Computer networking
Why people need it? Who and how is
using computer networks?
Uses of Computer Networks
•
•
•
•
Business Applications
Home Applications
Mobile Users
Social Issues
Business Applications
• Business – for information and resources
– many companies have a substantial number of
computers – to monitor production, keep track of
inventories, and do the payroll
– initially, these computers worked in isolation from the
others, but at some point a need to be connected
arose to be able to extract and correlate information
about the entire company
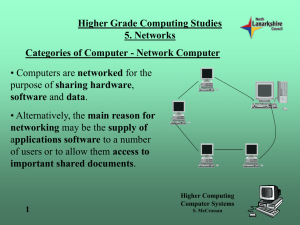
– resource sharing – for example - networked printer is
often cheaper, faster, and easier to maintain than a
large collection of individual printers
Business Applications
• Business
– companies are vitally dependent on computerized
information
– A failure of the computers may block completely the
functioning of a company
– In big companies – computers and employees –
scattered over a number of offices (and for some – in
many countries)
– Data is stored on servers (powerful computers), most
employees use more common machines - clients
Client-server model
Client-server model
•
The client-server model involves requests
and replies
Client-server model
• In the client/server architecture, clients request
services (client’s process) and servers provide
those services (server process) - widely used
architecture/mode that forms the basis of much
network usage
• Servers may be Web servers, mail servers, FTP
servers, etc., server can be on-site or remote
• client/server architecture - example of a
centralized architecture, where the whole
network depends on central points, namely
servers, to provide services
Business Applications
• A computer network can provide a powerful
communication medium among employees
– E-mail
– Sharing and working at the same time on common
documents, sheets, data, shared virtual
blackboard, etc.
– ICQ, Skype, etc.
– Video conferencing
Business Applications
• Faster, more efficient and convenient
business
– Companies can carry out business electronically with
other companies, suppliers and customers – for ex.
orders can be placed electronically, in real time, thus
reducing the need for large inventories and making
the process more efficient
– Airlines, bookstores, music vendors were the first to
discover that many customers like the convenience of
shopping from home
– Today almost all companies provide catalogs of their
goods and services online and most are capable to
take orders on-line
Business Applications
• On-line support
– In the past, a problem with an application (for example
accounting program, program forming salaries,
store/available goods, invoice issuing program, etc)
running on your computer might take 2-3 days to solve –
until the engineer comes to your site and solves/repairs
the problem
– Nowadays a customer can grant access to his/her systems
to a remote site/user and the problem can be solved in a
matter of one or few hours
– Update of your server or application can also be
performed on-line, saving a lot of time and efforts
Home Network Applications
•
•
•
•
Access to remote information
Person-to-person communication
Interactive entertainment
Electronic commerce
Home Network Applications
•
Access to remote information - interaction
between a person and a remote database of
information
– surfing the World Wide Web for information
(arts, business, cooking, government, health) or
for fun (too many ways to mention..)
– Newspapers/news sites, on-line digital libraries,
Wikipedia, etc.
Home Network Applications
• Person-to-person communication
– the 21st century's answer to the 19th century's telephone
– E-mail - on a daily basis, used almost universally - contains
audio, video as well as text and pictures
– Instant messaging - derived from the UNIX talk program in
use since around 1970, now with applications like Skype,
ICQ, Instant messenger, etc.
– Worldwide newsgroups/forums - discussions on every
conceivable topic
Peer-to-peer communication
• Another type of person-to-person communication is
the peer-to-peer communication
• Different from the client-server model
• Individuals who form a loose group can communicate
with others in the group
• Every person (or its computer) can, in principle,
communicate with one or more other people
(computers) - there is no fixed division into clients
and servers
Peer-to-peer communication
•
In peer-to-peer system there are no fixed
clients and servers.
No fixed clients and servers in peer-to-peer systems
Peer-to-peer communication
• Peer-to-peer communication - big hit around 2000
with a service called Napster - over 50 million music
fans swapping music!
• Members registered the music they had on their
hard disks in a central database maintained on the
Napster server
• When a member wanted a song - checked the
database to see who had it and directly get it Napster
did not keeping any music on its machines, so it was
not infringing anyone's copyright. The courts did not
agree and shut it down
Peer-to-peer communication
• New generation peer-to-peer systems eliminates the
central database by having each user maintain his
own database locally, as well as providing a list of
other nearby people who are members of the system
• A new user can go to any existing member to see
what he has and get a list of other members to
inspect for more video or music
• The lookup process can be repeated indefinitely to
build up a large local database of what is out there
• Torrents for movies, music, books, etc are the
popular peer-to-peer type of communication today
Home Network Applications
• Other communication-oriented applications
include
– telephone calls
– video phone
– Internet radio
– telelearning – one can attend 9 A.M. class without
the inconvenience of getting out of bed (not the
present case)
Home Network Applications
• Interactive entertainment
– video on demand - select any movie or television
program, in any country, and have it displayed on
your screen instantly
– game playing - multiperson real-time simulation
games - such with goggles and three-dimensional
real-time, photographic-quality moving images
form a worldwide shared virtual reality
Home Network Applications
• Electronic commerce
– Home shopping – users can seek in on-line
catalogs of thousands of companies
– Companies also provide on-line technical support
– Banking - many people pay their bills, manage
their bank accounts, and handle their investments
electronically
– Trading (person-to-person) – advertising personal
goods for sale (instead going to the flea market)
Home Network Applications
•
Forms of e-commerce
Home Network Applications
• Computer networks are getting hugely important, changing
the need people to live at a big city (where are more
opportunities for work), for many types of business - with the
proper quality internet access, one can perform the same job
at a village or in another country!
• Telelearning may affect education - universities may go
national or international
• Telemedicine is likely to become ever more important remote patient monitoring, even remote surgeries!
• Smart homes are also at the development – one can use a
webcam to see if the coffee is ready, or sensors connected to
the home network can inform you on events in rooms/places
which need your immediate attention and response
Mobile Users
• Mobile computers - notebook computers,
tablets, smart phones, personal digital
assistants (PDAs), are one of the fastestgrowing segments of the computer and
communication industry
• Wired connection is impossible at a lot of
places - in cars, trains, ship, airplanes, some
remote villages, so there is a lot and growing
interest in wireless networks
Mobile Users
• People on the road or at place different from their home or
office want to use their portable electronic equipment to send
and receive telephone calls, faxes, and electronic mail, surf
the Web, access remote files, and log on to remote machines regardless if they are on land, sea or air
• At conferences and meetings, the organizers often set up a
wireless network in the conference area and participants turn
their computers on and connect to the Internet
• Universities have installed wireless networks on campus so
students can sit in the open and consult the library's card
catalog or read their e-mail
Mobile Users
• Wireless networks are of great value to those,
whose work is mobile - trucks, taxis, delivery
vehicles, and repair persons – both for
business and keeping in touch with home
• Wireless networks are also important to the
military – they can’t rely on the local
networking infrastructure but have to set their
own
Mobile Users
• Wireless networking and mobile computing are often
related but they are not identical
• There are fixed wireless (at a university campus, at a
hotel) and mobile wireless
• On the other hand – a notebook computer can be
wired - if a traveler plugs a notebook computer into
the telephone jack in a hotel room, he has mobility
without a wireless network (usually for higher speed
network)
• There are mobile, wireless applications – for example
checking whether you have paid your parking fee is
done by PDA (pers dig assistant)
Mobile Users
•
Wireless networks and mobile computing
Mobile Users
• Food, drink, and other vending machines can issue a
wireless report once a day announcing their current
inventories
• Electricity, gas, water, and other meters in people's
homes can report usage over a wireless network –
eliminates the need of employees of those
companies to go on-site
• Wireless PDAs can be used for banking and shopping
- kind of electronic wallet, authorizing payments in
stores, replacement for cash and credit cards
Mobile Users
• A lot of mobile services appear - for example,
it may be possible to ask for a nearby
bookstore or Chinese restaurant
• Mobile maps are widely used nowadays, and
so is local weather forecast
• Other used mobile applications include
tracking inventory, packages, birds, mammals,
dolphins, sharks, whales…
Social Issues
• The widespread introduction of networking
has introduced a whole new world of social,
ethical, and political problems
• Social networking – in forums, bulleting
boards, Facebook, Twitter, etc., where people
can exchange messages, photos, materials and
other information with like-minded individuals
or representatives of organizations can bring
offense to other users
Social Issues
• Views posted on topics like politics, religion, or
sex may be deeply offensive to some people
• Certain materials (on particular countries, or
on religions, pornography, etc.) may be
unacceptable in either moral or judicial aspect
as different countries have different and
conflicting laws in this area
Social Issues
• Another issue is the employee rights versus
employer rights
• Many people read and write e-mail at work
but some employers claim the right to read
and possibly censor employee messages - not
all employees agree with this
• Some employers restrict the use and access to
certain programs/sites at the workplace
Social Issues
• It is not only the employee versus the employer issue
but also governments versus people
• The FBI has installed a system at many Internet
service providers to snoop on all incoming and
outgoing e-mail for nuggets of interest to it - its goal
is to spy on millions of people in the hope of finding
information about illegal activities
• China has denied access to Google and on other
instances has blocked sites like Twitter, Facebook,
Youtube, other examples for similar actions are Iran,
Egypt, Pakistan that limit the access to
sites/programs. Russia has also passed an “Internet
blacklist law”
Social Issues
• Computer networks offer the potential for sending
anonymous messages – in some cases this may be
desirable. For example, it provides a way for
students, soldiers, employees, and citizens to blow
the whistle on illegal behavior on the part of
professors, officers, superiors, and politicians
without fear of reprisals
• On the other hand – in USA anonymous accusations
cannot be used as evidence
• Anonymous accusations can be also a form of
unsupported blackmailing harming individuals or
organizations
Social Issues
• The world wide network allows ordinary citizens to
express their views in different ways and to different
audiences on a number of unsolved social, political,
and moral issues
• At the same time a lot of the information available
on Internet is ill-informed, misleading, or downright
wrong
• Computer networks have also introduced new kinds
of antisocial and criminal behavior - E-mail messages
or some sites may contain active content (basically
programs or macros that execute on the receiver's
machine) with viruses
Social Issues
• Identity theft is becoming a big problem thieves collect information about a victim and
can obtain credit cards details and other
private data on the victim (political and
religious view, medical records, etc)
• Massive copyright violations is also carried out
– music and video are digitally transmitted
and companies have problems of enforcing
their copyrights
Social Issues
• Having widespread use of electronic
payments, banking and business the need of
secured networks is becoming more and more
vital
• The technology of encryption and
authentication is well established but is
constantly developing with the new features
and challenges of networking
Social Issues
• With the development of the computer and
computer networking industry the World has
become a Digital World in the 21st century
bringing with that not only advantages but
serious problems
• New legislations and approaches to almost all
areas of human life are needed – just like the
introduction of cars a century ago required
new skills, rules and legislation but today –
this is needed in a larger scale!