01_1
advertisement

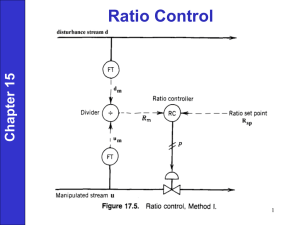
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Advanced Process Control Lecture one 1- Syllabus, Marking Scheme and Reference Books 2- Introduction to Single Input – Single Output Control (SISO) - Feedback Control - Feedforward and Cascade Control Lecturer: M. A. Fanaei Ferdowsi University of Mashhad 1 Syllabus Review of SISO control Introduction to feedback control theory Process modeling Control valve characteristics Types and modifications of PID controllers Tuning of PID controllers (offline and online) Discrete version of PID controllers Dynamic simulation and control of chemical processes using MATLAB/SIMULINK 2 Syllabus Advanced SISO control topics Performance and robustness Cascade control Feedforward control Ratio, Override and Selective Control Predictive control (IMC and Smith predictor) State-space model (Continuous and Discrete) 3 Syllabus MIMO control topics Centralized and decentralized control Interaction and relative gain array Design of static and dynamic decoupler Predictive control (DMC) 4 Marking Scheme & Reference Books Marking scheme Mid-term exam: Final exam: Homework: 35% 40% 25% Reference books C. A. Smith and A. Corripio, Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control, 3rd edition, Wiley, 2006. K. J. Astrom and T. Hagglund, Advanced PID Control, ISA, 2006. T. E. Marlin, Process Control: designing processes and control systems for dynamic performance, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, 2000. K. Ogata, Modern Control Engineering, 3rd edition, McGraw-Hill, 1997. K. J. Astrom and B. Wittenmark, Computer Controlled Systems, 3rd edition, Prentice Hall, 1997. C. C. Yu, Autotuning of PID controllers: A relay feedback approach, 2nd edition, 5 Springer, 2006. Control objectives and structures Safety Environmental protection Equipment protection Smooth plant operation and production Product quality Profit optimization Structures Feedback Feedforward Feedback/Feedforward Cascade Objectives 6 Feedback control Final Control Element Controller Sensor Transmitter Controller Final element Sensor Manipulated variable Controlled variable Process Disturbances Other outputs 7 Advantages and disadvantages of feedback control Disadvantages • Very simple technique • Effective for all disturbances • Provides zero ss offset • Works with minimum knowledge of the process • Does not take control action until the process output has deviated from set point • Affects the closed-loop stability Advantages 8 Feedforward control 9 Advantages and disadvantages of feedforward control Disadvantages • Compensates for a disturbance before the process output is affected • Does not affect the stability of the control system • Can not eliminate steady-state offset • Requires a sensor and model for each disturbance Advantages 10 Feedback / feedforward control 11 Cascade Control When the simple feedback control structure don’t have an acceptable performance, a cascade structure may improve the performance (speed up the closed loop response). A cascade structure can be used, when a process has some series dynamics and the output variables between theses dynamics can be measured. 12 Cascade Control (a process example) 13 Cascade Control (a process example) 14