Solicitation Essentials
advertisement

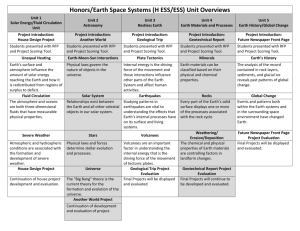
2014 CAPPO/NIGP Joint Conference Solicitation Essentials October 9, 2014 Demographics The Growler 1. The Good 2. The Marginal 3. The Bad Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Definitions Solicitation Planning RFx Process Specification Types SOW Solicitation Execution Evaluation Criteria Scoring RFP Responses / Evaluation Team Additional Sources Definitions 1. Solicitation Planning 2. GAP – Assessing difference between current state and solicitation objectives (needs) 3. Design or Performance Specs. 4. SOW – Statement of Work / Scope of Work 5. Solicitation Execution 6. Evaluation Criteria – Factors specified in the RFP that will be considered for award (Mandatory/Desirable) 7. Best Value – Determined by comparing solutions against customized criteria 8. Life Cycle Cost – Total cost of acquiring, support, operation, maintain and disposal (as applicable) Planning Stage • • • • • • • Define Business Goals Internal and/or External Expertise Market Research GAP (Comparing Actual w/ Potential Perf.) Outsource or Insource Make or Buy Bidding and Contracting Strategy Statement of Work Development 6 RFI, RFB, RFP, RFQ? 1. Request for ……. What is a RFP? • Rely on Market Expertise • Innovation or Creativity is Sought • Should reflect business objectives to allow matching solutions • Promotes Best Value vs. Low Bid • Criteria based Award Determination • Follows a structured evaluation procedure to demonstrate impartiality 8 When to use the RFP method? • Needed items and/or services are not clearly identified • Department need is goal or results-driven • Proposal requirements allow potential bidders the flexibility to respond • Procurement may be political in nature • Relatively high dollar amount • Highly competitive market • Protest Potential *SOW should provide a clear and thorough description of the goods or services 9 RFP Planning Checklist Did you perform market research? What are the evaluation team activities? Do you have an evaluation methodology? Do you have an evaluation guide? Do you have debriefing/protest procedures? Consultant roles COI & Ethics Evaluation rules of conduct Obtain Board/Council blessing BAFO Option proposals What makes a good RFP? • Well organized procurement goals, objectives, and evaluation process • Risk management assessment • Performance risk management • Well defined statement of work • Well organized deliverables • Well defined criteria • Well defined evaluation process 11 RFI/RFB/P/Q or Single/Sole Source? • • • • • • • • • Bus shelters Hybrid buses Parking lot management system project Professional SAP consulting services Enterprise Network Storage system replacement Annual Microsoft Software support Annual custodial services Mobile data computers/terminals and installation Professional consultation services 12 Does the prospective bidder know which one you want? 13 Specification Methods • Performance vs. Design –Performance = vendor risk –Design = buyer risk –Performance + Design = joint risk • Consensus Standards ANSI, ASME, ASTM, IEEE, ISO, NIST, NFPA, SAE, UL 14 What is a SOW? Statement of Work Vs. Scope of Work Statement of Work • Provides a clear and thorough description of the goods or services to be provided • Provide the relevant environment where the product/service will be used • Provides a description of the existing business processes and desired performance • Should be organized into logical groups 16 SOW Format and Contents • • • • • • • • • • • Background and Objectives Scope Tasks / Work Description Project Schedule Place of performance Deliverables Government-furnished resources Applicable specifications and standards Security Requirement Acceptance Criteria/Project Management Payment Schedule Statement of Work Demo/POC 18 Writing an Effective SOW SOW Objectives Specific Measurable Attainable Realistic Timely Execution Stage • • • • • • • • Bidding and Evaluation Procedures Procurement Team(s) Conflict of Interest / Rules of Conduct Solicitation Specific Evaluation Criteria Outreach Bidder’s Conferences Demonstration Script Documentation 21 Evaluation Criteria • Must represent key areas of importance and reflect user’s needs • Qualitative (subjective) and Quantitative (obj.) • Always include Costs, think in terms of TCO • Relied on to facilitate proposed solutions • Published • Acceptance Criteria (Demo/POC) • Criteria must sync with RFP Data Requests 22 Developing the RFP Evaluation Criteria • Well developed Criteria produce market solutions targeting your needs • Involve stakeholders knowledgeable about goals • How will responses be measured against criteria • Rating Scales • Scoring Phase(s) consideration • Determine relative importance (Criteria Weight) • Concurrently develop the scoring matrix / evaluation worksheet 23 Sample Criteria • • • • • • • Technical Approach and Understanding Key Personnel Capabilities Demonstrated Successful Experience Project Management Plan / Timelines Risk Assessment / Fiscal Strength Ability to meet standards Cost (TCO) 24 Evaluation Methodology Objectives • Encourage accurate comparison of potential suppliers against individual RFP criteria • Align weighting to reflect overall procurement goals • Allow criteria to be grouped into sections • Allow the scores of multiple evaluators to be contrasted or aggregated • Enable multiple evaluators to contribute to the scoring process • Compare TCO • Fairness/Transparency 25 Criteria Publishing Decisions Proposal criteria must be established prior to the release of the RFP and published in the RFP document. The evaluation criteria (not the weights?) were included in the RFP document. Weights? Evaluation Criteria Company Qualifications and References System Capabilities Customer Service and Support Pricing Risk Assessment Total 26 Weighting Methodologies • Fixed Weights • Variable Weights • Trade-off Analysis (overall value determined as a trade-off between technical differences and their relative worth to the agency) • Go, no-go (are minimum technical and/or managerial needs met?, if yes then the proposal clears to cost evaluation) 27 Evaluation Scoring Methods • • • • • • Comparing relative proposal cost Low cost vs. points Assigning weighting TCO/Life Cycle Consensus scoring Demo/POC *Develop standard evaluation scoring sheets. 28 Typical RFP Cost Evaluation “Normalization” Price of Lowest Cost Proposal / Price of Proposal being rated X Maximum cost points available = Awarded Price points Example: The total points available for cost in the RFP was fifty (50) points. The cost of the lowest acceptable proposal is $100,000. Therefore the lowest proposal cost of $100,000 would be awarded fifty (50) points. The second lowest acceptable proposal submitted a cost of $125,000. The second lowest proposal cost of $125,000 would be awarded forty (40) points. $100,000 / $125,000 = .80 X 50 = 40 29 Evaluation Phases Step 1 - Responsiveness Review Step 2 - Mandatory elements met Step 3 - Minimum / steps / threshold score Step 4 - May include interviews, demos, presentations Step 5 - Post Award POC 30 Scoring Proposals Sample Scoring Scale (0-3) 3. Exceeds requirements 2. Meets requirements 1. Minimally meets requirements 0. Does not meet requirements *Should match proposal strengths/weakness 31 Rating Considerations 90-100%: 80-89%: 70-79%: 60-69%: 0 - 59%: Meets or exceeds all requirements Meets all requirements and standards Proposal indicates a basic understanding Proposal indicates only a marginal Proposal demonstrates a significant lack of understanding of the requirements. * Rating should match description 32 Bad things do happen! • • • • • • • • Unbalanced and missing bid prices Bid Calculation Errors Material vs. immaterial Bid price conflict between words and numbers Protests Mismatch between specifications and goals Missing information Communication and politics 33 Only One Response? • • • • • • Open or Not to open Call potential suppliers Review specifications Review pricing methods/formulas Review terms and conditions Too many projects on the table * Consult with your legal folks 34 Scoring Examples 35 Weighted Criteria – Ex1 Criterion PM Strengths Previous Experience Understands Problem Financials Project Support Project Price Total Weight Weight 10 20 20 5 5 40 100 * Determine importance 36 Scoring – Ex2 Qualifications and References Score (20 points) System Capabilities Score (25 points) Customer Service/Support Score (20 points) Pricing Score (25 points) Risk Score (10 points) TOTAL Score (100 points) Redflex 18.60 16.88 12.50 25.00 10.00 82.98 ATS 19.40 18.44 12.50 18.83 10.00 79.17 Xerox 17.94 15.94 14.50 15.69 10.00 74.06 Gatso 14.13 16.25 8.50 9.55 10.00 58.44 Proposer 37 Score Variance – Ex1 Evaluator Michael Raymond Diana TOTALS Proposal B Proposal C PM Strengths PM Strengths PM Strengths 0 4 5 9 2 5 6 12 5 2 2 9 Proposal A * Variance in evaluator scores 38 Score Variance – Ex2 Evaluator Michael Raymond Diana TOTALS Proposal A Proposal B Proposal C 1 9 7 17 4 10 6 20 10 6 8 24 39 Balancing price and qualifications Proposer Vendor A Vendor B Vendor C Vendor D Total Proposal Price $985,142,530 $1,085,111,111 $1,365,770,098 $1,537,049,000 Price Technical Total Proposal Proposal Proposal Score Score Score 70.00 20.55 *90.55 63.55 26.13 89.68 50.49 27.71 78.20 44.87 21.41 66.28 * Test scoring 40 Differences in Total Scores Vendor A Vendor B Vendor C Total Score (Pts) 87 *86.5 83 * Check decimal placement 41 Need for Documentation Decision Maker Data Repository Auditor or Administrative (Board) needs should an issue arise relative to selection Facilitates FOIA requests Facilitates final Contract Development 42 Recap 1. 2. 3. 4. RFP Planning Process Statement of Work Specification Types Evaluation Criteria and Scoring Methodology 5. Document the Process Nugget Successful solicitations always involve: • Sound Planning • Solid Execution 44 Sources • • • • http://cappo.org Leginfo http://www.rfpmentor.com/ http://www.nigp.com 45 The End Beginning 46