Networks - Crieff High School
advertisement
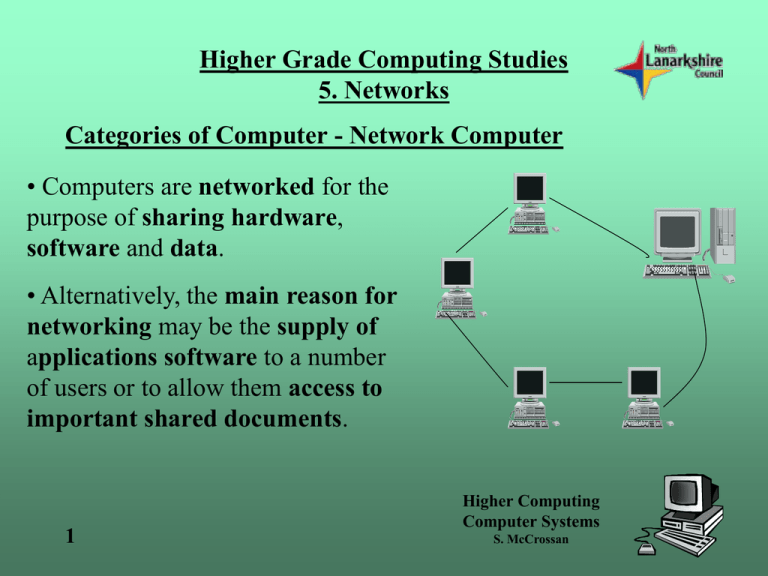
Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Categories of Computer - Network Computer • Computers are networked for the purpose of sharing hardware, software and data. • Alternatively, the main reason for networking may be the supply of applications software to a number of users or to allow them access to important shared documents. 1 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - LANs • A Local Area Network is a network of computers that are all situated close together for example in a room or building. Since the distance between computers is relatively small wire cables are frequently used to connect the computers together. LANs are usually set up to allow users to share data, communicate and share expensive peripherals. 2 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - LANs Network Type LAN Transmission Media • • • • • 3 Coaxial cable Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Fibre optic Wireless Bandwidth Between 10Mbps and 100Mbps Geographical Spread Up to 500 metres Functions Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Share data Share peripherals Communication Centrally store data Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - WANs • This is a network of computers connected across a distance. Telephone lines, satellites or other communication technology is required for WANs to work. Most major companies need a WAN in order to communicate with other branches either nationally or internationally. 4 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - WANs Network Type WAN 5 Transmission Media • • • Fibre optic Leased line Wireless Bandwidth Between 10Mbps and 100Mbps Geographical Spread Kilometres Functions Share data Communication Centrally store data Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - Intranet • This is a network that allows a private connection access to Internet services. This usually happens within a particular company or organisation. Authorised users only are allowed to access these services and this makes the network relatively secure. It allows secure email communication and the distribution of information similar to the World Wide Web. 6 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - Intranet Network Type Intranet 7 Transmission Media • • • Fibre optic Leased line Wireless Bandwidth Between 10Mbps and 100Mbps Geographical Spread Kilometres Functions •share data •share peripherals •shop, bank, travel, etc. •communication •centrally store data •advertise Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - Internet • This is the most common example of a WAN. It uses telecommunications to transfer data between computers and distribute information. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a collection of information held on the Internet. The WWW is made up of millions of documents called web pages and these pages are available to any user of the Internet. 8 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Networks - Internet Network Type Internet 9 Transmission Media • • • Fibre optic Leased line Wireless Bandwidth Between 10Mbps and 100Mbps Geographical Spread Kilometres Functions •share data •share peripherals •communication •centrally store data Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Mainframe Computer • A mainframe computer system has very fast powerful multiple processors, large fast memory and backing storage systems and the ability to support many network terminals at the same time. • Terminals usually consist of a keyboard and monitor only and rely on the mainframe to carry out all the processing and backing storage required. 10 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network of Computers • Most computer networks have stations (computers) that can work efficiently on their own without the aid of a mainframe. These networks usually consist of desktop computers being linked together. 11 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Client Server Networks • Servers are powerful computers used to carry out various tasks across the network. Clients are computers that form the network. The user logs in to the server from the clients (username and password) and is permitted access to some resources on the network and denied access to others. • Servers can have a variety of functions .... 12 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Client Server Networks • File server This provides a central disk storage area for any users across the network. The file server stores users files separately. Users can then access their files from any workstation on the network. • Web server A computer connected to the Internet that stores and distributes Web pages upon request to users on the network. The "server" is actually a software program running on the computer . 13 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Client Server Networks • Print server This computer allows the management of printing across the network. It uses a spooler to store users' files and can provide a queuing facility with prioritising if necessary. • CD-ROM server This server allows all workstations across the network to obtain data from CD-ROM disks. 14 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Client Server Networks 15 Network Type Advantages Disadvantages Client Server •Backups of data stored on servers can be carried out regularly. •All shared files are stored on servers which means data is up to date and correct. •Security is controlled more easily due to the central storage of data and setting up of users’ access rights. •Servers can fail and hence stop data, applications, etc, being shared across the network. •Servers are expensive to buy. Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Peer-to-Peer Network • In a peer-to-peer network there are no dedicated servers among the computers. All of the computers on the network handle security and administration for themselves. The users must make the decisions about who gets access to what. 16 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Peer-to-Peer Network • Security on a peer-to-peer network is not very powerful. So if you have security concerns go for something you can control (like a server). Because the users will be required to give access to folders, they can choose to not require passwords. 17 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Peer-to-Peer Network Network Type Peer-to-peer Advantages No need to pay for servers No or little network congestion due to smaller number of users Network can still function if any clients fail to work on the network Disadvantages 18 No central storage of files Security across the network is poor since it is not centrally controlled Backups of network data is difficult since there is no central storage Each client on the network has equal rights Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology • The design of a network is called its topology. • A node is any device on the network, e.g. workstation (computer), server, printer. • A channel is the path over which the data is transmitted between computers, e.g. telecommunications links, wireless connection, fibre-optics or twisted pair copper cables. 19 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology • Mesh • Ring • Bus • Star = Node = Channel 20 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology TYPE OF NETWORK Mesh ADVANTAGE • Fault in one DISADVANTAGE • Lots of wiring. channel doesn't affect network messages rerouted. • Multiple transmissions can occur at the same time. 21 AFFECT ON PERFORMANCE • Excellent performance • Expensive Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology TYPE OF NETWORK Star ADVANTAGE DISADVANTAGE between any 2 nodes. • Fault in the central node means network is unusable. • Easy expansion. • Congestion at • Short path central node. 22 AFFECT ON PERFORMANCE • Control computer gives more robust network but slows down communication between nodes Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology TYPE OF NETWORK Bus ADVANTAGE • Fault in one station has no effect on rest of network. • Very easy to DISADVANTAGE • All stations use the same channel - each station has to compete for the central channel. AFFECT ON PERFORMANCE • Instant access but high rate of data crash. expand. • Cheap 23 •Central channel breaks – network Higher Computing fails. Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 5. Networks Network Topology TYPE OF NETWORK Ring ADVANTAGE • Control system in charge of transmissions. • Stations guaranteed access to transmissions. 24 DISADVANTAGE • Additional expense for control software and system. • May have to wait to transmit. AFFECT ON PERFORMANCE • Network down to add new station but thereafter, few if any data crashes. Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan
![Systems Software 1 [pps]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005419302_1-897cf02cd0c88c582e0cc1a66dfe3efe-300x300.png)


![Systems Software 2 [pps]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005446651_1-28fd8fabbd88a37f2534ff5d4707c83a-300x300.png)