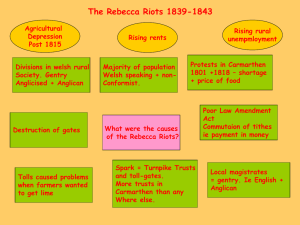
Cyflwyniad Cadeirydd Bwrdd yr Iaith Gymraeg: "Hawl i`r
advertisement

Language Planning: The Welsh Model Gwyn Jones Director of Policy and Terminology 6th century: Welsh spoken here "From henceforth no person or persons that use the Welsh speech or language shall have or enjoy any office or fees.... unless he or they use and exercise the speech or language of English" The Acts of Union1536 a 1543 Changing Attitudes: Increasing social status of the Welsh language 1893 – University of Wales 1911 – National Library of Wales 1964 – Welsh Office: Part of the UK Government 1967 – First Welsh Language Act 1982 – S4C: Welsh language TV channel 1988 -- Education Act designates Welsh a ‘core subject’ in the curriculum 1993 – Welsh Language Act & Welsh Language Board 1999 – National Assembly for Wales Census Language Results 1961-1991 1961 1971 1981 1991 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1901 1911 1921 1931 1951 1961 1971 1981 Siaradwyr Cymraeg/Welsh Speakers 1991 2001 2001: % able to speak Welsh by age 50 40 % 30 20 10 0 3-4 5 - 14 15 - 24 25 - 34 35 - 44 45 - 54 55- 64 65 - 74 Age 75+ Welsh Language Act 1993 Welsh Language Schemes Welsh Language Schemes • 526 Public Sector bodies have approved Statutory Welsh Language Schemes • 73 Voluntary Sector bodies have approved Welsh Language Schemes Characteristics of Successful Schemes • Corporate ownership • Support for non-Welsh speakers • Bilingual identity • Forward Planning • Normalising bilingualism in the workplace • Clear guidance to staff • Regular language awareness training • Marketing Welsh language services Use of Welsh in the Private Sector: Over 150 companies have agreed a Welsh Language Policy with the Board Development of Welsh Medium Education in Wales • 1947 – First LEA funded Welsh Medium Primary School (4-11) 1956 – First LEA funded Welsh Medium Secondary School (11-18). • Initially for children from Welsh speaking homes. Post 1970 – increasing numbers from non-Welsh speaking homes. Welsh-medium education: 3 main influences on its development • Some local authorities • Parental demand • Her Majesty’s Inspectors of Schools Scale of Welsh Medium Education • Numbers of Welsh Medium Schools: 448 Primary Schools 54 Secondary Schools 51,977 Primary Pupils 39,458 Secondary Pupils • Pupils in years 7-11taught Welsh as a first language: 1995 – 21,658 (12.2%) 2005 – 27,895 (14.8%) 1998 – 2002: 22 LEA’s agree Welsh Language Education Schemes. Getting Young People To Speak Welsh • Provision of opportunities to use Welsh socially; • opportunities to use Welsh in the workplace. Urdd Gobaith Cymru Community Development • Mentrau Iaith • Language Action Plans What is important to know about the Welsh language • Increased numbers speaking the language • Fewer people using the language on a day-to-day basis Language Planning Strategy Developing a strategy for language planning in Wales: • • • • 1996 – A Strategy for the Welsh Language 1999 – Vision and Mission 2003 - Iaith Pawb 2005 - The Future of Welsh: Welsh Language Board’s Strategy • Discussions for the future - 2009-11 Aim: “To enable the language to become selfsustaining and secure as a medium of communication in Wales” Objectives of the 1996 Strategy: • Increasing the number of people who are able to speak Welsh; • providing opportunities to use the language; • changing habits of language use and encouraging people to take advantage of the opportunities provided; • strengthening Welsh as a community language. The Welsh Language Board has engaged in four different types of language planning that are needed for language survival: • acquisition planning; • usage planning; • status planning; • corpus planning Priority Areas (1) • Language transmission in the family • Children aged 0-7 • Welsh Language and bilingual education and training • Use of Welsh by young people • Promoting and facilitating the use of Welsh in the community Priority Areas (2) • Using Welsh in the private sector • Welsh Language Schemes and developing and providing services in the welsh language • Normalising bilingualism • Promoting language rights as part of the equal opportunities field • Information Technology and Corpus Planning • Research and data WLB’s Strategic Priorities: 2009 • • • • • • Extending the influence of Language Schemes Welsh Language Policies (for businesses) Education Families and the community Youth (increasing the use of Welsh among young people) Cross-cutting Work: Research, Information Technology, The Centre for the Standardization of Terms, Europe, Marketing Frequency of use by age and fluency Not fluent Every day Weekly Less often Never Bob dydd Bob wythnos Llai aml Byth Fluent Ddim yn rhugl Yn rhugl 100 80 60 Canran 40 % 20 0 3 - 15 16 - 29 30 - 44 45 - 64 65+ 3 - 15 16 - 29 30 - 44 45 - 64 Oedran Age 65+ Cross party support for the language • Language is no longer a political football. • Political agreement on the importance of the language to Wales as a nation. Funding for the promotion of the language £15million = €16.5million Balance...... • Important to have a good balance between central policy and grassroot support Government Policy WLB Community Activities/Grassroot Support One Wales Seek enhanced legislative competence on the Welsh language, with a view to a new Assembly Measure to confirm official status for both Welsh and English, linguistic rights in the provision of services and the establishment of the post of Language Commissioner. What next? Diolch Thank you www.byig-wlb.org.uk