Threats - Apneadda
advertisement

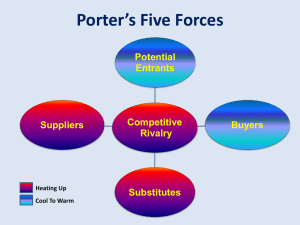
Strategic Management Environmental scanning (Unit 2) 1. Environmental analysis 2. Industry and competitive analysis 3. EFE matrix 4. CPM matrix 5. Internal analysis 6. IFE matrix 7. Porters five force 8. SWOT 9. VRIO framework Pre read: The five competitive forces that shape strategy Basic Elements of the Strategic Management Process Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 1-4 What is business environment? • Business environment consists of two parts. They are: External and Internal • Environment is complex, dynamic, uncertain and turbulent. (Nuclear disaster in Japan, Turbulence in Middle East, Fall of the Euro, Debt in Europe, High inflation in India, Credit crunch, Downgrading of India…) • Understanding your environment should be continuous, and holistic. • Remember that while some may be of advantage to your firm (opportunities), some would trouble your firm…(threats) External environment It is divided into: 1. Macro environment (PESTEL framework: Political, Economic, socio cultural, demographic, technological, ecological, legal) and of course global factors…. 2. Operating environment (Suppliers, Customers, competitors, creditors, labour market, distributors and retailers, regulations) 3. Industry or micro environment Exercise • You own a retail chain. What are the external factors you should be worried about?? Measuring the external environment • EFE matrix • CPM matrix EFE MATRIX Steps in developing the EFE matrix: •Identify a list of KEY external factors (critical success factors; identify Opportunities and Threats). •Assign a weight to each factor, ranging from 0 (not important) to 1.0 (very important). •Assign a 1-4 rating to each critical success factor to indicate how effectively the firm’s current strategies respond to the factor. (1 = response is poor, 4 = response is extremely good) •Multiply each factor’s weight by its rating to determine a weighted score. •Sum the weighted scores. Highest score can be 4 and the lowest 1. A score of 4 means the response of the company to opportunities and threats is ‘OUTSTANDING’, while 1 means ‘poor’. Exercise STEP 1: You own a retail chain. What are the external factors you should be worried about?? STEP 2: Do an EFE matrix evaluation… Competitive profile matrix (CPM) • ‘The CPM identifies a firm’s major competitors and their particular strengths and weaknesses in relation to a sample firm’s strategic position’. David 2001, p. 115 • Key success factors (KSFs) – Technology related – Distribution related – Marketing related – Skills related – Organisational capability – Other types of KSFs Competitive profile matrix (CPM) (Cont) Developing the CPM - Example Company A Company B Company C Key success factors Weight Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Advertising 0.1 3 0.3 3 0.3 4 0.4 Product quality 0.3 4 1.2 2 0.6 3 1.2 Customer loyalty 0.2 3 0.6 2 0.4 2 0.4 Financial position 0.2 3 0.6 2 0.4 4 0.8 Global expansion 0.1 2 0.2 2 0.2 1 0.1 Market share 0.1 3 0.3 2 0.2 2 0.2 Total 1.00 3.2 2.1 3.1 Rating: 1=major weakness, 4=major strength Internal environment • Strategy is matching ‘external environment’ to strengths. • This is to find, where the strengths are, the weaknesses. • These are internal. • There are four criteria which is used for division into strengths or weakness. They are: historical, norm in the industry (capacity utilisation), competitive parity or CSF (advertising is critical for success). • There are various models to understand whether the various factors are strengths or weaknesses, like VRIO, 7S etc… Measuring the internal environment • IFE matrix IFE Matrix Ratings are thus company based, whereas the weights in Step 2 are industry based. Steps to develop IFE Matrix 1. List key internal factors as identified in the internal audit process. Use a total of from ten to twenty internal factors, including both strengths and weaknesses. List strengths first and then weaknesses. Be as specific as possible, using percentages, ratios, and comparative numbers. 2. Assign a weight that ranges from 0.0 (not important) to 1.0 (all important) to each factor. The weight assigned to a given factor indicates the relative importance of the factor to being successful in the firm’s industry. Regardless of whether a key factor is an internal strength or weakness, factors considered to have the greatest effect on organizational performance should be assigned the highest weights. The sum of all weights must equal 1.0. 3. Assign a 1 to 4 rating to each factor to indicate whether that factor represents a major weakness (rating = 1), a minor weakness (rating = 2), a minor strength (rating = 3), or a major strength (rating = 4). Note that strengths must receive a 4 or 3 rating and weaknesses must receive a 1 or 2 rating. Ratings are thus company based, whereas the weights in Step 2 are industry based. 4. Multiply each factor’s weight by its rating to determine a weighted score for each variable. 5. Sum the weighted scores for each variable to determine the total weighted score for the organization. A score of 2.5 is weak and above it is strong…. Industry and Competitive Analysis Industry Analysis Industry Analysis covers two important parts: 1. Industry environment 2. Competitive environment Industry Analysis 1. Industry Features: Size, growth rate, geographical boundaries, size of competition, pace of technological change and product innovation 2. Industry Boundaries: Breadth of market, Product service quality, Geographical distribution, vertical integration, profit motives 3. Industry environment: Fragmented and consolidated. Can also be classified into: Emerging, mature, declining and global 4. Industry structure: Concentration(extent to which industry sales are dominated by only a few firms), Economies of scale, product differentiation and Barriers of entry 5. Industry attractiveness: Profit potential, growth prospects, competition and industry barriers 6. Industry performance: Production, sales, profitability and technological advancements. 7. Industry practices: Various policies on product, price, promo, distribution, R&D and competition 8. Industries future prospects… Competitive environment What is competition???? The purpose of Five-Forces Analysis • The five forces are environmental forces that impact on a company’s ability to compete in a given market. • The purpose of five-forces analysis is to diagnose the principal competitive pressures in a market and assess how strong and important each one is. Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Threat of New Entrants Economies of Scale Barriers to Entry Product Differentiation Capital Requirements Switching Costs Access to Distribution Channels Cost Disadvantages Independent of Scale Government Policy Expected Retaliation Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Suppliers Suppliers are likely to be powerful if: Supplier industry is dominated by a few firms Suppliers exert power in the industry by: * Threatening to raise prices or to reduce quality Powerful suppliers can squeeze industry profitability if firms are unable to recover cost increases Suppliers’ products have few substitutes Buyer is not an important customer to supplier Suppliers’ product is an important input to buyers’ product Suppliers’ products are differentiated Suppliers’ products have high switching costs Supplier poses credible threat of forward integration Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Buyers Bargaining Power of Buyers Buyer groups are likely to be powerful if: Buyers are concentrated or purchases are large relative to seller’s sales Buyers compete with the supplying industry by: Purchase accounts for a significant fraction of supplier’s sales Products are undifferentiated Buyers face few switching costs Buyers’ industry earns low profits Buyer presents a credible threat of backward integration Product unimportant to quality Buyer has full information * Bargaining down prices * Forcing higher quality * Playing firms off of each other Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Buyers Threat of Substitute Products Threat of Substitute Products Keys to evaluate substitute products: Products with similar function limit the prices firms can charge Products with improving price/performance tradeoffs relative to present industry products Example: Electronic security systems in place of security guards Fax machines in place of overnight mail delivery Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Rivalry Among Competing Firms in Industry Threat of Substitute Products Bargaining Power of Buyers Porter’s Five Force’s Model • 1. Rivalry Among Existing Competitors – Innovation; First to enter the market • 2. Substitute Products – Competitors with similar products • 3. Powerful Suppliers – Forward Integration • 4. Powerful Buyers – Backward Integration • 5. Threat of Entry – Advanced Knowledge – Capital Requirement Porter Competitive Model Heavyweight Motorcycle Manufacturing Industry • Parts Manufacturers • Electronic Components • Specialty Metal Suppliers • Machine Tool Vendors • Labor Unions • IT Vendors Bargaining Power of Suppliers • Foreign Manufacturer Potential New Entrant Intra-Industry Rivalry SBU: Harley-Davidson • Established Company Entering a New Market Segment • New Startup Bargaining Power of Buyers Rivals: Honda, BMW, Suzuki, Yamaha • Automobiles • Public Transportation • Mopeds • Bicycles Substitute Product or Service • Recreational Cyclist • Young Adults • Law Enforcement • Military Use • Racers Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways: Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions Occurs when a firm is pressured or sees an opportunity Price competition often leaves the entire industry worse off Advertising battles may increase total industry demand, but may be costly to smaller competitors Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Cutthroat competition is more likely to occur when: Numerous or equally balanced competitors Slow growth industry High fixed costs High storage costs Lack of differentiation or switching costs Capacity added in large increments Diverse competitors High strategic stakes High exit barriers The overall attractiveness of the industry If all the five forces are strong, industry profitability would be expected to be low regardless of the products/services being produced. Conversely, weak forces permit higher prices and above-average industry profitability. Firms can influence the five forces through the strategies they pursue. Some innovations can lead to a short-term advantage. But if every player in the industry is forced to follow suit, it can result in the whole industry being worse off. For example, the first firm to advertise on television may gain an increase in market share. If everyone else imitates this strategy, it may result in a stalemate with the only winners being the advertising agencies and the television companies. The crucial question, in determining profitability is whether firms in the industry can capture and retain the value they create for buyers, or whether this value is lost to others in fending off competition. Industry structure determines who captures the value : New entrants can compete away value, passing it on to buyers through lower prices, or they dissipate the value created by raising the costs of competing. Buyers who are powerful can retain most of the value created for themselves. Substitutes place a ceiling on prices. Suppliers that are powerful can appropriate the value created for buyers. Rivalry, like entry, results either in value being passed on to buyers (in the form of lower prices) or it raises the costs of competing (e.g. greater investments in product development and marketing). The Five Forces are Unique to Your Industry • Five-Forces Analysis is a framework for analyzing a particular industry. – Yet, the five forces affect all the other businesses in that industry. EXERCISE Presentation on an industry of choice and how the five forces act on one another SWOT Strengths: Weaknesses: Margins are good Perishability Flexibility of product mix: Tremendous. Lack of control over yield Availability of raw material: Abundant. Logistics of procurement Technical manpower: Professionally-trained, technical human resource pool, built over last 30 years. Problematic distribution Competition SWOT Opportunities: Value addition Export potential Threats: Threat from the unorganized sector Indian Dairy Industry The purpose of SWOT Analysis • It is an easy-to-use tool for developing an overview of a company’s strategic situation – It forms a basis for matching your company’s strategy to its situation SWOT is the starting point • It provides an overview of the strategic situation. • It provides the “raw material” to do more extensive internal and external analysis. Opportunities • An OPPORTUNITY is a chance for firm growth or progress due to a favorable juncture of circumstances in the business environment. • Possible Opportunities: – Emerging customer needs – Quality Improvements – Expanding global markets – Vertical Integration Threats • A THREAT is a factor in your company’s external environment that poses a danger to its well-being. • Possible Threats: – New entry by competitors – Changing demographics/shifting demand – Emergence of cheaper technologies – Regulatory requirements EXERCISE Do a SWOT analysis of a company of your choice. VRIO FRAMEWORK Checking your companies internal capabilities and resources Creating Strategic Fit to Leverage Internal Strengths What Does Internal Analysis Tell Us? Internal analysis provides a comparative look at a firm’s capabilities • what are the firm’s strengths? • what are the firm’s weaknesses? • how do these strengths & weaknesses compare to competitors? Why Does Internal Analysis Matter? Internal analysis helps a firm: • determine if its resources and capabilities are likely sources of competitive advantage • establish strategies that will exploit any sources of competitive advantage The Resource-Based View Resources and Capabilities Resources: • tangible and intangible assets of a firm tangible: factories, products intangible: reputation • used to conceive of and implement strategies Capabilities: • a subset of resources that enable a firm to take full advantage of other resources » marketing skill, cooperative relationships The Resource-Based View Four Categories of Resources • Financial (cash, retained earnings) • Physical (plant & equipment, geographic location) • Human (skills & abilities of individuals) • Organizational (reporting structures, relationships) Tangible and Intangible Resources Capabilities • Organizational capabilities: Routines and standard operating procedures Outstanding customer service Excellent product development capabilities Innovativeness or products and services Ability to hire, motivate, and retain human capital 54 Resources and Capabilities Firm Assets: Are these resources or capabilities? Machinery ? Collective Product Design Skill ? Recruiting Skill ? Engineering Skill of Individuals ? Mineral Deposits ? Linking Resources and Capabilities to Firm Performance EXHIBIT 4.3 Company Examples of Core Competencies & Applications The Internal Analysis Tool The VRIO Framework Four Important Questions: • Value • Rarity • Imitability • Organization The Question of Value: "Is the firm able to exploit an opportunity or neutralize an external threat with the resource/capability?" The Question of Rarity: "Is control of the resource/capability in the hands of a relative few?" The Question of Imitability: "Is it difficult to imitate, and will there be significant cost disadvantage to a firm trying to obtain, develop, or duplicate the resource/capability?" The Question of Organization: "Is the firm organized, ready, and able to exploit the resource/capability?" 1–60 The VRIO Framework If a firm has resources that are: • valuable, • rare, and •costly to imitate, and… • the firm is organized to exploit these resources, then the firm can expect to enjoy a sustained competitive advantage. The VRIO Framework Valuable? Rare? Costly to Imitate? No Exploited by Organization? No Competitive Implications Disadvantage Economic Implications Below Normal No Parity Normal Yes Yes No Temporary Advantage Above Normal Yes Yes Yes Sustained Advantage Above Normal Yes Yes EXHIBIT 4.5 Applying RBV: Decision Tree Competitive Implications THANK YOU