Lanore West - Curry School of Education
advertisement

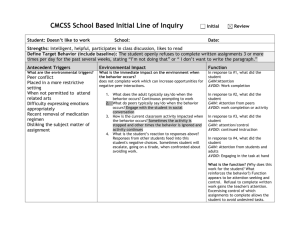
To complement standardized assessments Two types: video vs. live What can be observed? The first article examining play behaviors among pre-school children Observed children’s play behavior and categorized play based on what she observed Play stages include › › › › Onlooker Independent Solitary play Parallel activity Cooperative/Organized supplementary play Parten, B. Mildred. (1932) School Participation Among Pre-school Children Developed a code that was appropriate for our population of interest (children enrolled in HeadStart, Preschool, externalizing/internalizing behavior) Incorporated Parten’s play research and work from others in the field (Fujuki, Brinton, Isaacson, & Summers, 2001; Parten, 1932; Qi & Kaiser, 2004; Rubin, 2001) Important points to consider when developing definitions: › Behaviors must be observable › Coders must be able to observe the same behaviors › Reliability Event-positive/negative measures of autonomous behaviors or aggression while playing Duration-codes used to specify play behaviors of children Child Initiated (CI): interactive behavior (verbal or physical) by the target child toward a peer Peer Initiated (PI): interactive behavior (verbal, non-verbal, physical) by a peer toward the target child that is complimentary and is followed by a peer behavior Aggression (CA): any physical touch that is intended to be aversive, negative, or restrictive of the child’s activity Following directions (FD): child is on task, following teacher’s directions or engaging in appropriate behavior. Parallel play (PP): the child is playing with toys similar to those used in the vicinity. Associative play (AP): child plays with peer without role assignment. Distinguishing feature is the focus of the child. Equal cooperative play (CPE): child is engaged in activity with others equally. Conversation should be present. Using hand-held computers Live Video clips Following directions (FD) Parallel play (PP) Equal Cooperative Play (CPE) Associative Play (AP) Solitary Play (SP)