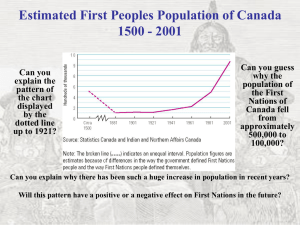
Intro to Construction 1 - Civil and Environmental Engineering
advertisement

Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Managers must be both… …business and technically oriented Construction Education Options Education Format • Traditional • CEM • BC • CM Construction Education Options • Engineering (civil or architectural) –Specialization/area of concentration –Curriculum Elective Construction Management Education • National CEM Programs – Stanford University – University of Michigan – Virginia Tech – Purdue University – University of Illinois-UC – Oregon State University – University of Colorado – NC State Construction Management Education • National BCM Programs – Georgia Tech – University of Florida – Purdue University – Virginia Tech – Auburn University – Georgia Southern University – University of North Florida Construction Education Options • National CM Programs – – – – – – – – Arizona State University Florida International University Colorado State Clemson University of Washington Michigan State University Brigham Young Wentworth Institute of Technology Construction Education Options • Graduate Construction Programs – – – – – – – – Stanford University University of Colorado University of Michigan Virginia Tech University of Southern California Arizona State University Florida International University Texas A&M Construction Education Options Construction Management • Interdisciplinary Education • Practice rather than theory based • Foundation of Business and Science Courses • Architectural & Engineering Coursework • Core of Construction Management Courses Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 B.S.C.M. Coursework Engineering subjects • • • • Strength of Materials Statics and Structures Soil Mechanics Steel and Concrete Design • Surveying Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 B.S.C.M. Coursework Business Management • • • • • Accounting Economics Statistics Financial Mgt. Contract Law Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Licensing/Certifications • Professional Engineer’s License issued by state or local governing board. • Certified Constructor issued by the American Institute of Constructors (AIC). • Certified Construction Manager issued by Construction Management Association of America (CMAA) • Project Management Professional (PMP) by the Project Management Institute (PMI) Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Basic Skills needed by Construction Managers – Estimating – Computer – Leadership/supervisory – Communication = writing and oral skills – Negotiating – Team Building Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Management Functions • Coordination • Planning & Scheduling • Purchasing & Expediting • Supervision • Cost Control • Documentation and Reporting Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Management Functions • Quality Control/Quality Assurance • Estimating • Safety and Risk Management • Contract Administration • Claims Analysis/Avoidance Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Additional Skills & Knowledge needed by Construction Engineers • Surveying (GPS, GIS, Hydrographic) • Structural Design • CADD/Drafting • Specialization in Mechanical, Electrical, Chemical, or Environmental disciplines Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction Engineering Functions • Preparation and Review of Shop Drawings • Constructibility & Sequencing Studies • Value Engineering • Erection Diagrams and Procedures • Survey & Layout Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Executive Functions • Corporate Management • Strategic Planning • Marketing & Business Development • Public Relations • Labor Relations Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Executive Functions • Ultimately responsible for quality, safety, production, and general financial health. Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction training can be valuable to design professionals…… • To enable them to produce practical and efficient designs • Develop needed management skills • Learn scheduling techniques that can be applied to the preconstruction process Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Project Life Cycle Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Life Cycle of a Constructed Facility 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Concept and Feasibility Engineering and Design Procurement Construction Startup and Implementation Operation or Utilization Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 What is Construction? Application of art and science Inherently dangerous Organized chaos Mankind using creativity, knowledge, strength, determination, and persistence to control his environment Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction differs from manufacturing in that: • Not performed in controlled conditions, therefore highly impacted by weather and other environmental conditions • Seasonality • Each project is unique • Remotes sites with various access problems Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction differs from manufacturing in that: • Process is not as predictable • Difficulty in applying automation • High potential for encountering unforeseen conditions • Costs can vary according to conditions Construction differs from manufacturing in that: • • • • • Difficult to manage and supply utilities and other resources. Technical innovations are adopted slower. Success is dependent upon the quality of its people. Very custom-oriented Product can be of mind-boggling size, cost, and complexity Problems Facing Construction Industry: • • • • • Highly traditional and fragmented; slow to embrace new technology Restrictive/outdated building codes Labor agreements and craft jurisdictional issues Liability and legal considerations Lack of profit motive or other incentive Problems Facing the Construction Industry: • Government regulation • Environmental constraints • NIMBY syndrome • Global competition Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 “The Blame Game” Overview of the Construction Industry • 10% of GNP • Employs over 10,000,000 workers • Annual Volume exceeds $800 billion • Vital to the Nation’s economic health and quality of life Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Industry Divisions 1. Residential Construction 2. (Institutional & Commercial) Building Construction 3. Heavy Construction 4. Industrial Construction Overview of the Construction Industry Industry Divisions 1. Residential Construction 2. (Institutional & Commercial) Building Construction 3. Heavy Construction 4. Industrial Construction Overview of the Construction Industry Residential • Types – Single family houses – Multi family dwellings – High-rise apartments & condominiums • 30-35 % of the industry • Low capital and technology requirements Overview of the Construction Industry Residential (continued) • Largely private • Often speculative • Developers = surrogate owners • Designed by architects, builders/developers Overview of the Construction Industry Building Construction • Institutional and Commercial Construction – Schools and universities – Medical clinics and hospitals – Recreational facilities and sports stadiums Overview of the Construction Industry Building Construction – – – – Retail stores and shopping centers Warehouses and light manufacturing Office buildings (single story to sky scrappers) Hotels, convention centers, and theaters Overview of the Construction Industry Building Construction • Institutional and Commercial Construction – Churches and Synagogues – Prisons – Courthouses and other government buildings Overview of the Construction Industry Building Construction • • • • 35-40 % of construction market Larger and more complex than residential Various owners (mostly private) Designed by architects and engineers Overview of the Construction Industry Heavy Construction • Horizontal Construction • 20-25% of the construction industry • Mostly public financing or large consortium Overview of the Construction Industry Heavy Construction • • • • • • Highway & Bridges Railroads & Urban Transit Systems Tunnels and Dams Airports Canals Port & harbor structures Overview of the Construction Industry Heavy Construction • Pipelines • Sewer Systems • Water treatment & distribution systems • Power & communication networks • Landfills Overview of the Construction Industry Heavy Construction • Mass quantities of basic materials: earth, rock, steel, timber, and concrete • Constructors need knowledge of engineering and geology • Engineers and builders are often specialized Overview of the Construction Industry Heavy Construction • Greatest impact on land and water • High degree of mechanization • Contracts awarded through competitive bidding Overview of the Construction Industry Industrial Construction • Very large scale projects • High degree of technological complexity • Designed and built by the largest firms with the highest level of technical sophistication Represent 5-10% of the market • Overview of the Construction Industry Industrial Construction • Petroleum refineries • Steel mills & aluminum plants • Chemical processing plants Overview of the Construction Industry Industrial Construction • Fossil fuel & nuclear power plants • Other heavy manufacturing facilities Overview of the Construction Industry Industrial Construction • Complex mechanical systems, process piping, and instrumentation • Civil, but also mechanical, chemical, and electrical engineering disciplines involved • Mostly private ownership (in western countries) Overview of the Construction Industry Industrial Construction • Negotiated contracts are typical • “Turnkey” contract arrangements are common • Design-constructor must be intimately familiar with the technology and operations of the facility Overview of the Construction Industry Construction Industry is further subdivided into sectors or segments by: • • • • • Public vs. private ownership/funding Union labor vs. open shop Organization and method of project delivery Type of work: new vs. rehab/retrofit/restoration Contract type Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 1. Owner • • • Private or public Conceives the construction project Increasing level of sophistication Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 2. Designer • • Architects • Size of firms ranging form single practitioner to large integrated firms • Mostly building and residential construction Engineers • Civil, mechanical, structural, electrical,chemical, environmental, geotechechnical, and multidiscipline Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 3. General Contractor • • • • General contractor also called “Prime” contractor Specialty contractors working as subcontractors Organization ranges from small, one-person company to large, integrated A/E/C firms Part of a design-build team Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 4. Construction Manager Two principle divisions of CM • • • • CM for Fee (management services only) CM At Risk – Operates similarly to a GC or DB with no labor or capital equipment Can encompass the management of the design process as well as construction CM services including inspection and overall project or program management Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 5. Suppliers 6. Fabricators 7. Manufactures, distributors, research, promotions Materials and equipment sales Equipment Rental Structural steel, pre-castors, wood products Labor/Trade Unions Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 8. Government Federal, State, local, and quasi-government Owner/client GSA, DOT’s, School Districts, USACOE Non-ownership functions Taxation and regulation Federal: IRS, OSHA, USACOE, DOL, NLRB, HUD (FHA), FHWA, FAA, EPA, and several others State: DOL, DEP/DNREC, historic preservation (SHPO) Local: County/City/Township Building Officials, Planning Boards, and Zoning Commissions Quasi-government agencies: development authorities, bridge and turnpike commissions Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 9. Utility Companies Electric, communications, water, gas,sanitary sewer Private petroleum pipelines Owner or service provider Integral part of the process Existing facilities in conflict with new construction Interruption of service can be very costly Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 10. Industry Associations Organizations of construction contractors Organizations of the design and management professions Construction material and equipment suppliers and product research Construction labor organizations Coordination and arbitration Inspection, specifications, and costs Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 10. Industry Associations Functions and services • • • • • • Industry information and communication Development and maintenance of standards Interindustry coordination Collective bargaining Statistics (market & industry) Meetings and conventions Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 10. Industry Associations Functions and services • • • • • • • • Public relations Joint industry promotions Management education Market development Apprenticeship training Legislative Government relations Product research Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 11. Professional Services Business/management consultants Legal council CPA firms Surety Companies Financial Institutions/Lenders Insurance agents Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Participants in the Construction Process 12. Adjacent Owners and the Public AtLarge Existing businesses, institutions, and residences adjacent to the constructed facility Civic organizations and community groups Railroads and public lands Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Project Delivery Organization • • • • • Construction by owners forces Owner-managed construction Construction by general contractor Design-build team CM Contract Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction employing owner forces – Usually small in-house construction or renovations – Industrial projects or institutional (such as hospitals or schools Owner-managed construction – Residential/commercial building developers – Industrial or institutional Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Construction by General Contractor – Also referred to as “Prime Contractor” – Most common method of delivery – Contractor bears substantial risks and financial responsibility – Facility designed by in-house architect/engineer or by design consultants – Often requires specialty subcontractors Specialty contractors might include those specializing in one of the following: • Excavation • Steel erection • Concrete – Cast-in-place – Prestressed/Precast • Masonry • Timber/wood framing • Piping/plumbing • • • • • • Clearing and grubbing Blasting/demolition Electrical Painting HVAC Environmental remediation • Many, many others Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 Design-Build (Turnkey) – Single firm or team responsible for design and construction minimizes coordination problems – More efficient designs with the interjection of constructibility and innovation – Often employs fast-track construction – Benefits include reduced overall delivery time and “onestop shopping” for the owner – Disadvantages include complexity of evaluating proposals Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 CM Contract -- Fee (management services only) also referred to as “Agency” – Specialized construction skills through all project stages including preconstruction – Provides close coordination between design and construction – Eliminates impact of conflicts of interest – Independent and objective evaluation of costs, schedules, and performance – Potential saving in time and cost – Disadvantages include no risks associated with costs increase Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010 CM Contract – “At-Risk” – CM assumes financial risks similar to a GC – CM manages all phases of the work without performing any actual work tasks – CM’s only resources are management personnel – Contractors/subcontractors have a direct contract privity with CM – Contract form is often a negotiated guaranteed maximum price arrangement – Disadvantages includes lack of impartiality Construction Methods & Management CIEG 486-010