Operations Management Supply Chain Management
advertisement

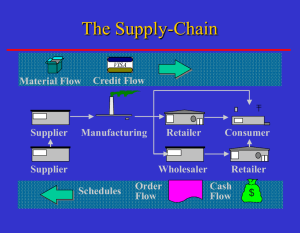
Operations Management Supply Chain Management 1 Volkswagen Resende Plant Volkswagen • Brazilian plant employs 1565 workers – 265 work for VW – 1300 work for other sub-contractors/suppliers: • VW employees responsible for overall quality, marketing, research and design • Supplier/subcontractor employees responsible for supply of parts/components and overall assembly of truck, being provided space in the VW plant • VW looks to innovative supply-chain to improve quality and drive down costs Supply-Chain Management • Management of all activities concerned with – Procurement – Transformation – Distribution • Involves everyone in supply-chain • Objective: Maximize value & lower waste • Key is to make suppliers “partners” in firm’s strategy The Supply-Chain ® Material Flow Supplier Credit Flow Manufacturing Supplier Schedules Retailer Consumer Wholesaler Retailer Order/Cash Flow Mkt research data Importance of Purchasing • Major cost center – More wise to reduce cost than increase sales to increase overall profits • Affects quality of final product • Aids strategy of low cost, response, and differentiation Objectives of the Purchasing Function • Helps identify the products and services that can be best obtained externally – Make / Buy decisions – outsourcing? • Develops, evaluates, and determines the best supplier, price, and delivery for those products and services Supply-Chain Strategies • Must be in sync with OM strategy which in turn should support overall company strategy • Affects long-term competitive position • Strategic options – Many suppliers – Few suppliers – Vertical backward integration Many Suppliers Strategy • Many sources per item • Lowest bidder wins order – focus on low cost • Infrequent, large lots • Long-term relations is not a goal • Negotiated, sporadic • Suppliers held responsible for reqd technology, expertise, cost, quality and delivery competencies Few Suppliers Strategy • 1 or few sources per item • Partnership (JIT); long-term, stable relations • Allows suppliers to have economies of scale and a learning curve, thus cutting down on prodn costs • Reliability and quality given primary importance • Frequent, small lots • Delivery to point of use • Drawback – both buyer and supplier run risk of becoming captives to one another Vertical Integration Strategy • Ability to produce goods previously purchased – Setup operations – Buy supplier • Results in cost reduction, quality adherence, timely delivery • Issues – Major financial commitment – Hard to do all things well – Dangerous for firms in industries undergoing technological change if management not knowledgeable enough about the next wave of change Forms of Vertical Integration Iron Ore Silicon Farming Raw Material (Suppliers) Backward Integration Steel Automobiles Integrated Circuits Distribution System Circuit Boards Dealers Computers Watches Calculators Flour Milling Current Transformation Forward Integration Baked Goods Finished Goods (Customers) Vendor Selection • Vendor evaluation Engineering/research/innovation skills Production capability Distribution capability Quality systems Facilities Financial and managerial strength • Vendor development Integration of the chosen supplier to the system • Negotiations Cost based; market based; competitive bidding