Week 2 Powerpoint Slides
advertisement

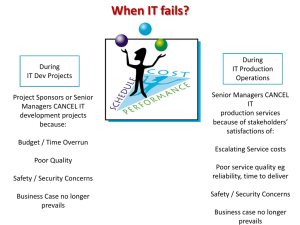
2 Chapter Fueling Globalization through Information Systems “The idea of charging for calls belongs to the last century.” Niklas Zennström, Skype MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-1 Learning Objectives MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-2 Learning Objectives MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-3 Globalization • Globalization created a new world characterized by: o Worldwide communication o Collaboration without barriers MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-4 Evolution of Globalization • Mainly • • • Globalization 1.0 European countries are globalizing Power is the primary driver Industries changed Slow pace of change MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-5 Evolution of Globalization • • • Globalization 2.0 Companies are globalizing Reduction in transportation and telecommunications costs Mainly Europe and America involved MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-6 Evolution of Globalization Globalization 3.0 • Individuals • • and small groups are globalizing Fast changes Emergence of new industries MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-7 Evolution of Globalization: Summary • The World is Flat (Thomas Friedman) • “10 Flatteners” o Key factors enabling globalization 3.0 MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-8 Flattener #1: The Fall of the Berlin Wall • • • November 9, 1989 Fall of communism People from the former communist countries gained more freedom MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-9 Flattener #2: Netscape Browser THEN • August 9, 1995 • First • NOW MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers mainstream browser Gave individuals access to the Internet 2-10 Flattener #3: Work Flow Software • • • Applications that allow people worldwide to communicate XML allows applications to “talk” to each other New possibilities for information sharing MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-11 Flattener #4: Supply Chaining • Integration of • • retailers, suppliers, and customers RFID tags used Wal-Mart became an early leader MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-12 Flattener #5: Open Sourcing • Software and source code freely available to everyone • Wikipedia a huge success MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-13 Flattener #6: Outsourcing • • Outsourcing companies profited from the drop in telecommunications costs Companies can now use talented engineers from anywhere MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-14 Flattener #7: Offshoring • Companies set up entire factories in countries such as China o Mass production o Low Costs MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-15 Flattener #8: In-Sourcing • Delegation of company’s key operations to a subcontractor o E.g.: UPS provides complete supply chain solutions to companies MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-16 Flattener #9: In-Forming • In-Forming is to • individuals what outsourcing, offshoring, and in-sourcing is to companies Individuals have access to massive amounts of information MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-17 Flattener #10: The Steroids • Technologies that support different types of collaboration o Greater mobility o Convergence MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-18 Learning Objectives MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-19 Opportunities of Operating in the Digital World • Opportunities of Reaching New Markets o Former Eastern Bloc countries provide new opportunities for international companies to reach new customers MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-20 Opportunities of Operating in the Digital World • Opportunities of a Global Workforce Engineering Graduates in the US, Europe and India o Low communications costs o Highly-skilled labor pool MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-21 Learning Objectives MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-22 Challenges of Operating in the Digital World • Globalization also created a set of unprecedented challenges: o Governmental challenges o Geoeconomical challenges o Demographic challenges o Cultural challenges MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-23 Governmental Challenges • Political System Challenges o Political stability • Regulatory Challenges o Tariffs o Embargoes o Export regulations o Quotas MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-24 Governmental Challenges II. • Data-Sharing Challenges o Transborder data flow regulations • Internet Access and Individual Freedom o Content blocking by governments/censorship • China – Use of VoIP restricted • Germany – Sites with fascist symbols prohibited o Internet access blocking • Cuba, North Korea MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-25 Geoeconomic Challenges • Time Zone Challenges o Real time meetings across continents difficult o Working around the clock possible MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-26 Geoeconomic Challenges II. • Infrastructure-Related Challenges o Traditional infrastructure – roads, electricity o Connectivity – reliable Internet connections • Challenges Related to Economic Welfare o GDP growth not distributed evenly throughout the world MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-27 Demographic Challenges • Differing rates of population growth MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-28 Demographic Challenges II. • Expertise related challenges o Different concentration of skilled workers o Different costs of workers MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-29 Cultural Challenges • National Cultures o Power Distance – differences in how societies handle the issues of human inequality o Uncertainty Avoidance – risk taking nature o Individualism/Collectivism – value placed on an individual vs. a group o Masculinity/Femininity – degree to which a society is characterized as masculine/feminine o Concept of Time – long term vs. short term o Life Focus – quantity vs. quality of life MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-30 Cultural Challenges II. • Cultural Barriers o Language – communication language and norms o Work Culture – work skills, habits and attitudes o Aesthetics – art, music and culture o Education – attitudes towards education and literacy o Religion, Beliefs and Attitudes – spiritual institutions and values o Social Organizations – family and social cohesiveness MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-31 Cultural Challenges III. • Other Challenges o Differences in what is regarded as appropriate o Standards of dealing with intellectual property o Different standards • E.g., writing paper, pillowcases MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-32 Learning Objectives MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-33 Going Global: International Business Strategy in the Digital World Multidomestic Business Strategy Global Business Strategy Transnational Business Strategy MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-34 Multidomestic Business Strategy • Low degree of • • integration between subunits Flexible and responsive to the needs and demands of local markets E.g.: General Motors o Opel in Germany o Vauxhall in Great Britain MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-35 Global Business Strategy • Centralized • Used to achieve • economies of scale E.g.: Coca-Cola o Same core product o Some different tastes made for local markets MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-36 Transnational Business Strategy • Some operations • • centralized while others decentralized o Flexibility o Economies of scale Difficult to manage E.g.: Unilever MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-37 Business Strategies: Summary • Different types of information systems can support these organizational forms MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-38 Information Systems Strategies • Multinational Information Systems Strategy o Often used by multidomestic companies o Decentralized systems o Communication between home office and subsidiaries o No focus on communication between different subsidiaries o Decentralized local data processing centers MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-39 Information Systems Strategies II. • Global Information Systems Strategy o Used by companies with global business strategy o Centralized infrastructure o Home office coordinates most of the strategic decisions o Communication and data sharing networks between home office and subsidiaries o Data does not stay with local subsidiaries but flows back to the home office MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-40 Information Systems Strategies III. • Transnational Information Systems Strategy o Pursued by transnational businesses o Extensive communication between home office and subsidiaries as well as among subsidiaries o Key data shared throughout the company MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-41 IS Strategies: Summary MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-42 End of Chapter Content MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-43 Opening Case: Managing in the Digital World: Casino Gaming • • • RFID tags will revolutionize the gambling industry by providing real time information such as the amount held in chips Mobile gambling using PDAs Online gambling on the rise MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-44 Detecting Intermittent Electrical Faults • Hard to find intermittent electrical faults caused by small damage to wires • Pulse arrested sparks discharge (PASD) – developed to help find these faults o Nanosecond bursts of high voltage sent through wires o Problem areas light up and are identified • Boeing uses the technique • U.S. military is interested in the technology MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-45 Online Searching • To “Google” has become a household verb meaning search MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-46 Niklas Zennström: Cofounder and Chief Executive Officer, Skype • “The idea of charging • • for calls belongs to the last century.” Skype has 28 million subscribers Among the 100 most influential people transforming the world MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-47 Underground Gaming Economy • Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing • Game – MMORPG o Virtual world – players live through avatars Players started selling virtual tools for real money – farmers o Banned from various gaming sites due to behavior being unethical and fear of turning users away MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-48 E-Waste • Disposal of electronics containing hazardous materials is a rising issue • U.S. exports much of its e-waste to third world countries o China banned the import in 2002 o Other countries to follow • In mid 2006, EU banned toxic ingredients o Production of “green” hardware • US government working on making changes – currently state-level legislation most effective MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-49 Transnational Development • Wrigley Company o World’s largest manufacturer of chewing gum o Sold in 150 countries • Good information systems key to conducting marketing research o Russian marketing research branch initiated the development of a marketing research work flow automation system o After successful testing, system was implemented in other marketing research branches MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-50 The Automobile Industry • The automobile industry is feeling the pressure of globalization • Failed attempts at making a “world car” • o Consumers have different tastes o Differences in infrastructures derive needs o The price of gasoline o Variations in emission standards Cultural and economic conditions need to undergo more globalization to make a world car successful MGT 330 - Information Systems for Managers 2-51