Robert_Fox_Presenation_MDM 1105KB Feb 10 2014 12:05:34
advertisement

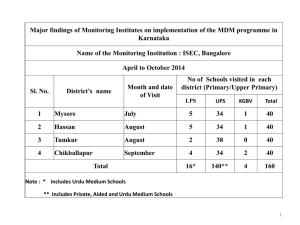
Master Data Management (MDM) ARKANSAS BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD RSFOX@ARKBLUECROSS.COM (501) 396-4160 Tuesday 9/25, 8:40 - 9:20 Biography Robert Fox - Data Architect, Arkansas Blue Cross Blue Shield •17 years of data architecture and warehousing experience in the finance, telecom, and health insurance industries. •Installed over 50 data warehouses worldwide, some loading more than 4.5 terabytes of new transactional data per day. •Guest lecturer in information management masters degree programs at 3 universities. •Speaker at national conferences for Oracle, Fidelity, and MDM-CDI. 2 Abstract – MDM is bigger than you think Master Data Management (MDM) is critical to effective managing the information assets of your company. Unfortunately, however, the meaning of the term Master Data Management has become more limited in scope over time. To understand the full scope of MDM, you must ask yourself two questions: 1. What is “master data”? 2. What all is involved in “managing” it? How you answer these two questions determines whether your MDM program is a departmental or enterprise solution, and whether you are managing the information or managing a process. This presentation will propose a framework for MDM that is broad in terms of both data and functionality. 3 Why is Information Important? The Evolution of Competition 1. The Land Grab • Acquiring unclaimed customers • Investment in infrastructure, name recognition, and geographic territory 2. The Killer App • Stealing customers from the competition by offering new and better products and services • Investment in software development 3. The Information War • Stealing and retaining customers from the competition by knowing more about the customer and giving them individually customized treatment • Investment in business intelligence, customizable offerings 4 First: What is “Master Data”? Application-specific, non-duplicated, nonshared data … App A App B App C Data duplicated in multiple apps App Z Other Data shared with enterprise There seem to be three different definitions: 1. Master Data is all the data, everywhere. 2. Master Data is just the data that is duplicated in multiple applications. 3. Master Data is any data that is exposed outside of an application, whether it is duplicated or not. 5 Second: What does it mean to “manage” data? 6 First Generation IT Architecture • • • Reporting … … Product Application Z Customer Reporting … Product Application B Customer Reporting … Product Customer Application A Business Logic Business Logic Business Logic User Interface User Interface User Interface Monolithic applications with proprietary, embedded data Custom point-to-point integration Very little ability to establish enterprise architecture 7 The Evolution of Data Architecture Monolithic Modular 3 Tier Client/Server DB Server Custom Data DB Data Access Presentation DB Server DB Data Access Business Logic Custom Application 5 Tier SOA DB Data Access Services App Server App Server Business Logic Client Presentation Business Services Integration Bus Web Server Presentation Client 8 Effective MDM cannot be a component of application development Traditional Location of Information Management Responsibility Emerging Location of Information Management Responsibility IT IT Application Development Technology Systems Information Management Application Development Technology Systems Information Management 2 Make sure your MDM program has the authority to be effective 9 Three legs on the IT “stool” Financial View Profitability Now Business View Customer Value Investment for the Future Operational Efficiency Strategic Planning Reduce Expense Grow the Company Application Information Technology (How?) (What?) (Where?) Increase Revenue IT View The goal of IT is to support the business. The goal of the business is to make money. 10 MDM Components 11 Customer Data Integration (CDI) App A CDI App B App C 1. Analytical CDI 2. Synchronization CDI 3. System of Record CDI WH App 12 MDM Components: Enterprise Logical Data Model Party Member Name Demographic Risk Provider Claim Product Claim Drug Header ServiceLine Adjustment Payment NPI Specialty Clinic Location • • • • Diagnosis Procedure • • • • DB Design SOA Services Mapping Sources Defining System of Record Define Stewards Global Dictionary Standard Terms Document Bus. Relationships Data Standards • • • • • • • • • • • • • No duplicate data SoA same as SoR unless proven untenable Only one warehouse All data is owned by the enterprise, not individuals or departments Data storage and transmission must comply with security standards Services used by multiple applications must use data structures derived from the enterprise data model All data structures must be documented All new data structures must be derived from enterprise data model Data quality should be addressed at the point of entry into corporate network Information should be as accurate and current as possible Data access should always be directed to the SoA The data model should drive the choice and architecture of applications, and should be based in turn on business requirements Any exceptions should go through Data Governance Dimensions of Data Quality for an Analytical Repository • INTEGRITY – does the data accurately reflect the source system? • VALIDATION – is the data valid for the field? • VERIFICATION – is the data actually true? • BALANCING – does the data compare to other systems (i.e. GL)? • AUDITING – Are there outlying values? 15 Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Project Pipeline Business Requirements Data Quality Architectural Approach Escalation Process Project Supervisors Resource Assignment Senior Leadership Team Executive Sponsor Technical Design Project Process Design Review 4 Development Unit Testing/ QA Testing Waiver Process Standards Review Board Standards Committee Executive Sponsor Code Review System/User Testing Implementation Develop an SDLC and infrastructure to support it 16 Business Intelligence: Closing the loop INFORMATION DECISION/ACTION Recommend product X, sign up for ePay, Offer free upgrade… RESPONSES KNOWLEDGE Profitability, Churn Propensity, Customer segment… BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE DATA Customers, accounts, inventory, payments, activity, products… 17 Maturity Model For Business Intelligence 5 4 3 2 1 Real-Time Decisioning Batch Campaigns Enriching with 3rd-party data Modeling, Scoring, and Segmentation Enterprise Reporting 18 Summary • Figure out what “Master Data Management” means in your organization • Think larger than the warehouse. – Make sure your program is empowered with authority to be effective within the enterprise. – Develop a functional area framework and assign responsibilities • Develop efficient MDM strategies for each functional area: Software development process, standards and waivers, aging and archiving, data quality, data delivery, security, etc. 19 • Always remember that you work for the business! Questions? 20