeper concern for group members needs and includes such behavior as allowing subordinates’ more participation in decision making and encouraging more two way communication. Relationship between structure and consideration • Each dimension is independent • High structure-low consideration characteristic of “proficient” supervisors. • Same pattern led to high turnover, grievances, absences, accidents, low morale Patterns of leadership behavior related to employee grievances and turnover (Fleishman and Harris) • Significant correlation between leadership behavior (IS & C) and organizational effectiveness (grievances and turnover). • Grievances and turnover increase most sharply at the extreme ends of consideration(low) and structure(high). – Increase consideration-grievances and turnover decline initially. – Continued increases in consideration get decreasing results Patterns of leadership behavior related to employee grievances and turnover (Fleishman and Harris) • Consideration is the dominant factor. – High consideration – increased structure perceived as helpful in a climate of mutual trust and respect – Low consideration – increased structure perceived as oppressive and self serving. – High consideration formen could initate almost any amount of structure without increasing greivances or turnover. Patterns of leadership behavior related to employee grievances and turnover (Fleishman and Harris) • Low consideration-low structure perceived as irrelavent. • Low consideration-high structure perceived as tyrannical University of Michigan • Examined high producing groups and low producing groups • Leaders characterized as “production centered” or “employee centered” Production Centered • Analogous to initiating structure • Leaders do the following – – – – Tight work standards Well organized tasks Prescribed work methods Sounds like transactional leadership, doesn’t it? Employee centered • Encourages subordinate participation • Employee participates in goal setting activities The most productive groups were led by employee centered leaders Yes, but what do leaders do when they initiate structure or demonstrate consideration? Task related activities and attitudes • Adaptability – Sizes up people, situations and tactics • Direction Setting – Northbound train • Set high performance standards – Pygmalion effect Task related activities and attitudes (cont’d) • Risk taking/action oriented • Provides hands on guidance • Provides frequent feedback – Takes corrective action – Reinforces favorable activities Task related activities and attitudes (cont’d) • Remain calm and consistent under pressure • Asks tough questions rather than provide answers – Reverse delagation • Strong customer orientation Relationship Oriented actions • Alignment – Everyone pulling in the same direction and persuing a common vision • Mobilization – Getting group to work together smoothly • • • • Communication Care for each other Confidence in each others’ ability Letting people know how they fit and how they are doing Relationship Oriented actions (cont’d) • Concert building – The goal is to produce a system that is self evaluation, self correction, self renewing, ongoing. • Inspiration • Satisfaction of the needs of members Relationship Oriented actions (cont’d) • Making work meaningful • Emotional support and encouragment • Promotion of principles and values