Lecture 7: Bus Architecture
advertisement
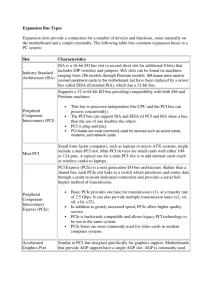
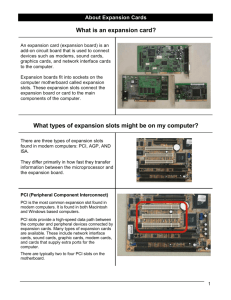
Bus Architecture What is a bus? In computer architecture, a bus is a subsystem that transfers data or power between computer components inside a computer or between computers. Unlike a point-to-point connection, a bus can logically connect several peripherals over the same set of wires. Each bus defines its set of connectors to physically plug devices, cards or cables together. Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) ISA originated as an 8-bit system in the IBM PC in 1981, and in 1984 a 16-bit version was introduced. Bus speed: 8.33Mhz PnP support: Original version none, Later version offered poor PnP support. ISA Expansion Slots 8-bit slot 16-bit slot Micro Channel Architecture (MCA) 16-bit bus which operates at 10Mhz which was introduced by IBM in its PS2 systems. First bus to be software configurable. Incompatible with ISA cards. Proprietary architecture. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) 32-bit PnP bus capable of operating as a 64-bit bus. Bus Speed: 33 or 66Mhz By far the most widely used in modern computers. Permits IRQ sharing. PCI Express (PCIe) PCI Express is a serial connection that operates more like a network than a bus. Instead of one bus that handles data from multiple sources, PCIe has a switch that controls several point-to-point serial connections. PCIe Architecture and Connectors Smaller PCIe cards will fit into larger PCIe slots. The computer simply ignores the extra connections. For example, a x4 card can plug into a x16 slot. A x16 card, however, would be too big for a x4 slot. PCIe Motherboard Connectors PCI Express slots (from top to bottom: x4, x16, x1 and x16) Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) The Accelerated Graphics Port (also called Advanced Graphics Port) is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a graphics card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Some motherboards have been built with multiple independent AGP slots. AGP is slowly being phased out in favour of PCI Express. Available Versions AGP 1x, using a 32-bit channel operating at 66 MHz resulting in a maximum data rate of 266 megabytes per second (MB/s); 3.3 V signaling. AGP 2x, using a 32-bit channel operating at 66 MHz double pumped to an effective 133 MHz resulting in a maximum data rate of 533 MB/s; signaling voltages the same as AGP 1x. AGP 4x, using a 32-bit channel operating at 66 MHz quad pumped to an effective 266 MHz resulting in a maximum data rate of 1066 MB/s (1 GB/s); 1.5 V signaling. AGP 8x, using a 32-bit channel operating at 66 MHz, strobing eight times per clock, delivering an effective 533 MHz resulting in a maximum data rate of 2133 MB/s (2 GB/s); 0.8 V signaling. Compatibility AGP cards are backwards and forwards compatible within limits. 1.5 V cards will not go into 3.3 V slots and vice versa, though "Universal" slots exist which accept either type of card. AGP Pro cards (rarely used) will not fit into standard slots, but standard AGP cards will work in a Pro slot. Universal Serial Bus (USB) A serial standard for connecting devices. Up to 127 devices can be connected to the USB bus. USB current standard is USB 2.0 which supports a transfer rate of 480Mbps. USB Connectors and Hubs USB A and B female connector USB Hub USB male A connector