Getting ready for Advanced Metering Infrastructure
advertisement

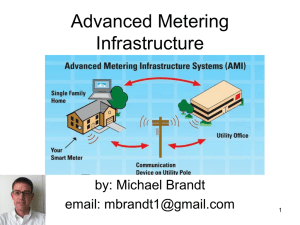
Getting ready for Advanced Metering Infrastructure Paper by : Rajesh Nimare Presented by : Prashant Sharma AMI by definition • Infrastructure of metering systems • Automates most of the metering centred repetitive activities • Collects granular consumption data to deploy dynamic pricing mechanisms • New payment and customer service options • Control of electrical load control within the home and or businesses to improve system diversity Is AMI same As AMR AMR is primarily focused on the ability to collect data Primary purpose of AMR systems is customer billing, and reduced costs of meter reading. AMR systems typically comprise of static meters fitted with communication devices, communication network (media) as well as supporting software to manage the data. AMI includes not only automated meter reading, but, a system that collects timedifferentiated energy usage from advanced meters The system is capable of providing usage information enables utilities to provide demand response products, Customers participation. AMI also supports additional features and functionality related to systems operation and customer service, e.g. outage management, connect/disconnect, customer load management etc. Business processes Meters Automatic Meter Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Reading (AMR) · Electronic with LAN, HAN, load profile and · Electronic Data Collection · Monthly Data recording · Cumulative kWh · Business opportunities · Monthly consumption based billing Key business processes · · · · · · · · disconnect. Remote using LAN communication, more frequent Half hourly so that dynamic prices can be applied. Customer payment option Pricing options Utility Operations Demand response Emergency response Billing · Customer · information system · Customer’s participation None Additional devices None Billing Customer information system Customer data display · Outage management · Emergency demand response. In Home Display, cost environmental consciousness. Demand response programs Utility controlled customer load Smart thermostats / Compressor and Components • • • • In home Display An advanced electricity meter, A central back-end software system Two way communication system Stake holder benefit • Consumers to better manage their electricity use; • Electricity retailers to make innovative time-ofuse price offers to suit consumers’ needs; and • Electricity distributors to better detect supply faults and respond to them more quickly. • Industry Benefits: – Carbon Credits – Catering to increasing demand with existing generation Technical Architecture / Landscape SMART meter • Record electricity consumption by the half hour; • Be remotely read so a meter reader does not have to visit your home or business; • Provide consumption and price information via an inhome display • Enable billing queries to be resolved quickly • Allow remote connection of your electricity • Help electricity distributor to detect and locate outages and restore supply more quickly; and • Monitor the quality of your electricity supply Programs using AMI • • • • • • Demand Response Dynamic Pricing Critical Peak Pricing Real Time Pricing Emergency Demand Response Economic Demand Response Planning AMI Deployment Identify the current challenges of your business process. Identify the future challenges that your business, your customer and the society at large may encounter. Remember, it is not easy to find “problem” or “inconvenience” or “sluggish system” if these have become a routine. Each business process: meter data collection, revenue collection and customer satisfaction should be challenged with efficient alternatives. Define your AMI vision statement considering the current and future challenges Planning AMI deployment • Start with a pay-back analysis. Telescopically plan your AMI rollout keeping the most rewarding benefits in the first few phases. • Don’t re-invent the wheel; take suitable help from vendors and consultants as the cost of advice is insignificant in terms of benefits and avoiding rework. Thank You