Mobile Commerce
advertisement

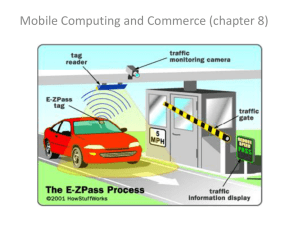
Chapter 6 Mobile Commerce and Ubiquitous Computing Learning Objectives 1. Discuss the value-added attributes, benefits, and fundamental drivers of m-commerce. 2. Describe the mobile computing infrastructure that supports m-commerce (devices, software, and services). 3. Describe the four major types of wireless telecommunications and networks. 4. Discuss m-commerce applications in banking and financial services. 5. Describe enterprise mobility applications. Learning Objectives 6. Describe consumer and personal applications of m-commerce, including entertainment. 7. Understand the technologies and potential applications of location-based m-commerce. 8. Define and describe ubiquitous computing and sensory networks. 9. Describe wearable Google Glass, driverless cars, and mobile apps. 10. Describe the major implementation issues from security and privacy to barriers of m-commerce. Mobile Commerce: Concepts, Landscape, Attributes, Drivers, Applications, and Benefits • Basic Concepts, Magnitude, and the Landscape o o o o *Mobile commerce (m-commerce) The Magnitude of M-Commerce The Landscape of M-Commerce Mobile and Social: A Powerful EC Combination • The Attributes of M-Commerce o o o o o Ubiquity Convenience and capabilities Interactivity Personalization Localization The Landscape of Mobile Computing and M-Commerce The Drivers of M-Commerce Mobile Commerce: Concepts, Landscape, Attributes, Drivers, Applications, and Benefits • An Overview of the Applications of MCommerce o o o o Field mobility Fleet mobility Warehouse management Direct store delivery (DSD) route accounting • The Benefits of M-Commerce o o o o Benefits for Organizations Benefits for Individuals and Customers Benefits to Society Other Benefits M-Commerce Applications and Their Classifications The Enabling Infrastructure: Components and Services of Mobile Computing • Overview of Mobile Computing o *Wireless mobile computing (mobile computing) • Mobile Devices *Smartphones Tablets Google’s Smart Glasses Personal Digital Assistants: Enterprise Tablets • *Personal digital assistant (PDA) o Wearable Devices o Other Mobile Devices o *Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) o o o o The Enabling Infrastructure: Components and Services of Mobile Computing • Mobile Computing Software and Services o Mobile Portals and Content Providers • *Mobile portal o o o o *Short Message Service (SMS) *Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS) Location-Based Services Voice-Support Services • *Interactive voice response (IVR) systems • *Voice portals The Enabling Infrastructure: Components and Services of Mobile Computing • Wireless Telecommunications Networks o *Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) o *Personal area network (PAN) • *Bluetooth o *Wireless local area network (WLAN) • *Wi-Fi o o o o Municipal Wi-Fi networks (WMAN) *WiMAX *Wireless wide area network (WWAN) LTE (Long Term Evolution) • Putting It All Together How Wi-Fi Works An M-Commerce System at Work Mobile Financial Applications • *Mobile banking (m-banking) • Other Mobile FINANCE Applications o Mobile Stock Trading o Real Estate Mobile Transactions Mobile Enterprise Solutions: From Supporting the Workforce to Improving Internal Operations • *Enterprise mobility • Defining Mobile Enterprise (enterprise mobility) o A Working Definition of *Mobile Enterprise • The Framework and Content of Mobile Enterprise Applications o Mobile Collaboration • *Mobile Workers Mobile Enterprise Solutions: From Supporting the Workforce to Improving Internal Operations • Other Enterprise Mobile Applications o Transportation Management o iPad in the Enterprise o Trends for 2014 and Beyond Mobile Entertainment, Gaming, Consumer Services, and Mobile Shopping • Overview of Mobile Entertainment o *Mobile entertainment • Mobile Streaming Music and Video Providers • Entertainment in Cars • Mobile Games o Hurdles for Growth • Mobile Gambling • Mobility and Sports Mobile Entertainment, Gaming, Consumer Services, and Mobile Shopping • Service Industry Consumer Applications o o o o Healthcare Hospitality Management Public Safety and Crime Prevention Other Industries • Mobile Shopping and Advertising Location-Based Mobile Commerce and Mobile Social Networks • *Location-based m-commerce (lcommerce) • Basic Concepts in L−Commerce o o o o o o Location Navigation Tracking Mapping Timing *Real-time location systems (RTLS) LBS Components Creating a System Location-Based Mobile Commerce and Mobile Social Networks • L-Commerce Infrastructure 1. Location finder (positioning) component 2. Mobile Positioning Center 3. User 4. Mobile devices 5. Mobile communication network 6. Service or application providers 7. Data or content provider 8. Geographical Information System (GIS) 9. Opt-in application Location-Based Mobile Commerce and Mobile Social Networks o o o o o o *Geolocation *Global Positioning System (GPS) Location-Based Data Locating Customers in Physical Stores *Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Location-Based Services and Applications • *Location-based service (LBS) o *Social Location-Based Marketing Location-Based Mobile Commerce and Mobile Social Networks • Barriers to Location-Based M-Commerce o o o o o Lack of GPS in some mobile phones Accuracy of devices The cost–benefit justification Limited network bandwidth Invasion of privacy Ubiquitous (Pervasive) Computing and Sensory Networks • Overview of Ubiquitous Computing o Definitions and Basic Concepts • • • • *Ubiquitous computing (ubicom) *Pervasive computing *Context-Aware Computing *Internet of Things (IoT) o Machine-to-Machine Technology • Smart Application: Grid, Homes, Cars, and More o o o o *Smart grid Smart Homes and Appliances Smart and Driverless Cars Smart Cities Smart Grid Environment Source: National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce nist.gov/smartgrid/upload/FinalSGDoc2010019-corr010411-2.pdf (accessed July 2014). Ubiquitous (Pervasive) Computing and Sensory Networks • Wireless Sensor Networks o Sensor Network Basics • *Sensor network o Smart Sensor Applications • Implementation Issues in Ubiquitous Computing Emerging Topics: From Wearables and Google Glass to Smart Cities • Wearable Computing Devices • *Google Glass • Smart Cities Implementation Issues in Mobile Commerce: From Security and Privacy to Barriers to M-Commerce • M-Commerce Security and Privacy Issues • Technological Barriers to M-Commerce • Failures in Mobile Computing and MCommerce • Ethical, Legal, Privacy, and Health Issues in M-Commerce o Privacy Implementation Issues in Mobile Commerce: From Security and Privacy to Barriers to M-Commerce • Enterprise Mobility Management o The BYOD Issue o Mobile Apps and their Management • * Mobile app • Build (or Bring) Your Own App (BYOA) o Other Managerial Issues Managerial Issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is your m-commerce strategy? Are there any clear technical winners How should BYOD be managed? Is it wise to embark on l−commerce? Which applications should be implemented first? Summary 1. What is m-commerce, its value-added attributes, and fundamental drivers? 2. What is the mobile computing environment that supports mcommerce? 3. Which type of networks support mobile devices? 4. Financial and banking applications. 5. Enterprise mobility applications. Summary 6. Consumer and personal applications and mobile entertainment. 7. Location-based commerce. 8. Ubiquitous computing and sensory systems. 9. Google Glass, driverless cars, and mobile apps. 10.Security and other implementation issues.