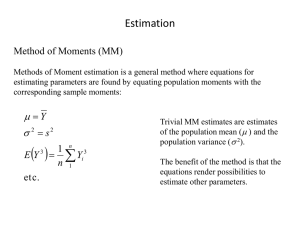
Estimation Presentation
advertisement
Project Estimation and Project Cost Pankaj Sharma Agenda • • • • • • • What is a project? What are project costs? What is an estimate? Why do we need to estimate? How do we estimate? When do we estimate? Improving Estimates through a process What is a project? • A Project is a temporary undertaking to create a unique product or service with a defined start and end point and specific objectives that, when attained, signify completion • Example: – Banner Implementation was a Project – Banner maintenance effort is not a Project but an operational undertaking What are project costs? Costs Onetime Costs Recurring Costs – Costs can be broken down into Onetime costs and Recurring costs – Recurring costs are incurred on a periodic basis (quarterly, biannually or annually) and may be time bound or perpetual in nature. – Onetime costs are for a definite duration and are incurred only once. What are project costs? Typical IT Cost Components Labor/Time Material •Typically includes labor •Typically includes costs directly related to hardware, software and the work or task licensing costs •Examples are costs incurred due to the involvement of Software/System/Network Engineers, DBAs, Production Support et al. Overhead •These costs are not directly related to the work at hand but are an important component in the accomplishment of tasks •Infrastructure costs such as electricity •Management and Administration of the tasks What are project costs? IT Costs Tree Onetime Costs Labor/Time Recurring Costs Labor/Time Material Material Overhead Overhead What are project costs? IT Costs Tree Project Costs Labor/Time Operational Costs Labor/Time Project Costs are typically Onetime costs Material Overhead Material Overhead What are project costs? Project Costs Operational Costs Time Cost Cost Comparison Operational Costs tend to be higher over the product’s or service’s lifetime since they are incurred for multiple years Project Start Project End Maintenance Start Product or Service Lifetime Maintenance End What is an estimate? • According to Webster, – “the act of appraising or valuing” – “a statement of the cost of work to be done” • PMO defines an estimate as, – a rough calculation of the costs and the amount of work prior to the commencement of work What is an estimate? • When estimating for a project cost we can also estimate ongoing costs • Outputs of an estimation exercise are: – Project Costs Estimate – Ongoing Costs Estimate Why do we need to estimate? • To get an idea of the costs of a project • To get an idea of the time needed to complete the project – Very important from a scheduling and project planning standpoint • To identify resource needs • To identify ongoing costs and resource needs How do we estimate? • Three step process – Identify the high level tasks – Identify the various groups that need to be involved with each task – Estimate time for each task • Consult a knowledge expert for an estimate. Do not put an estimate for someone else. How do we estimate? Identify groups involved • Typical groups involved in an IT project Training Networking Enterprise Application Services UPC DBA’s Reporting Systems Unix/Windo ws Helpdesk How do we estimate? Estimation techniques • Single Point Estimate – We take a single estimate per task • Three point Estimate – We take three estimates per task • Optimistic Estimate – Best Case Scenario • Pessimistic Estimate – Worst Case Scenario • Most Likely Estimate – Average the three estimates to get a three point estimate How do we estimate? Estimation techniques • Three point Estimate Example: – Optimistic = 6 hours – Pessimistic = 10 hours – Most Likely = 8 hours • The three point estimate is (6+10+8)/3 = 8 hours How do we estimate? Estimation techniques • Six point Estimation (PERT) – We take three estimates per task • Optimistic Estimate – Best Case Scenario • Pessimistic Estimate – Worst Case Scenario • Most Likely Estimate – Multiply the Most Likely estimate by 4, add to the Optimistic and Pessimistic estimates and divide by 6 How do we estimate? Estimation techniques • Six point Estimate Example: – Optimistic = 6 hours – Pessimistic = 10 hours – Most Likely = 8 hours • The three point estimate is (6+10+6x8)/6 = 10.66 hours How do we estimate? Estimation techniques PMO currently uses a single point estimate How do we estimate? Estimation techniques • Examples: – DARS Project • Estimation done after requirements were completed – OFS Enterprise Facilities Project • Estimation done during initiation When do we estimate? •An estimate can be calculated during initiation •An estimate can also be calculated during planning but before a schedule or project plan is created •The later the estimate is done the more accurate it is Initiation Planning Execution Closure •Main body of work is performed here •Coding, Testing, Installation et al. •We say Goodbye and Goodluck •Formally change product or service state to “in production” and “in maintenance” mode •Lessons learnt Project Lifecycle •Start of a project •Very Little information is available •Requirements are defined •Tasks are defined •Project Schedule and plan is created •A lot more information is available Improving Estimates through a process Project Initiation or Planning Execution Feedback and Improve Estimation Project Estimate Request Project Budget Measure Actual Request Ongoing Budget Measure Actual Estimation Process Ongoing Maintenance Estimate Feedback and Improve Estimation Improving Estimates through a process • Estimations are guesses • No two projects are alike and context plays a big part in estimates • Always find a Knowledge Expert for a task and obtain their estimate • With a process our guesses can improve by measuring Actual for every project Improving Estimates through a process • Estimation template is available at http://pmo.nmsu.edu/documents/estimate s_templatev1.0.xls