Chapter 1 and 2
advertisement

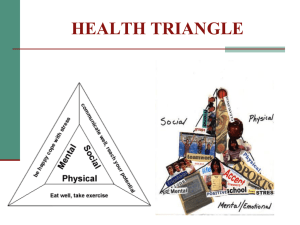
HEALTH & WELLNESS Chapter 1: Leading a Healthy Life Health in the Past: Infectious diseases were the leading causes of death prior to the 20th Century. Health Today: Lifestyle diseases caused partly by unhealthy behaviors lead to most health problems. What is the leading cause of death among children and infants today? a. Diseases b. Suicide c. Homicide d. Motor vehicle accidents MOTOR VEHICLE ACCIDENTS Four leading causes of death for young people are (making up about 75% of teen deaths): Motor vehicle accidents Homicide Suicide Other accidents What is Health? Definition of Health: Health is the complete state of well-being in which all of the components of healthphysical, emotional, social, mental, spiritual, and environmental-are in balance; not just the absence of disease or sickness. SOCIAL HEALTH • • • • • Respects others Supportive relationships with friends and family Interacting well with other people Maintaining values and beliefs; not being persuaded Expresses needs to others MENTAL HEALTH • • • • • Ability to cope with life’s demands Free of mental illness (i.e. phobia) Enjoys trying new things High Self-Esteem Feeling comfortable about who you are PHYSICAL HEALTH • • • • • • Eating a well-balanced diet Exercising Regularly Sufficient Sleep Good/Clean Hygiene Free of disease Free of tobacco, drugs, and alcohol EMOTIONAL HEALTH • Expressing emotions constructively • Can cope with unpleasant emotions • Asking for help when sad SPIRITUAL HEALTH • Sense of purpose in life • Follows morals and values • Feels a unity with other human beings ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH • Access to clean air and water • Clean and un-crowded living space • Recycles used paper, glass products, and aluminum SOUND MIND SOUND BODY What is Wellness? • Wellness: the achievement of a person’s best in all six components of health-optimal health – Life long effort to live a healthy life – Allows us to achieve our goals and find meaning and purpose in our lives Risk Factors Risk Factor: anything that increases the likelihood of injury, disease, or other health problems Types of Risk Factors Controllable Risk Factors: Risks that you can do something about - “behavior risks” Uncontrollable Risk Factors: Risks that you can NOT change (age, race, gender, heredity) 6 Health Risk Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sedentary Lifestyle Alcohol & Drugs Sexual Activity Behaviors That Cause Injury Tobacco Use Poor Eating Habits RISK FACTORS CONT. 1. Sedentary Lifestyle- LAZYNESS or not doing physical activity 2. Alcohol & Drugs- liver disease, cancer, heart disease, car accidents, fights, depression, suicide, mental disorders, STDs 3. Sexual Activity- sexual activity outside a committed relationshipunplanned pregnancy, HIV infection, and other sexually transmitted diseases 4. Behaviors That Cause Injury- dangerous behaviors, weapons, extreme sports, seatbelts 5. Tobacco Use- Smoking: Single Most Preventable cause of death in U.S. 6. Poor Eating Habits- Heart Disease, foods high in fat, empty calories HEALTH ADVOCATE A person who works in a health field or speaks out or promotes health. ? Question: Are you a “Health Advocate” 3 Ways You Can Take Care of Your Health KNOWLEDGE: Knowing the information needed to make healthy choices (health classes, current issues) ATTITUDE: The way you feel about yourself directly affects your health LIFESTYLE: Putting knowledge into action = behavior changes WHICH IS THE MOST IMPORTANT?? ATTITUDE Health Literacy The knowledge you need to know to make good choices about your health. -Current Issues -Health Educators -Library Resources -Health Professionals Public Health The practice of protecting and improving the health of people in a community. -Medical Advances -Technology -Public Policy-most control over environmental health component -Education THE END… http://www.poodwaddle.com/clocks2.htm Friedman, David P., Curtis C. Stine, and Shannon Whalen. Lifetime Health. Orlando, [Fla.: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 2009. Print. Health & Wellness Cont. Chapter 2: Skills for a Healthy Life QUICK REVIEW • What is the definition of HEALTH? • What is “Wellness?” • What is “anything that increases the likelihood of an injury, disease, or other health problem?” • What is a “Health Advocate”? QUICK REVIEW • What is the definition of HEALTH? Health is the complete state of well-being in which all of the components of health-physical, emotional, social, mental, spiritual, and environmental-are in balance; not just the absence of disease or sickness. • What is “Wellness?” The achievement of a person’s best in all six components of health-optimal health • What is “anything that increases the likelihood of an injury, disease, or other health problem?” Risk Factor • What is a “Health Advocate”? A person who works in a health field or speaks out or promotes health. Life Skills • Tools for building or improving health Example: (Public Speaking or good decision making skills) 10 “Good” Healthy 8 “Good” Life Life Skills Skills -Assessing Your Health -Communication Skills -Coping (dealing with problems in an effective way) -Being a wise consumer (a person who buys products) -Evaluating Media -Refusal Skills -Goal Setting -Practicing Wellness -Using community resources (something you can use to help achieve a goal) -Making GREAT decisions GREAT Decisions Give thought to the problem Review your choices Evaluate the consequences of each choice Assess and choose the best choice Think it over afterward Consequences Consequences: The effect, result, or outcome of our actions Part of good decision making skills is considering consequences. Stop, Think, and Go STOP – Stop and admit you made a poor decision THINK – Think about who can discuss the situation with you GO – Go and correct the situation Collaboration Collaboration: working together to achieve a goal or reach an objective - Getting a second opinion - Realizing how your decisions affects others Who can you collaborate with? • • • • • • Teachers Friends Parents Siblings Counselors Neighbors SETTING HEALTHY GOALS 2 Types of Goals Short Term Goal: • achieved quickly • within a few days or few weeks Long Term Goal:• take longer to achieve • may take months or even years • may be more rewarding once accomplished Action Plan: set of directions that will help you reach your goal – should include rewards AND a way to track progress 6 Suggestions for Setting Goals… • Sensible-Realistic • Safe-Can this goal harm you? • Satisfying-Should feel good when you reach • Similar-Should not contradict earlier goals • Specific-Steps to achieve are very clear • Supported-Would responsible adults approve of this goal? GOOD EXAMPLE OF GOALS SETTING…. Peer Pressure Peer Pressure: a feeling you get that you should do something because somebody else wants you to do it Direct Pressure: someone tries to convince you to do something that you normally wouldn’t do Indirect Pressure: swayed to do something because people you look up to are doing it Refusal Skills Refusal Skill: A strategy to avoid doing something that you do not feel comfortable doing – remember to be respectful and not put anyone down Refusal Skills 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Blame someone else Give a reason Ignore the request Leave the situation Say “No, Thanks” Say NO and mean it Make a joke out of it Make an excuse Suggest something else to do Change subject Team up with somebody else Something to consider… QUICK REVIEW • • • • • What is a life skill? What are 4 of the life skills we mentioned? What are 2 types of goals? Which type of goal is more rewarding? What does sedentary mean? QUICK REVIEW • What is a life skill? Tools for building or improving health • What are 4 of the life skills we mentioned? Assessing Your Health, Communication Skills, Coping , Being a wise consumer, Evaluating Media, Refusal Skills, Goal Setting, Practicing Wellness, Using community resources, and Making GREAT decisions • What are 2 types of goals? Long-term and Short-term • Which type of goal is more rewarding? Long-term • What does sedentary mean? LAZYNESS or not doing physical activity Friedman, David P., Curtis C. Stine, and Shannon Whalen. Lifetime Health. Orlando, [Fla.: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 2009. Print. Group Activity • Groups of no more than four people assigned by teacher. • Create skit of at least 1 minute where student(s) suggests another does something harmful to health. Incorporate peer pressure (pg 33/34), GREAT decisions (pg 30/31), and refusal skills (pg 35). • Each person must have a speaking part. • This is your daily participation grade. • BE CREATIVE!!