Financing Agriculture: Risks and Risk Management Strategies
advertisement
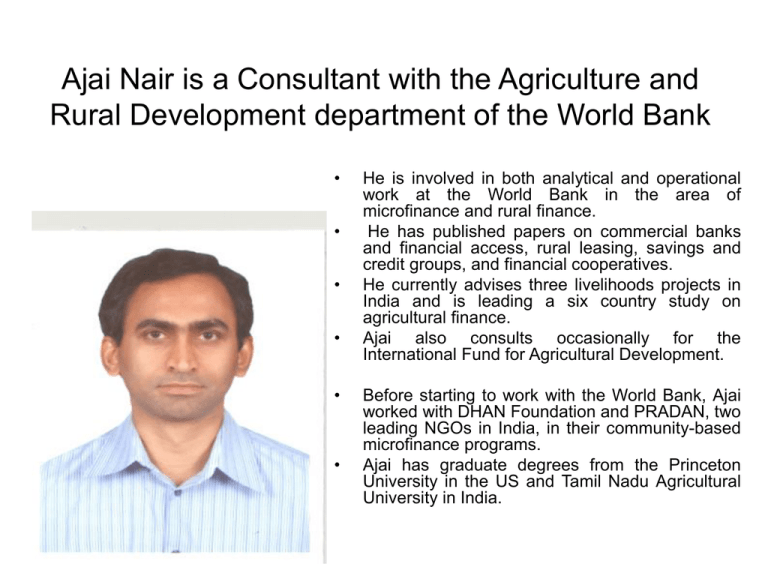
Ajai Nair is a Consultant with the Agriculture and Rural Development department of the World Bank • • • • • • He is involved in both analytical and operational work at the World Bank in the area of microfinance and rural finance. He has published papers on commercial banks and financial access, rural leasing, savings and credit groups, and financial cooperatives. He currently advises three livelihoods projects in India and is leading a six country study on agricultural finance. Ajai also consults occasionally for the International Fund for Agricultural Development. Before starting to work with the World Bank, Ajai worked with DHAN Foundation and PRADAN, two leading NGOs in India, in their community-based microfinance programs. Ajai has graduate degrees from the Princeton University in the US and Tamil Nadu Agricultural University in India. Financing Agriculture: Risks and Risk Management Strategies Ajai Nair, Consultant, World Bank 3rd Agribanks Forum, theme ‘Africa Value Chain Financing’, October 16-19, Nairobi, Kenya . What are the major risks agricultural financing? Systemic/Correlated Risks – – – Production Risks –weather, pests, farming practice. Price Risks – for inputs and outputs. Political Risks – export bans, price caps, debt write offs Idiosyncratic/Independent Risks – – – Willful default Over-financing, under-financing, wrong pricing. Life, Health, Asset What is the impact of these risks? At a proximate level, – – Low availability of finance for farming and agribusiness. Slow adoption of agricultural technology and private sector investments in agribusinesses. Ultimately, – – High volatility in household income / food security for households Higher impact on low income households because of reduction in consumption and liquidation of assets. What are the solutions? Reduce / better manage Systemic and Idiosyncratic Risks – – Development and improved access to seeds, farming practices and technology, agricultural development services. Development and improved access to physical (forward sales, minimum price guarantee contracts, etc) and financial tools (insurance, derivatives) Better credit-risk assessment and management by lenders. World Bank’s work on Commodity Risk Management Ongoing work – – Price Risk Management: Options (Tanzania, Zambia, Mozambique, Malawi) Weather Risk Management: Rainfall Index Insurance (India, Malawi, Ethiopia, Thailand) Users: Governments, Financial Institutions, Producer Organizations, Agribusinesses, and producers. Services offered – – Policy advice Technical assistance: Risk Assessment, Contract Design, Pricing, and Program management. Experience so far: Price Risk Management Price risk management products have been offered: – – Product for intermediaries linked to financial services Product for governments to manage food-security. Pilot in Tanzania – – – – CRDB, a local bank, has offered product tthrough coffee producer organizations and cotton ginning companies Hedging helped coffee producer groups offer a higher purchase price to farmers Demand for contracts has varied with rise and fall in commodity prices. Better ability of bank and borrowers to manage price risk. Experience so far: Weather Risk Management Index based weather insurance offered as: – – – a stand alone insurance contract, part of a loan package or linked to other services such as seed provision, and portfolio coverage for a bank or lending institution` Pilot in Malawi: – – 3rd year of program development through NASFAM. Insurance contracts helped ground-nut farmers use improved varieties as contracts enabled access to finance from MRFC and Opportunity International. Lessons Learned: Price Risk Data: Robust historical commodity price data needed to design good contracts. Technical Skills: Local institutional capacity needs to be developed in price risk assessment (duration, volume) and accessing derivatives markets. Institutions/Markets: – – – Presence of robust, liquid market in the specific commodity to transfer risks. Local supply chain participants willing to undertake the significant investment in staff time and financial resources, and market the product and provide necessary education. Link to finance critical for take up. Lessons Learned: Weather Risk Data: Good quality historical data required to design contracts and reduce basis risk. Technical Skills: Local expertise in contract design, pricing, reinsurance, and program management are critical and must be developed. Institutions/Markets: – – – Local insurer willing to take risk or intermediate transaction Marketing organization able to market the product and provide necessary education Link to finance critical for take up In Conclusion… Risks in financing agriculture involves not only production and price risks, but also risks to life, health, and assets. Optimal production and price riskmanagement involves a combination of physical and financial tools. There are no silver bullet solutions. Contacts Price Risk: Roy Parizat royparizat@hotmail.com Weather Risk: Erin Bryla ebryla@worldbank.org