Application
advertisement

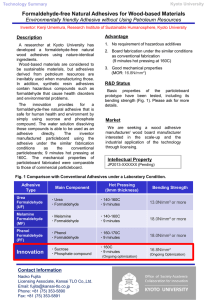
Adhesives for LSE substrates Joining Methods Non structural (<1000 psi OLS) Adhesives Hot melts (3M Jet-meltTM 3731) Spray adhesives (3M Hi-Tack 76 Spray Adhesive) PSA Tapes (3M 300LSE High Strength Laminating Adhesive or Double-Coated Tape) Re-closable fasteners Hook & loop (3M ScotchmateTM SJ-3506 and SJ-3507) Joining Methods Structural (>1000 psi OLS) Adhesives Traditionally, surface preparations (priming, etching, flame treatment) that alter the surface energy are necessary (3M Scotch-weldTM DP-420 after flame treating) 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-80XX (other than light cleaning no surface prep necessary) Mechanical joining Machine screws ( nut and bolt or threaded insert) Self threading screws/nuts Other Joining Methods Snap fit Hook/beam,annular, ball and socket, Press fit Heat staking/ hot air cold staking Radio frequency dielectric heating Ultrasonic welding Multi-shot molding Adhesive & Cohesive Strength Adhesion – Force between dissimilar surfaces Cohesion – Internal strength of material Substrate Substrate Adhesive Adhesive Substrate Substrate Stresses on a Joint That Can Lead to Bond Failure Shear Tensile Cleavage Peel Joint Design Designing the joint to minimize peel or cleavage stresses on the bond line and maximize tensile, shear or compressive stresses is desirable Improving joint design to accommodate applied stress Bonding Process Surface prep (cleaning) Applying liquid adhesive WGT Closing up the bond Apply pressure during cure (clamping) Bonding Process Adhesive Wetting Zisman's Equation cos 1 b( c lv ) θ Contact Angle Q c criticalsurface energyof substrate lv surface energyof liquid c-lv Surface Treatment Effects of Surface Treatment on Polyethylene Surface Energy (mN/sq.m.) 42 40 38 36 34 32 30 Untreated Exposed to UV Light Flame Treated Treatment Exposure to UV Light in presence of solvent Etched in chromic acid Key Performance Characteristics of a Structural Adhesive Bond making properties Usability in manufacturing process Degree of surface preparation necessary Open time (work-life) Time to handling strength (50 psi OLS) Cure conditions (temperature, pressure) Viscosity (non sag, pump ability) Delivery equipment Key Performance Characteristics of a Structural Adhesive Cured bond properties Environmental resistance Thermal Shock Weathering Chemical resistance Solvents Moisture Substrate Processing Effects Processing of substrate impacts the bulk and interfacial properties of the substrate Adhesive performance is coupled not only to the material type but also to the process conditions used to make the substrate 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 2 part – 10:1(B:A) mix Base (B) - acrylic Accelerator (A) - amine Density B = 8.2 lbs/gal A = 8.9 lbs/gal Viscosity B = 23,000 cps nominal A = 45,000 cps nominal 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 Open time (work life) Time to handling strength 2-3 minutes @ 23C 2-3 hrs @23C 15 minutes @ 80C Full cure time 8 hrs @ 23C 1 hr @80C 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 Mechanical properties Shore D hardness = 55 Peak strain = 5.3 % Peak stress = 1889 psi Thermal properties Tg = 34-38 C (DSC @ 10c/min.) CTE = 6.6 ppm/degC 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 Overlap Shear 3M Scotch-weld TM DP-8005 On Various Substrates 3000 SY = Substrate yield SF = Substrate failure AF = Adhesive failure CF = Cohesive failure MM = Mixed failure 2000 CF CF SF SF 1500 SY 1000 SF SY SF SY SY AF SY MM SY SY SY 500 PE / HD Substrate Translucent Black HD G S O ily CR PE / HD an ea le d G G al v PE / HD P HD G -F R Ny l on -6 ,6 S HI P C Ri g id PV M A PM ar bo na te PE LD AB S Po lyc UH M W PE PP PE 0 HD Strength (psi) 2500 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 Environmental & Chemical Exposure of 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8005 14 days exposure at 75 F (unless another temp is noted) on HDPE 1200 SY Mix SY SY SY SY Mix SY Mix OLS (psi) 1000 800 600 CF CF 400 200 SY = Substrate yield CF = Cohesive failure Mix = Some of both Translucent Black ne lu e To el ie s G as ol Fu el in e ze tif re e Chemical D 20 % An Bl IP A ea ch l C H % 16 aO H N % 10 R H 0F /W at er So ak 16 16 0F /1 C 00 % on t ro l 0 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-8010 Similar to 3M Scotch-weldTM DP8005 with regard to performance characteristics on LSE substrates Longer work life – 10 minutes Slightly shorter time to handling strength – Just under 2 hours More flexible – better peel performance Less sensitive to process history of substrate 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-80XX Applications • Bonding Polypropylene with polyethylene 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-80XX Applications • Dashboard 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-80XX Applications • Building industry Application: House connectors Bonding a flexible pipe (PE) with a rigid one (stainless steel) 3M Scotch-weldTM DP-80XX Applications • Electronics 3MTM Jet-MeltTM Polyolefin Bonding Adhesive 3731 Description: A 100% solids, high heat resistant adhesive that bonds to a variety of substrates including polyethylene, polypropylene and many other plastics. 3MTM Jet-MeltTM Polyolefin Bonding Adhesive 3731 Features: • • • • • Solvent free, 100% solids High temperature resistance Bonds well to polyolefin based plastics Light tan color Fast setting 3MTM Jet-MeltTM Polyolefin Bonding Adhesive 3731 Typical Physical Properties: Color : Light Tan Specific Gravity: 0.92 Flash Point (C.O.C.): 525°F (273°C) Viscosity @ 375°F(1) (191°C): 12,000 cps Bonding Range - 1/8" (Bead sec. (3) ): 25-30 seconds Impact Resistance (Inch lbs @ 72°F): 80 3MTM Jet-MeltTM Polyolefin Bonding Adhesive 3731 Heat resistance: 3MTM Jet-MeltTM Polyolefin Bonding Adhesive 3731 Overlap Shear Strength: Future R&D Directions Longer open times Faster cure times Inherent in the product External techniques for accelerating Adhesive performance Adhesive Bonding process Substrate (material and processing history)