HHG4M
advertisement

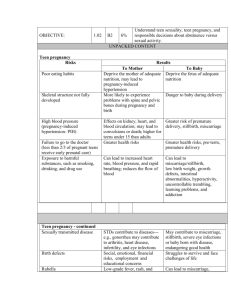
Chapter 1 Notes Overview: Ten reasons for studying children What is Social science Three main disciplines involved in the study of parenting – phsychology, sociology, anthropology Social Sciences include: Human Ecology Family Studies Research Methods pg. 7 Qualities of a good researcher Ways researchers record observations [Complete “Checkpoints” question #4 for notes pg 10] SOCIAL SCIENCE RESEARCH Scientific Method includes: Quantitative Research Qualitative Research The Research Process Qualities of a good research question – Asks exactly what you want to learn, can’t be answered with a “yes” or “no” answer., can be answered only by gathering information Possible Research Questions and Methods relating to: A. Child Care B. Poverty C. Child Development [Figure 1.7 pg 12] Organizing and Analyzing Research Information Primary Research Definition: You conduct the research yourself Example: An interview or survey Secondary Research Definition: Reading/recording what other researchers have already discovered or reporded. Example: Article Review/ Issue Analysis from published academic article Techniques for Gathering Information Print Materials: books, magazines, newspapers, journals Human Subjects Electronic Media: Web sites, Internet Fact or Opinion? Facts: Can be demonstrated to be true and based on scientific research, physical evidence or numeric datat. Eg. Mrs. Jasek’s HHG4M class 30 students Opinions: Describes peoples’ attidtudes, feelings, and thoughts about a topic. Less “exact” Eg. “people have a right to medical care” Opinion however can be measured. Eg. “92% of teenagers agree that people who cannot afford medical care have a right to it.”(Bibby, 2001) Ten questions to consider when analyzing information (pg 16) Research Presentation Eight Steps: 1. Introduce your topic 2. State the research question 3. Analyze 4. Organize 5. Give details 6. Cite your sources 7. Explain 8. Present a conclusion Ways to Present Research Research Paper Written Report Oral Report or Presentation Poster Presentation Multimedia Presentation Group Presentation Ethical Considerations during Social Science Research Informed Consent What are Ethics [Review the “Ethical Standards for Research with Human Subjects”] pg 20 Studying Theories and Issues Theory (Theorists in Ch.9 mainly and throughout the text) Theory: An explanation or view of events, behaviours or situations that make them easier to organize and understand . - some based on years of experimental research, patterns observed over and over again. All theories have an element of truth and that is why they are accepted and embraced. Dr. Benjamin Spock – Theorist – well accepted pg.23 Steps in an Issue Analysis Define the issue (e.g. teen pregnancy) Identify who is involved in the issue (e.g. both teen parents and their parents). Consider the position each person holds and why (e.g. his parents want her give the baby up for adoption, he wants her to marry him, she wants to drop out of school to raise the baby, her parents want her to stay single, raise the baby and stay in school). Determine current view that are held on the issue, and identify whose position these views support (e.g. a teen parent can stay in school and raise a child at the same time) Locate additional research from reliable sources that supports the different views(e.g. stats regarding how many teen parents live together/stay together, give their children up etc. Identify the argument in favour of each view Determine which view you hold and why. Explain Connections pg. 24 1. MAKE A LIST OF ISSUES OR CONCERNS THAT YOU THINK ARE IMPORTANT FOR CHILDREN, ADOLESCENTS, AND PARENTS IN OUR SOCIETY. SELECT ONE, AND CONDUCT AN ISSUE ANALYSIS USING THE STEPS OUTLINED ON PG.24.