Systems Software 1 [pps]
advertisement
![Systems Software 1 [pps]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005419302_1-897cf02cd0c88c582e0cc1a66dfe3efe-768x994.png)
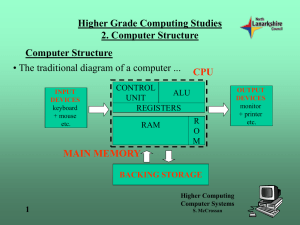
Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software System Software • This software is used to provide the computer system with all of the instructions it needs to function correctly. In modern computer systems, the system software is a large collection of programs, including the operating system, utilities and program translators. 1 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - System Software • A single user operating system handles communication with the user, manages memory storage, manages filing on backing store, deals with input/output communications with peripherals and schedules the processors time on tasks. • Older computers often had their operating system in ROM. This meant that it was ready as soon as the computer was switched on. It is impossible to corrupt the system. • But very difficult to upgrade it as it involved changing the ROM chips on the motherboard. 2 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - System Software • Most modern computers keep their operating system on hard disk and load it in to RAM on startup. • Even the modern disk-based operating systems need a small part of ROM – the bootstrap loader – which is the program that the processor runs on startup and whose task is to load in the rest of the operating system from the hard disk. • The main advantage of this is that it is very simple to upgrade the operating system. • The main disadvantage is that other programs can corrupt the operating system. Higher Computing 3 Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - System Software • There are basically five layers/modules to a single-user operating system; User level • User interface • File Management • Input/Output Management • Memory Management • Kernel 4 Machine level Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS – User Interface • The operating system has to take user commands from the keyboard, mouse etc., interpret the commands and pass them to the appropriate part of the operating system that deals with the command. If the command cannot be understood, a suitable error message should be given • The most common styles include: 5 • Form Filling • Menu driven • Command and GUI • Natural language Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - File Management • The operating system supervises the creation, deletion and updating of files. • A directory has to be kept which keeps track of where files are stored. Directory • It has to maintain the hierarchical directory structure Sub-directory 6 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - Input/Output Management • The main problem is that all the peripherals work at different speeds and have different characteristics. The I/O system hides these differences and makes them all appear to operate in a similar manner. • It is the task of the I/O system to do all the actual data transfers and issue the appropriate control signals to the peripherals. • If extra hardware is bought, say a printer, then the printer manufacturer will supply the appropriate software (driver) to control that peripheral. 7 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS - Memory Management • The operating system has to decide where programs and data will be placed in memory. • Memory Protection - in a multi-tasking environment, it has to keep track of what stage each program is at and ensure that no process tries to access the memory space of a different process. 8 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Single User OS – Kernel (Process Management) • The separate activities within the main memory are each called 'processes'. The Kernel is responsible for controlling all the processes running within memory. It has to decide which of the tasks in a multi-tasking environment gets to use the processor. • In a single-program operating system it only has to choose between the operating system itself and the package being run. 9 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Utility Program • Utility programs are those programs that are used to enhance the operating system. • Disk formatting programs - used to prepare the surface of writeable media for use. • Disk defragmentation tools - reorganises the files are laid out on the disk so that the blocks are near to each other. • File compression - reduce the amount of space that a file takes up on disk. • Virus checking tools – see next topic. 10 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan Higher Grade Computing Studies 7. Systems Software Graphic File Formats • JPEGs – use lossy compression. • GIFs – use lossless compression. • TIFFs – used to convert bitmap images. 11 Higher Computing Computer Systems S. McCrossan



![Systems Software 2 [pps]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005446651_1-28fd8fabbd88a37f2534ff5d4707c83a-300x300.png)